Recently, the United Nations has declared 2025 as the International Year of Quantum Science and Technology (IYQ) to boost research and development in the emerging area.
UN has declared 2025 as the International Year of Quantum Science and Technology (IYQ)

- Recognition of 100 years of Quantum Mechanics: The year 2025 was chosen for this International Year as it recognizes 100 years since the initial development of quantum mechanics.
- Matrix Mechanics: It marks 100 years since theoretical physicists Werner Heisenberg, Max Born and Pascual Jordan developed matrix mechanics, the first formulation to express quantum physics in mathematical form.
- Schrödinger wave Equation: Year 2025 also marks 100 years since Erwin Schrödinger postulated the Schrödinger equation that governs the wave function of a quantum-mechanical system – a landmark moment in quantum mechanics that proved to be seminal to the field and won him a Nobel Prize in Physics.
- Global Initiatives and Outreach: A steering committee is also “planning global initiatives and events, particularly those that reach audiences unaware of the importance of quantum science and technology.”
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
About International Year of Quantum Science and Technology (IYQ)

- Background:
- 2023: Led by the nation of Mexico, in May 2023 the Executive Board of the United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) endorsed a resolution encouraging official UN proclamation.
- It was followed by an endorsement of the full UNESCO General Conference in November 2023, which was co-sponsored by nearly 60 countries.
- 2024: In May 2024, the nation of Ghana formally submitted a draft resolution for official proclamation of the International Year to the U.N. General Assembly.
- On June 7, 2024 the U.N. General Assembly officially declared 2025 to be The International Year of Quantum Science and Technology.
- The proclamation has also received the endorsements of the International Union of Pure and Applied Physics, the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, the International Union of Crystallography, and the International Union of History and Philosophy of Science and Technology.
- Aim:
- Strengthening of Capabilities: To strengthen national capacities in the basic sciences and science education.
- To reflect the growing recognition of quantum science and technology as a key driver of future innovations and economic growth.
- Contribution and Future Potential: To highlight the contribution of quantum science to our increased knowledge and understanding of the physical universe, as well as the critical role of quantum science and technology in developing sustainable solutions in energy, education, communications, and human health.
- Awareness, Encouragement and Collaboration: It focuses on raising awareness about the importance of quantum technologies, fostering international collaborations, and encouraging educational and outreach activities.
About Quantum Science and Technology

- An Interdisciplinary Field: Quantum Science and Technology is an interdisciplinary field that harnesses the principles of quantum mechanics to develop new technologies with potentially transformative capabilities.
- Fundamentals of Quantum Computing: There are three fundamentals of quantum computing- Superposition, Entanglement and Qubits.
- Superposition: The ability of a particle to hold two “states” at the same time. It is a fundamental principle where a quantum system can exist in multiple states simultaneously.
- Entanglement: The strange property of quantum systems. If one particle is entangled with another and measures the spin of the first one (which resolves into either value), the entangled particle will instantly resolve into the same value.
- Quantum computing uses both of these principles — superposition and entanglement to solve certain types of problems much faster than classical computers, particularly for complex simulations, optimization, cryptography, and searching large databases.
- Qubit or Quantum Bit: A basic unit of quantum information. It is a two-state quantum-mechanical system, one of the simplest quantum systems displaying the peculiarity of quantum mechanics.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Application Areas of Quantum Science and Technology
- Quantum Computing: It is a multidisciplinary field comprising aspects of computer science, physics, and mathematics that utilizes quantum mechanics to solve complex problems faster than on classical computers.
- Quantum computers use quantum bits (qubits) which, unlike classical bits, can exist in multiple states simultaneously due to superposition.
- Quantum Communication: It uses the laws of quantum physics to protect data.
- These laws allow particles—typically photons of light for transmitting data along optical cables—to take on a state of superposition, which means they can represent multiple combinations of quantum bits (qubits).
- Quantum Key Distribution (QKD): It utilizes quantum mechanics to enable secure communication channels that are theoretically immune to eavesdropping.
- Quantum Internet: It is a future vision of a global network that uses quantum signals for ultra-secure communication and distributed quantum computing.
- Quantum Sensing and Metrology: It aims at harnessing new approaches that use the principles of quantum physics in order to overcome the noise produced by quantum fluctuations.
- The applications range from the improvement and synchronization of atomic clocks, the detection of the magnitude and direction of tiny magnetic fields, and interferometric measurements of phase shifts, medical imaging, navigation, and fundamental physics research.
- Quantum Materials: Exploration of materials with unique quantum properties, such as superconductors and topological insulators have applications in the development of new electronic devices, improved energy transmission, and advanced material science.
- Quantum Simulation: Quantum simulators can model complex quantum systems, helping in the understanding of high-temperature superconductivity, chemical reactions, and exotic phases of matter.
Advantages of Quantum Technology
- Increased Computing Power: Quantum computers are much faster than present computers and also have the capability to solve complex problems.
- Improved Security: Due to quantum mechanics, quantum encryption techniques are much more secure than traditional encryption methods.
- Faster Communication: Quantum communication networks can transmit information faster and more securely than traditional networks, with the potential for completely unhackable communication.
- Enhanced Artificial Intelligence (AI): Quantum machine learning algorithms can potentially enable more efficient and accurate training of AI models.
- Better Sensing and Measurement: Quantum sensors can detect extremely small changes in the environment, making them useful in areas such as medical diagnostics, environmental monitoring, and geological exploration.
- The advancements in quantum science and technology have the potential to revolutionize various fields, driving innovation in computing, communication, sensing, and beyond.
Obstacles to Mainstream Adoption for Quantum Technology
- Stability: Qubits are very sensitive to heat and are error-prone.
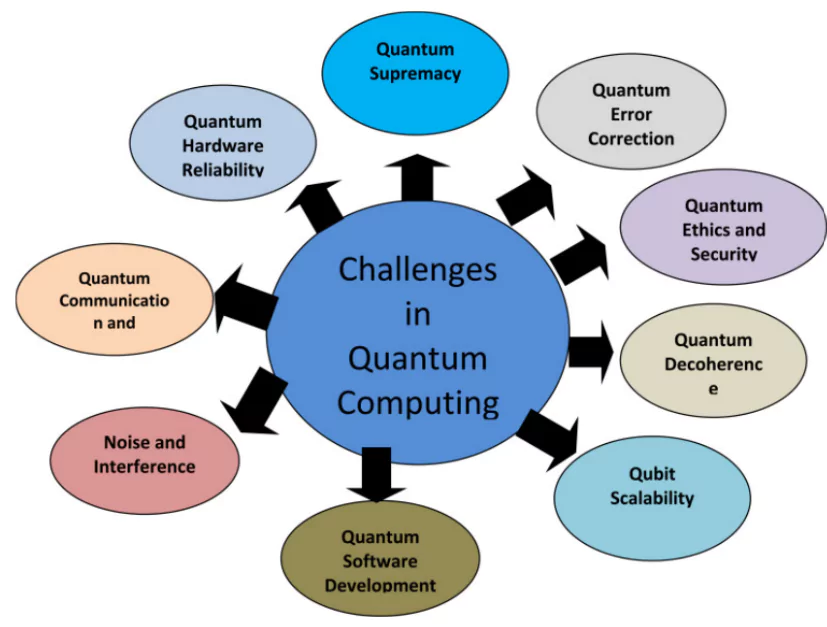 Scalability: Building larger quantum computers can be difficult.
Scalability: Building larger quantum computers can be difficult.- Connectivity: Qubits need to be connected to operate, which is difficult as the number increases.
- Integration: Combining quantum components with classical systems to create hybrid technologies.
- Decoherence: Over time, qubits can lose information stored in them.
- Programming: Completely new skills are needed as well as knowledge of quantum mechanics.
- Standardization: Establishing industry-wide standards will be essential for success.
- Access and Availability: Quantum computing services are expensive at this time.
- Algorithm Creation: Quantum computers can’t work like traditional computers, they need special algorithms to do tasks in their environment.
- Need for Low Temperature: Quantum computers require extreme temperatures (-460°F.) that are hard to maintain.
- Low Precision: Quantum computers have a low level of precision. Scientists have to create their own qubits, which is difficult.
- Software: The field of creating quantum algorithms and software is still developing, and qualified professionals are in short supply.
- High Cost: Building and maintaining quantum computers is currently relatively expensive, and this may prevent widespread deployment
- Interoperability: Due to the lack of standards in the realm of quantum computing, it might be challenging to compare and combine various quantum computers.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Way Forward
- Establishing Centers of Excellence: The government should create specialized centers of excellence dedicated to quantum science and technology within both academic institutions and government research institutes.
- Technology Development: India must harness the power of startups and Big Tech corporations involved in developing quantum technology and applications.
- Indigenization: Prioritizing the development of quantum computational capabilities is imperative for our nation, as obtaining this technology from foreign sources would pose significant challenges and cost hurdles.
- Effective Roadmap: To effectively monitor global advancements in quantum computing and evaluate and guide India’s efforts in this domain, the establishment of an Indian Quantum Computing Roadmap Group is essential.
- Research & Development with Collaboration: Continuous research and development, along with international collaboration, are crucial for overcoming current challenges and unlocking the full potential of quantum technologies.
Major International Quantum Computing Collaborations
- Quantum Technologies Flagship: It was established in 2018 by the European Union (EU), with aims to bring together research, private, and public institutions, and consolidate European leadership in the field of quantum technologies over a period of 10 years.
- The AUKUS Quantum Arrangement: It was initiated in 2022 with an aim to accelerate investments in “generation-after-next” quantum capabilities.
- Quadrilateral Security Dialogue: In 2021, the Quad leaders agreed to establish a Critical and Emerging Technology Working Group to ensure that the standards and frameworks for key technologies such as 5G, Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Quantum Computing are governed by “shared interests and values”
- CERN Quantum Technology Initiative: The European Council for Nuclear Research’s (CERN) Quantum Technology Initiative is a comprehensive R&D and academic programme initiated in 2020, which aims to set up collaborations between its 23 member states as well as international initiatives in quantum technologies
Various Government Initiatives
- Quantum Computing Applications Lab (QCAL): It was launched by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) in collaboration with Amazon Web Services (AWS).
- It aims to accelerate the adoption of quantum computing in India by providing access to quantum computers, tools, and resources to researchers and developers.
- The National Mission on Quantum Technologies and Applications (NM-QTA): It was launched in 2020 with the goal of creating a strong quantum technology ecosystem in India.
- National Quantum Mission: With a total cost of Rs.6003.65 crore from 2023-24 to 2030-31, it aims to nurture and scale up scientific and industrial R&D and create a vibrant & innovative ecosystem in Quantum Technology (QT).
|
![]() 12 Jun 2024
12 Jun 2024




 Scalability: Building larger quantum computers can be difficult.
Scalability: Building larger quantum computers can be difficult.