Wayanad, Kerala (which was struck by a deadly landslide event taking almost 200 lives) was ranked 13th on Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) ‘Landslide Atlas of India’ prepared in 2023 based on exposure to landslides in terms of key socio-economic parameters. The Landslide Atlas of India created by ISRO, identifies 147 high-risk districts across 17 states & 2 UTs. Northwest Himalayas (66.5%), Northeast Himalayas (18.8%), and Western Ghats (14.7%) are most prone.
Landslide in Wayanad

- Massive landslides struck between 1:30 a.m. and 4 a.m the villages of Mundakkai, Chooralmala, Attamala, and Noolpuzha in the Wayanad District of Kerala killing atleast 256 people and injuring over 200 and wiping entire villages off the map.
- The Landslide is touted as the worst landslide calamity to have struck the State of Kerala till date.
- The landslide was triggered by excess precipitation at Mundakkai in Mepadi panchayat, Wayanad.
- Magnitude: The landslide’s magnitude was such that, it spewed debris and water as far as six to seven kilometres down the valley and the heavy water surge from the hilltop altered the small Iruvazhinji river
- In normal landslides, the debris flow would be limited to 1–1.5 km,
- High-Susceptibility Zone: The area is considered a high-susceptibility zone by the GSI for landslides after the 2019 landslide at Puthumala, hardly 5 km away.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Landslide Atlas of Kerala
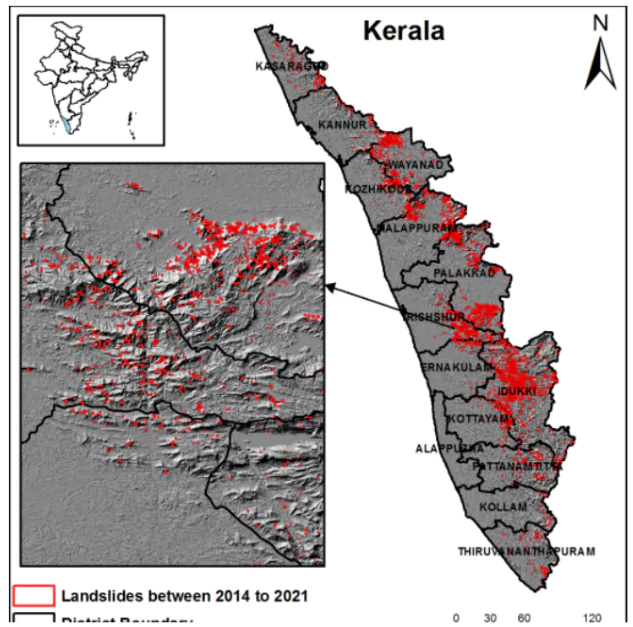
- Kerala saw the largest number of landslides 2,239 most of which occurred after the disastrous 2018 floods in the state, the highest in the country as per GSI Database.
- Top Landslide prone districts of Kerala include Thrissur, Palakkad, Malappuram and Kozhikode ranking third, fifth, seventh and tenth respectively in the Landslide Atlas of India
- Other Districts of Kerala: Ernakulam district in Kerala ranked 15th, Idukki 18th and Kottayam, (24th), Kannur (26), Thiruvananthapuram (28), Pathanamthitta (33), Kasaragod (44), Kollam (48) and Alappuzha (138).
- Compliance Audit Report of the CAG 2022: Forest land of Wayanad district reduced to 863.86 sq km in 2021 from 1,811.35 sq km in 1950 (a reduction of 947.49 sq km) leading to fragmentation of the once continuous vegetation cover, as per the Management Plan of Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary
The Landslide Atlas of India
- The Atlas has assessed and ranked 147 landslide prone districts in 17 States and two Union Territories of India
- The database covers landslide-vulnerable regions of India in the Himalayas and Western Ghats
- Prepared By: The Landslide Atlas of India is prepared by the National Remote Sensing Centre, in February 2023 .
- NRSC has prepared landslide hazard zonation (LHZ) map and Atlas on 1:25000 scale
- Data Source: Satellite data of high to very high resolution nature were extracted from IRS-1D PAN+LISS-III, Resourcesat-1, 2 and 2A LISS-IV Mx, Cartosat-1 and 2S and aerial images were used in the mapping of landslides.
 Landslide Inventories: The database mainly contains three types of inventory ie. seasonal, event-brd and route-wise landslide inventories for the 1998-2022 period showing the hotspot areas.
Landslide Inventories: The database mainly contains three types of inventory ie. seasonal, event-brd and route-wise landslide inventories for the 1998-2022 period showing the hotspot areas.-
- The inventory database is available in a web GIS platform in the Bhuvan portal.
- Geospatial landslide inventory database consist of approximately 80,000 mapped landslides in India under the (DMS)Disaster Management Support programme
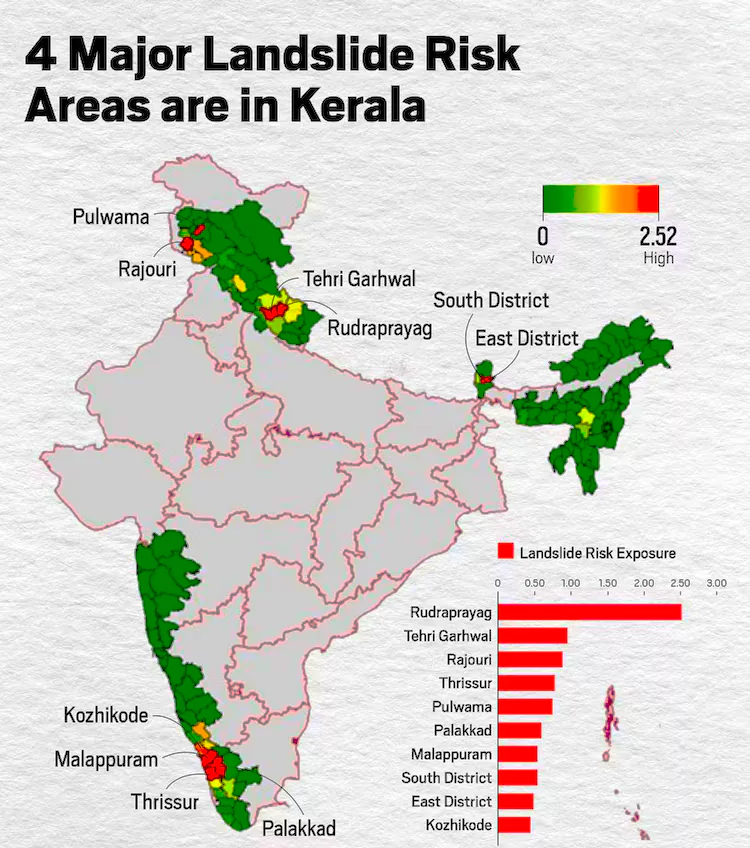
- Most Landslide Prone District: Rudraprayag in Uttaranchal was ranked first in the Landslide Atlas
- Vulnerability:
- The inhabitants and households of the Western Ghats are more vulnerable to landslides due to the very high population and household density, especially in Kerala.
- Western Ghats in absolute terms however has fewer landslides incidents than in the Himalayan regions.
- Steep escarpments of the Western Ghats record occurrences of landslides, but these are primarily controlled by the soil cover on the slopes.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
Landslides
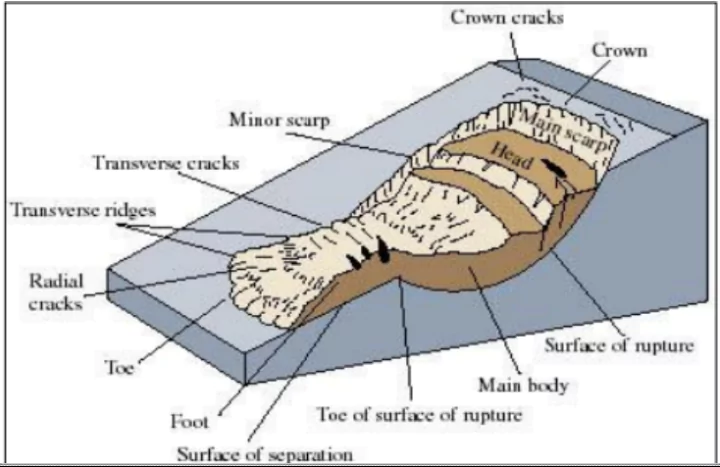
- Definition: Landslides are sudden movement of rock, boulders, earth or debris down a slope
- Vulnerability: India is among the top five landslide-prone countries globally, where at least one death per 100 sq km is reported in a year.
- According to the Geological Survey of India (GSI), About 0.42 million square km of India’s landmass, or about 13% of its area, spread over 15 states and four Union Territories, is prone to landslides,
- 0.18 million sq. km falls in North East Himalaya, including Darjeeling and Sikkim Himalaya
- 0.14 million sq. km falls in North West Himalaya (Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh and Jammu & Kashmir)
- 0.09 million sq. km in Western Ghats and Konkan hills (Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Karnataka, Goa and Maharashtra)
- 0.01 million sq. km in Eastern Ghats of Aruku area in Andhra Pradesh
 Types of Flow: Types of Flow:-
- Debris flow: It is a form of rapid mass movement in which a combination of loose soil, rock, organic matter, slurry that flows downslope commonly caused by intense precipitation or rapid snow melt.
- Earth flow: It is down slope viscous flow of fine grained material saturated with water.
- Mudflow: A mudflow is a wet or viscous fluid mass of fine and coarse grained material flowing rapidly along drainage channels.
- Creep: Creep is the slow, steady, downward movement of material under gravity that occurs in a large area.
- Causes: Landslides are triggered by,
- Natural Factors: rainfall, undercutting of slopes due to flooding or excavation, earthquakes, snowmelt
- Anthropogenic: overgrazing by cattle, terrain cutting and filling, excessive development, etc
|
![]() 1 Aug 2024
1 Aug 2024


 Landslide Inventories: The database mainly contains three types of inventory ie. seasonal, event-brd and route-wise landslide inventories for the 1998-2022 period showing the hotspot areas.
Landslide Inventories: The database mainly contains three types of inventory ie. seasonal, event-brd and route-wise landslide inventories for the 1998-2022 period showing the hotspot areas.