Context: Recently, Japan witnessed a series of major earthquakes and issued its highest-level tsunami alert.
What is a Tsunami?
- It is a Japanese term meaning “harbour wave,” is a series of large ocean waves caused by underwater earthquakes or volcanic eruptions.
- The sudden displacement of a substantial water volume leads to the formation of tsunami waves.
Tsunami Formation Process
- Earthquakes can displace large sections of the seabed, sending shockwaves through the water and creating towering waves.
- Similarly, underwater volcanic eruptions can displace water with explosive force, triggering tsunamis.
Characteristics of Tsunami Waves
- Tsunami waves can be hundreds of feet tall and travel as fast as jet planes over deep waters. However, they slow down upon reaching shallower waters.
Factors Influencing Tsunami Formation
- The formation of tsunamis depends on various factors, including the shape of the ocean floor, the distance, and direction of the earthquake or volcanic eruption.
Why is Japan Prone to Earthquakes and Tsunamis?
- Japan is situated along the ‘Pacific Ring of Fire,’ the most active earthquake tectonic belt globally, featuring the Pacific, Eurasian, and Indo-Australian Plates.
- The continuous meshing and colliding of these plates result in frequent earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and tsunamis.
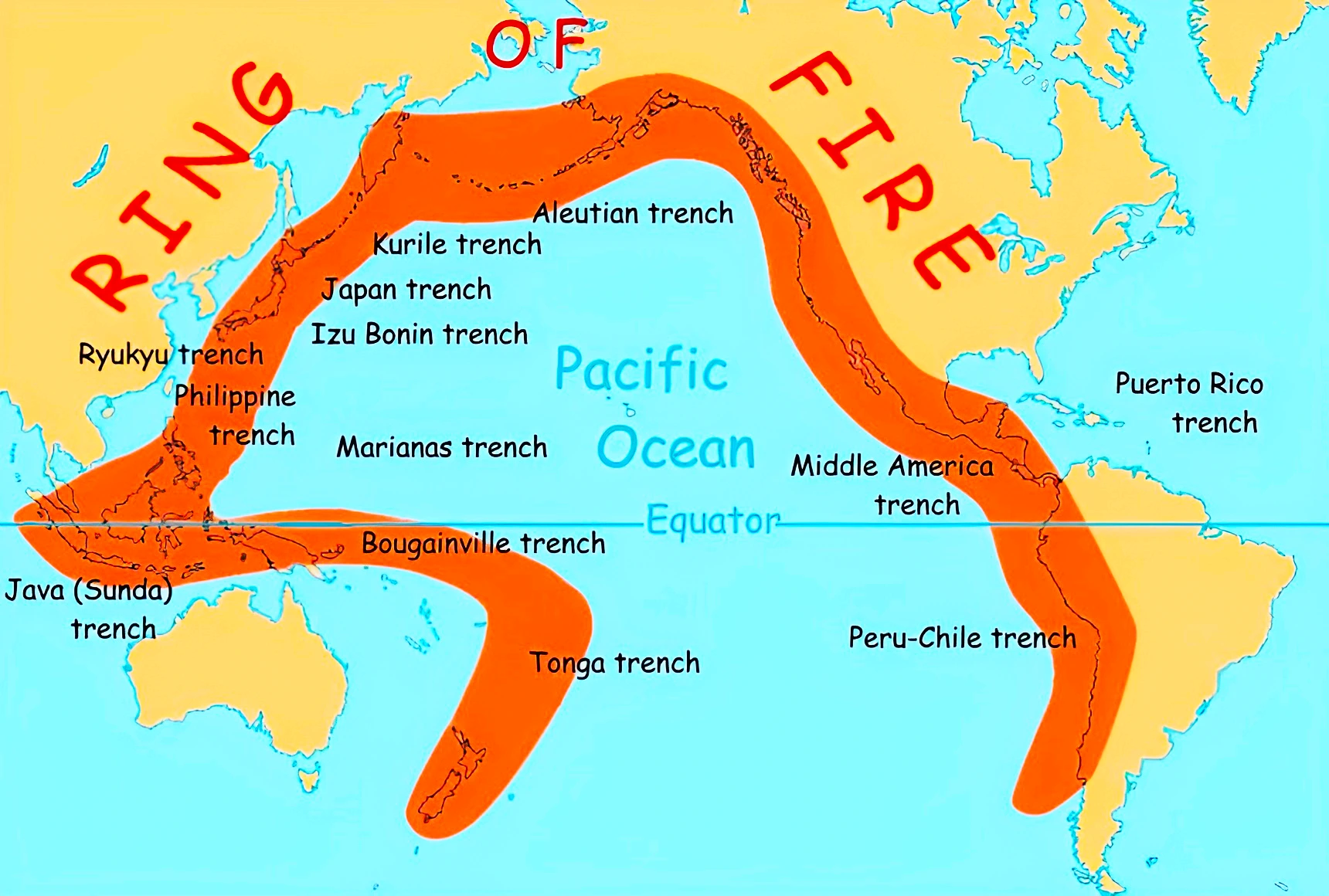
The Pacific Ring of Fire
The ‘ring’ refers to “an imaginary horseshoe-shaped zone that follows the rim of the Pacific Ocean, where many of the world’s earthquakes and volcanic eruptions occur”.
|
Must Read: Largest Volcanoes In The World List, Distribution, Location
News Source: Indian Express
![]() 2 Jan 2024
2 Jan 2024