At the 11th Joint Crediting Mechanism (JCM) Partner Countries’ Meeting, held during COP30 in Belém, Brazil, Union Minister Shri Bhupender Yadav emphasized the importance of cooperative climate mechanisms like the JCM for equitable, scalable climate action.
About Joint Crediting Mechanism
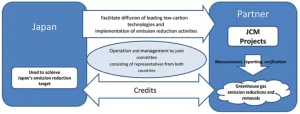
- The Joint Crediting Mechanism (JCM) is a bilateral carbon market mechanism initiated by Japan to promote low-carbon technologies in partner countries and share the resulting emission-reduction credits.
- Objective: The JCM aims to support decarbonization in developing countries by deploying advanced Japanese low-carbon technologies while allowing Japan to count a portion of the achieved emission reductions toward its own climate targets.
- How It Works:
-
- Under JCM projects, Japan provides technology, finance, and capacity-building, while the partner country hosts the project; the emission reductions are then measured, reported, verified, and credited jointly to both nations.
- The JCM complements Article 6 of the Paris Agreement, as it facilitates international cooperation in emission reduction through transparent monitoring and shared crediting.
- Current Status: The JCM has now expanded to 31 partner countries, with over 280 ongoing projects aligning with Article 6 of the Paris Agreement.
Importance of JCM for India’s Climate Goals
- Contribution to National Targets: The JCM supports India’s Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) and Long-Term Low Emission Development Strategy by facilitating the deployment of low-carbon technologies.
- Focus on Hard-to-Abate Sectors: The JCM is expected to support green hydrogen, green ammonia, and technologies for sectors like steel, cement, and chemicals.
- Domestic Ecosystem Development: The mechanism will help build a domestic ecosystem for localising high-technology interventions in India, contributing to sustainable development goals.
![]() 20 Nov 2025
20 Nov 2025



