Context:
The recent study Published in the Elsevier Journal emphasised that besides local emissions, rapidly changing climate is a significant factor affecting air quality in India.
La Nina Impacted Air quality in India in the Winter of 2022: Study
- The study was conducted by the National Institute of Advanced Studies, Bangalore and the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology, Pune.
- La Nina Influence on Air Quality: The Study has argued that the unusual air quality in some Indian cities in the winter of 2022 could be attributed to the La-Nina prevailing at that time.
- First Time Connection: This is the first time that air quality in Indian cities has been linked to a La Nina event — and indirectly to climate change, which is making El Nino and La-Nina more severe.
Key Finding of the Study
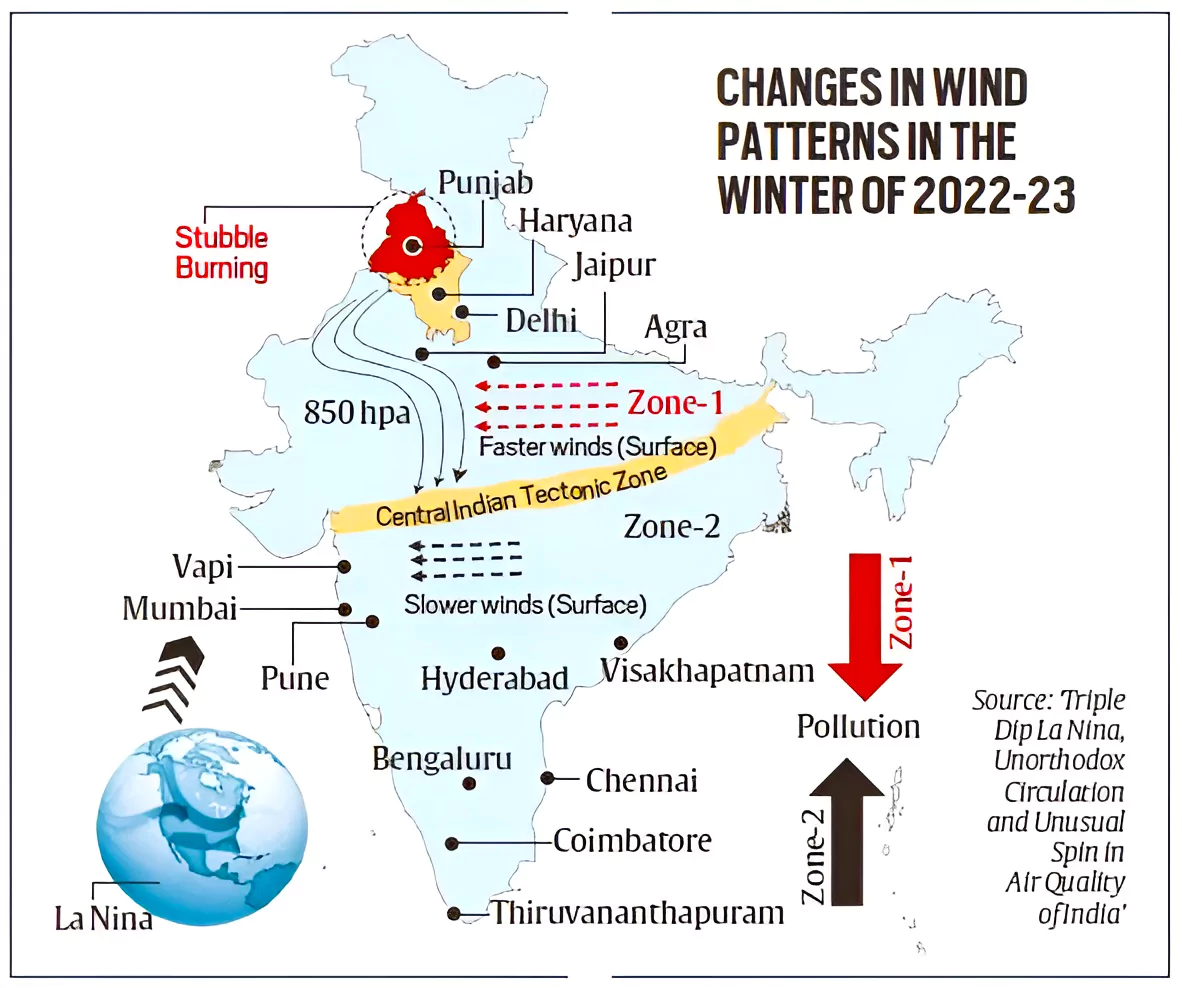
- Anomaly In Usual Condition (2022): West Indian and south Indian cities like Mumbai, Bengaluru and Chennai, experienced worse-than-usual air quality while Northern Indian cities, including Delhi, were cleaner than usual.
- For Example: PM2.5 concentrations in Ghaziabad in 2022 winter saw a reduction of about 33% from normal levels while Delhi saw a reduction of about 10% whereas Mumbai saw a rise in PM2.5 by 30%, and Bengaluru registered a 20% rise.
- Triple dip La Nina: The researchers used the global air circulation data as a result of La-Nina and equated it with the wind patterns over the Indian region.
- These anomalous wind patterns showed a strong sensitivity to the prevailing La Nina conditions and disappeared when these conditions were not present.
How Has La Nina Affected Air Quality?
- Change in Wind Direction: The normal wind direction ie, a North-westerly direction during winters changed to a North-South direction.
- As a result the pollutants and smoke from stubble burning being carried from Punjab and Haryana bypassed Delhi and Gangetic Plains and flew over Rajasthan and Gujarat to southern regions.
- Deviation in local wind circulation near Mumbai: In 2022, the local winds persisted in one direction for more than a week or 10 days instead of changing direction every four to five days.
- Wind currents alternate between blowing from the land to the sea every few days.
- It led to a greater accumulation of pollutants in Mumbai as the winds carried pollutants out of the city when they blew from the land towards the sea.
La Niña:
- It is cooling of the ocean surface, or below-average sea surface temperatures (SST), in the central and eastern tropical Pacific Ocean along the Peruvian Coast strengthening the cold Humboldt current.
- Impact: In reverse from El-Nino, Indonesia and South Asia receive higher rainfall while it decreases over the central and eastern tropical Pacific Ocean.
- The normal easterly winds along the equator become even stronger.
Triple Dip La-Nina:
- It is a rare phenomenon where La-Nina conditions persists for 3 consecutive years.
- 2020 to 2023: The world witnessed a ‘triple dip’ La Nina with the last event being in 1998-2001.
Impact of Triple dip La Nina in India
|
News Source: Indian Express
![]() 20 Feb 2024
20 Feb 2024
