According to new data published in the Lancet Global Health, half the adult Indian population does not meet the World Health Organisation’s (WHO) guidelines on sufficient physical activity.
- The highest rates of physical inactivity were observed in the high-income Asia-Pacific region (48%) and South Asia (45%) with levels of inactivity in other regions ranging from 28% in high-income Western countries to 14% in Oceania.
Key Highlights On Lancet Study on India’s Physical Fitness
Worldwide, nearly one third of adults, approximately 1.8 billion people did not meet the recommended levels of physical activity in 2022 and estimates indicate that India has the 12th highest prevalence of insufficient physical activity among 195 countries.
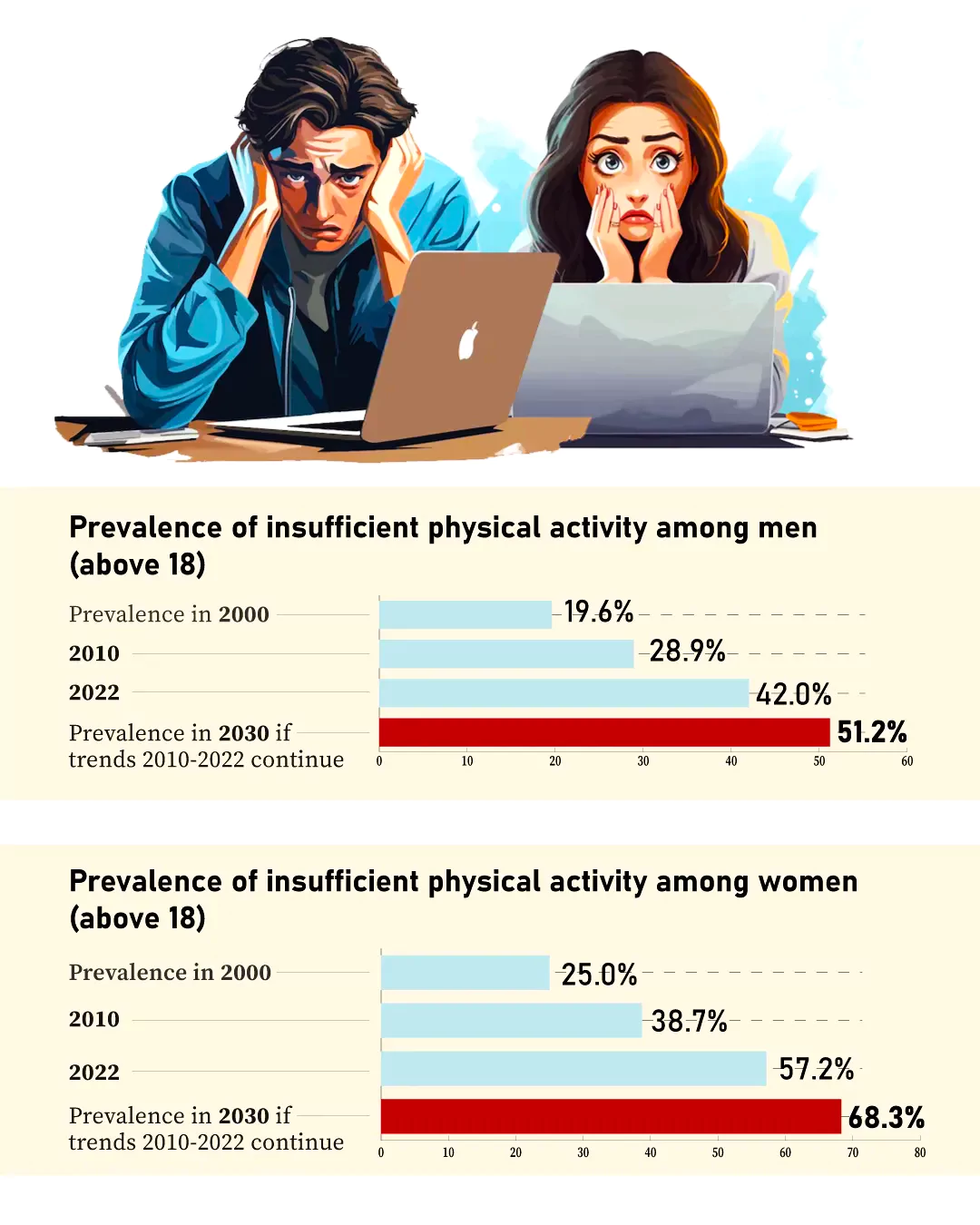
- Sharp Rise in Physical Inactiveness Numbers: The prevalence of insufficient physical activity among Indian adults has risen sharply from 22.3% in 2000 to 49.4% in 2022.
- More women (57%) than men (42%) are physically inactive.
- Risk of Disease: As per statistics, unchecked, 60% of India’s population would be unfit by 2030 and at risk of disease from not doing enough physical activity.
- As people in India are genetically more prone to developing non-communicable diseases like heart disease and diabetes at least a decade earlier than others. Lack of physical activity means aggravating risk factors.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Inactivity among Women
Inactivity is most evident in middle aged urban women, even though it is manifest to some degree across all age and gender groups.
- High Prevalence: Insufficient physical activity among women in India, Pakistan, Afghanistan is a worry as they lag behind men by over 14-20% points.
- However, women in neighboring Bangladesh, Bhutan and Nepal are more active and on track for achieving the global target of reducing the female prevalence of insufficient physical activity by 15% between 2010 and 2030.
- Reason: Women believe that household chores are a good form of physical exercise along with their caregiver role provide women lesser opportunities to prioritize themselves. Due to their multiple roles, women don’t have enough time and feel tired.
Reason for Increase in Physical Inactiveness
Physical inactivity is increasing globally because of many factors:
- Changes in work patterns (move towards more sedentary work)
- Changes in the environment. Increasing levels of global warming, manifesting as extreme weather, will pose greater challenges to outdoor physical activity to people.
- Making active transport more difficult.
- Changes in leisure time activities that are more screen based/sedentary activities.
- Increased levels of physical inactivity have followed delayed urbanization and industrialisation in some parts of the world, particularly South Asia (including India), which includes the Middle East.
-
- Cultural factors have interfered with outdoor physical activity in women in these regions.
WHO Recommendations on Physical Activity
- Defined as: Insufficient physical activity is defined as not doing 150 minutes of moderate-intensity activity, 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity activity, or an equivalent combination per week.
- Time Duration: WHO recommends at least 150 to 300 minutes of moderate aerobic activity per week (or equivalent vigorous activity) for all adults.
- Need for Physical Activeness: According to the WHO, physical activity is a must for good health.
- Physical inactivity puts adults at greater risk of cardiovascular diseases such as heart attacks and strokes, Type 2 diabetes, dementia and cancers of the breast and colon.
- Physical activeness also improves mental health and a stronger immune system.
Way Forward
Though the estimates of physical activity in 2022 may have been affected by Covid in many parts of the world, the trend of reduced physical activity is likely to persist, unless effective interventions are made by urban planners to create space for physical activity and people are willing to make behavioral changes.
- Group Activity Promotion: While Fit India and Let’s Move India have been launched in recent years, India needs settings-based group activity promotion efforts at school, worksite and community settings.
- Healthy Environment: Protected cycling lanes, safe pedestrian pathways, green community spaces and reduced air pollution will enable safe and pleasurable outdoor activity.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
World Health Organization (WHO):
- Established: October 24, 1945
- The WHO Constitution came into effect on April 7, 1948.
- WHO began functioning in 1951 after acquiring sufficient resources, emerging from the merger of the Health Organisation of the League of Nations and other entities.
- Headquarters: Geneva, Switzerland
- India’s Membership: India became a member of WHO on January 12, 1948.
|
![]() 27 Jun 2024
27 Jun 2024
