A recent study published in Science of The Total Environment found that turmeric samples from Patna, India, and Karachi and Peshawar, Pakistan contained lead levels exceeding 1,000 μg/g, far above the 10 μg/g regulatory limit set by FSSAI.
Key Findings of the Study
- Extent of study: Turmeric samples were collected from 23 cities across India, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, and Nepal between December 2020 and March 2021.
- Guwahati and Chennai also showed lead levels surpassing safe limits.
- Source of Contamination: Lead chromate is identified as the probable source, a yellow pigment used in paints and other industrial products, often added to enhance turmeric’s colour.
- Adulteration Patterns: Polished turmeric roots showed the highest contamination, followed by loose powder. Packaged powder and unpolished roots had lower levels.
- Unregulated, loose spices were more often adulterated compared to branded, packaged varieties.
- FSSAI Regulations: FSSAI requires turmeric to be free from lead chromate and any other colouring additives.
- Previous Findings and Supply Chain Issues: The researchers previously found widespread use of lead chromate in Bangladesh to improve turmeric’s appearance, dating back to the 1980s.
- Further investigation is recommended into the turmeric supply chain to identify contamination sources and understand the incentives for adulteration.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
About Lead and Lead Pollution
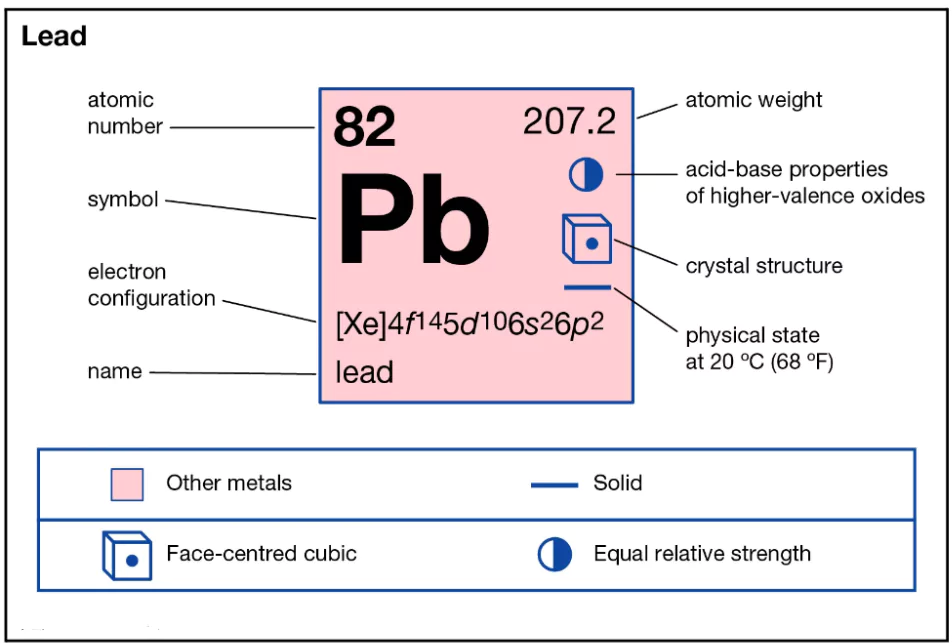
- Lead is a bluish-white Lustrous soft metal naturally found in the Earth’s crust.It is Usually found in ore with zinc, silver and copper.
- Used in production of Batteries (Automobiles and Inverters), ammunition, metal products (pipes), etc.
- Current Lead Use: Over 85% of mined or recycled lead is used in lead-acid batteries.
- Despite the phase-out of lead in gasoline, paint, and plumbing by 2000, lead demand has increased due to the affordability of lead-acid batteries.
Sources of Lead Pollution
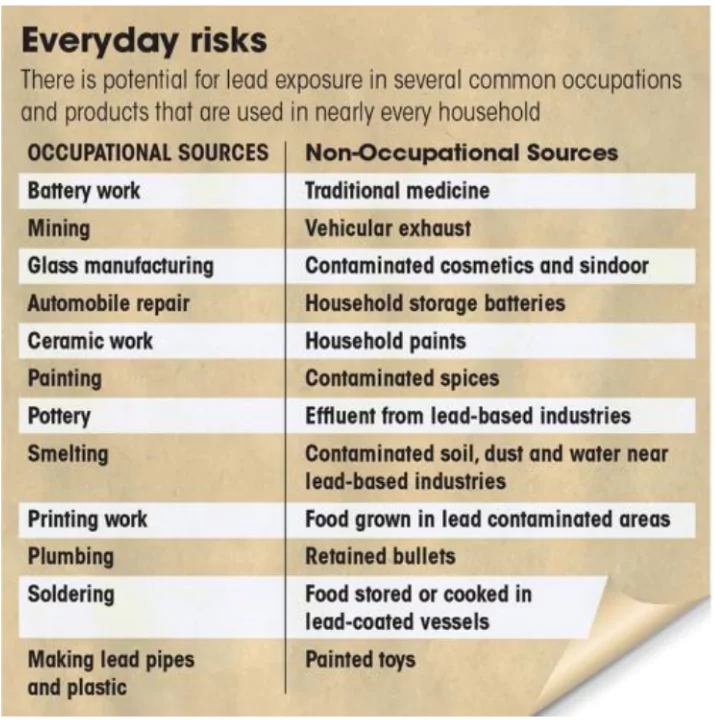
Primary Sources
- Lead-Based Paint: A major source of lead exposure, particularly in older homes.
- Industrial Emissions: Smelting of lead ores, battery manufacturing, and other industrial processes release lead into the air and water.
- Leaded Gasoline: Though largely phased out, residual lead from older gasoline can still contaminate soil and water.
- Occupational Exposure: Workers in industries like mining, smelting, and battery manufacturing are at risk.
Secondary Sources
- Soil Contamination: Lead from various sources accumulates in soil, especially in urban areas and near industrial sites.
- Drinking Water: Lead can leach from lead pipes, fixtures, and solder, contaminating drinking water.
- Consumer Products: Some traditional remedies, cosmetics, and imported products may contain lead.
- Food Contamination: Lead can contaminate food through soil, water, or additives used as adulterants.
- Dust and Soil Ingestion: Children often ingest lead-contaminated dust and soil, particularly in older homes or polluted areas.
Exposure Pathways
- Inhalation: Breathing in lead-contaminated air or dust.
- Ingestion: Consuming food or water contaminated with lead or ingesting lead-contaminated dust or soil.
- Dermal Absorption: Direct skin contact with lead-containing substances.
Impact of Lead Pollution
- Health Impact: Lead increases risk of heart disease, kidney failure, and premature death.
- Lead exposure is linked to 5.5 million premature adult deaths annually from cardiovascular diseases as per Lancet Public Health.
- Adverse Health Impact: Once lead enters the bloodstream, it goes directly to the brain, particularly in children.
- Children at Risk: An estimated 815 million children globally have blood lead levels over 50 µg/L, with 413 million over 100 µg/L.
- As per WHO Blood lead levels as low as 3.5 µg/dL can lead to reduced intelligence, behaviour issues, and learning disabilities.
- It is estimated to cause 765 million lost IQ points among children globally each year.
- Accumulation in body:Lead, which mimics calcium, accumulates in bones, disrupts metabolic processes, reduces intelligence, and increases risks of heart disease, kidney failure, and premature death.
- Economic Cost vs. Gains: The economic cost of lead-related premature deaths and cognitive impairments is estimated at $6 trillion.
- Lead contributes less than $100 billion to the global economy, primarily through the $50 billion lead-acid battery industry.
- The gross annual revenue from lead mining in 2020 was about $7.3 billion.
- Environmental Impact: Lead contamination affects soil microbes and is toxic to insects, birds, and animals, disrupting ecosystems.
-
- Toxic to plants: Increase in lead concentration in soil from 0 ppm (parts per million) to 1000 ppm reduced germination rate of wheat seeds from 98% to 50% and reduced biomass generated by 44%.
- Impact on Birds: They develop anaemia, and brain damage and can have difficulty flying, landing, and walking, and face increased mortality.
Check Out UPSC Modules From PW Store
Proposed Actions to Mitigate Lead Exposure
- International Treaty: Researchers advocate for a global treaty to eliminate lead mining and lead-containing products, though such agreements may take years.
- Immediate Measures: Implement progressive taxes on lead products and provide subsidies for safer alternatives.
- Establish a phase-out date by 2035 to stimulate development of substitutes.
- Legacy Lead Concerns: Lead contamination from previous uses will persist, but exposure would gradually decrease with reduced new lead use.
- Example: The U.S. saw a 94% decline in blood lead levels in children under age five after phasing out lead in gasoline over 40 years.
Indian Government Steps to Control Lead Poisoning
- Lead Battery Waste Management Rules, 2016: Mandates environmentally sound management of lead-acid batteries.
- Requires manufacturers, importers, and dealers to collect and recycle used batteries.Sets standards for recycling facilities to minimise lead emissions and waste.
- Import Ban on Non-Compliant Lead Acid Batteries: Prohibits the import of lead-acid batteries that do not meet specific quality and environmental standards.
- It aims to reduce the influx of low-quality batteries that may contribute to lead pollution.
- Global Alliance to Eliminate Lead Paint: An international initiative to phase out the production and use of lead paint.
- India is a signatory to the Alliance and has committed to reducing lead exposure from paint.
![]() 12 Nov 2024
12 Nov 2024


