Recently, the Supreme Court directed the liquidation of Jet Airways to commence as the “last viable resort” to protect the interests of the debt-ridden airline, its creditors, workmen and employees, following the failure of a resolution plan.
Key Highlights of the Case
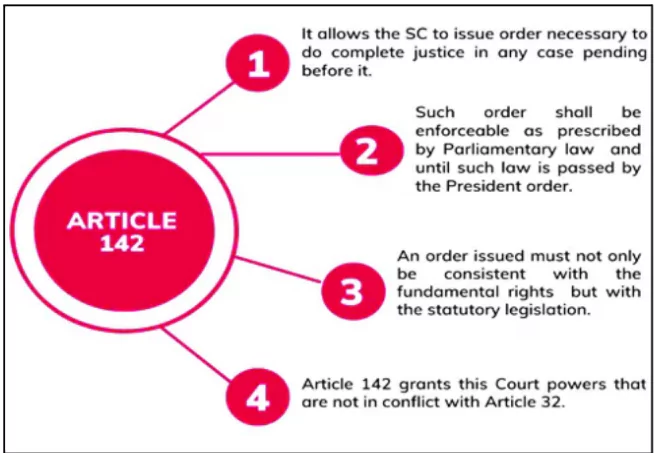
- Supreme court jurisdiction: The court’s plenary powers under Article 142 of the Constitution to direct the airline into liquidation in compliance with the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC) of 2016.Speedy Resolution Required: The court emphasized the need for a prompt resolution or, alternatively, a time-bound liquidation to prevent further depreciation of Jet Airways’ assets.
- Invocation of Article 142: The court used its plenary powers under Article 142 of the Constitution to mandate liquidation, asserting that over five years had passed with no significant progress on the resolution plan.
- Direction to NCLT: The apex court instructed the National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT) in Mumbai to initiate liquidation, appoint a liquidator, and complete all required formalities.
- Performance Bank Guarantee (PBG) and Funds: The Supreme Court criticized the NCLAT’s directive to adjust the PBG against the first payment tranche, calling it legally unsustainable, and allowed creditors to encash the PBG.
- The court also forfeited an additional ₹200 crore infused by the Jalan-Kalrock consortium.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
What Is Liquidation?
- Liquidation in finance and economics is the process of bringing a business to an end and distributing its assets to claimants.
- It is an event that usually occurs when a company is insolvent, meaning it cannot pay its obligations when they are due.
- As company operations end, the remaining assets are used to pay creditors and shareholders, based on the priority of their claims. General partners are subject to liquidation.
- The term liquidation may also be used to refer to the selling of poor-performing goods at a price lower than the cost to the business or at a price lower than the business desires.
National Company Law Appellate Tribunal (NCLAT)
- Establishment: Formed on June 1, 2016, under Section 410 of the Companies Act, 2013, NCLAT serves as the appellate authority for NCLT orders.
- Structure: Headed by a Chairperson, with Judicial and Technical Members assisting in the adjudication of cases. Members possess expertise in fields such as law, finance, and corporate governance.
- Primary Role: Acts as an appellate body to review decisions made by the NCLT, Competition Commission of India (CCI), and Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (IBBI).
- Function: Handles appeals related to company law matters, insolvency and bankruptcy cases under IBC, and competition law issues.
- Objective: Ensures a fair and efficient resolution of corporate disputes, fostering corporate governance and protecting stakeholder interests.
|
About Jet Airways’ Liquidation
- Failed Resolution Plan: Jet Airways, which ceased operations in April 2019, had a resolution plan approved by the National Company Law Appellate Tribunal (NCLAT). However, the plan faced ongoing issues and stalled progress, leading to the Supreme Court’s decision for liquidation.Role of the Jalan-Kalrock Consortium: The consortium, led by Murari Lal Jalan and Florian Fritsch, had committed to infusing funds but fell short of executing the resolution plan to satisfaction.
- Creditors’ Claims: The creditor banks, led by the State Bank of India, had claims worth around ₹7800 crore.
- The Supreme Court’s ruling aims to recover and distribute assets to these creditors and other stakeholders, including Jet Airways’ employees.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
Provisions for Liquidation under the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC)
- Liquidation as a Last Resort: The IBC allows liquidation when a corporate debtor’s resolution plan fails, as in the case of Jet Airways, where liquidation is deemed necessary after the lapse of five years with little progress.
- Role of Liquidator: The NCLT will appoint a liquidator responsible for the sale of assets and distribution of proceeds to creditors, employees, and other eligible parties.
- Asset Protection: The liquidation process aims to protect and maximise the value of Jet Airways’ assets to prevent further depreciation.
![]() 8 Nov 2024
8 Nov 2024


