A report by the Soil Association Exchange highlights that farms using a mixed enterprise system with both arable crops and livestock can increase soil organic carbon (SOC) by one-third compared to farms growing crops alone.
Key Research Findings
- Data was collected from 685 UK farms over a two-year period (2022-2024), covering 238,000 hectares.
- The study found that while livestock is a notable source of methane emissions, but it can significantly enhance soil carbon storage.
- Average soil organic matter across surveyed farms: 5.74%
- Average SOC across surveyed farms: 3.34%
- Arable-only farms (including potatoes): 2.54% SOC
- Mixed farms with cows and sheep: 3.47% SOC
- Farms with only cows and sheep: 4.92% SOC
- Additional Benefits of Mixed Enterprise Farms: Greater plant diversity and improved biodiversity were found on mixed farms compared to those solely for arable cropping.
- The Study assessed six key areas:
- Soil health
- Carbon storage
- Biodiversity
- Animal welfare
- Water quality
- Community and societal impact
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
About Soil Organic Carbon (SOC)
- SOC is the measurable component of soil organic matter (SOM) and specifically refers to the carbon content within organic compounds in the soil.
- Organic matter generally constitutes 2-10% of a soil’s mass, crucially affecting the soil’s physical, chemical, and biological functions.
Difference Between SOC and SOM
- SOC is strictly the carbon fraction of SOM, making it easier to measure in laboratory settings.
- SOM includes carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and other elements (like nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur), and it exists in both “living” (roots, fauna, microbes) and “dead” forms (decayed organic material).
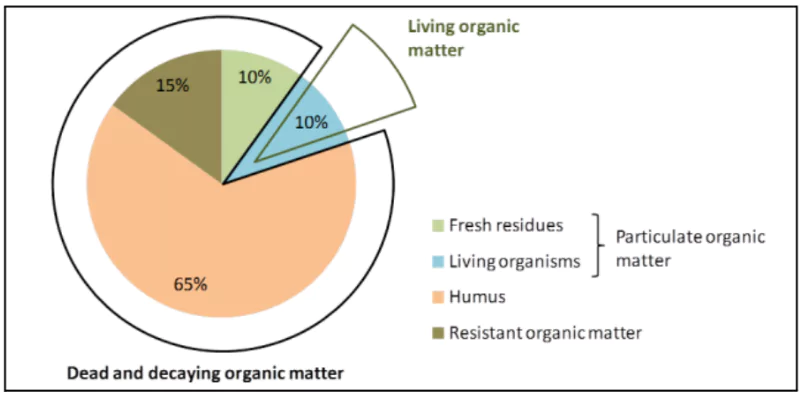 SOM consists of:
SOM consists of:-
- Dissolved Organic Matter
- Particulate Organic Matter
- Humus
- Resistant Organic Matter
- These fractions vary in size, stability, and how quickly they decompose, affecting their longevity and impact on soil health.
Carbon Sequestration
Carbon sequestration is the process of capturing and storing carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere to reduce the amount of carbon in the atmosphere and limit climate change.
There are two main types of carbon sequestration:
- Biological: A natural process that occurs as part of the carbon cycle, where plants absorb CO2 from the air and store it in their biomass.
- Humans can enhance this process through land use changes and agricultural practices, such as carbon farming.
- Geological: An artificial process that involves capturing CO2 from human activities and storing it underground or under the sea bed.
- This process is also known as carbon capture and storage.
|
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Soil Organic Carbon and Carbon Sequestration
- SOC is viewed as a potential method for climate change mitigation by sequestering carbon and lowering atmospheric CO₂.
- For lasting impact, SOC must be stored in stable fractions of SOM
![]() 30 Oct 2024
30 Oct 2024

 SOM consists of:
SOM consists of: