A new study published in the journal Nature has found that Marine heat waves ( MHW) can also be observed in the “twilight zone“, between the depths of 200 and 1,000 meters.
Key Findings of the Study
- Neglected Zone: MHWs in deep oceans such as Twilight zone have been under-reported because the usual focus is on surface temperature changes.
- Role of Eddy Currents: In the deep ocean, eddy currents, which are large swirling currents sometimes hundreds of kilometers wide, are primarily responsible for temperature changes, rather than atmospheric factors.
- Eddies carry warm or cold water over long distances, significantly impacting temperature fluctuations in the deep ocean.
- Increased Intensity of Eddies: Due to global warming, eddy currents are intensifying, leading to stronger and more frequent marine heatwaves (MHWs) and marine cold spells (MCSs) in the twilight zone.
- Measurement Techniques: The study used long-term moorings (buoys placed at depth) and Argo floats (robotic divers that measure temperature and salinity up to 2,000 meters deep) to record the temperature changes in deep waters.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
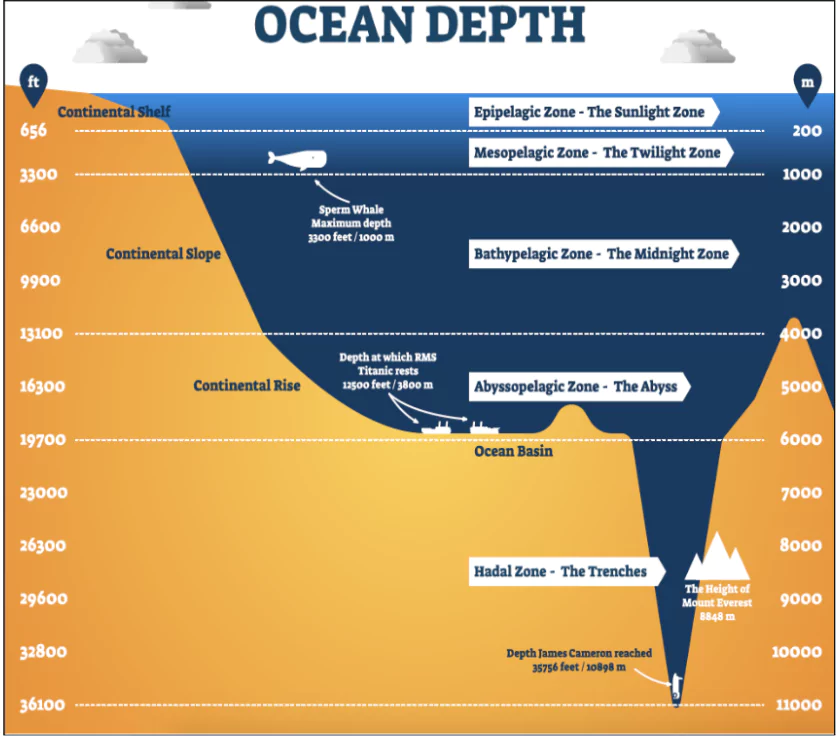
What is the Twilight Zone?
- The Twilight Zone is a layer of the ocean spanning across the whole of Earth beginning at two hundred metres below the surface, and ending at 1km down.
- The temperatures stay close to freezing and water pressure can reach 1,500 pounds per square inch in the twilight zone.
Importance of the ocean Twilight Zone
- Twilight zone: Whales and fish migrate and dead algae and zooplankton rain down from above providing food for twilight-zone animals.
- Heart of the Ocean’s carbon pump: Part of the natural ocean processes that capture about a third of all human-produced carbon dioxide and sink it into the deep sea, where it remains for hundreds of years.
|
Layers of Ocean
About Marine Heat wave
- An extreme weather event: MHW occurs when the surface temperature of a particular region of the sea rises to 3 or 4 degree Celsius above the average temperature for at least five days.
Causes of Marine Heatwaves
- Change in Wind Pattern: Wind patterns can enhance or suppress MHWs
- Natural Phenomenon: Events like the El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO)
- Intensification with Global Warming: Oceans absorb the additional heat caused by greenhouse gas emissions.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
Impacts of MHW
- Catastrophic for marine life: Destroyed kelp forests, which usually grow in cooler waters, providing habitat and food for many marine animals.
- Leading to Coral Bleach: Corals are very sensitive to the temperature of the water in which they live. When water gets too warm, they expel the algae known as zooxanthellae, living in their tissues, causing them to turn entirely white.
- Extreme weather: Higher ocean temperatures, which are associated with MHWs, can make storms like hurricanes and tropical cyclones stronger.
- Heightened Devastation for Humans: With warmer temperatures the rate of evaporation escalates the transfer of heat from the oceans to the air. When storms travel across hot oceans they gather more water vapor and heat.
- This results in more powerful winds, heavier rainfall and more flooding when storms reach the land causing loss of properties and life.
![]() 18 Oct 2024
18 Oct 2024
