Minerals Security Finance Network (MSFN), an offshoot of the Minerals Security Partnership (MSP) has been established on the margins of the United Nations General Assembly in New York.
- India is one of the founding member of the Minerals Security Finance Network (MSFN)
About Minerals Security Partnership (MSP)
- It is a global initiative to bolster critical mineral supply chains also known as the critical minerals alliance.
- Establishment: The Minerals Security Partnership (MSP) was officially announced at the annual Prospectors and Developers Association of Canada (PDAC) convention in Toronto, Canada in June 2022.
- It is the largest mining event in the world.
- Founding Members: The United States, Australia, Canada, Finland, France, Germany, Japan, the Republic of Korea, Sweden, the United Kingdom, and the European Commission
- India joined the initiative in June of 2023
- Aim: To accelerate the development of sustainable critical energy minerals supply chains via a public-private partnership to facilitate targeted financial and diplomatic support for strategic projects along the value chain.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
- Objective :
- Entire Mineral Value Chain: The MSP considers projects along the full clean energy value chain, from mining, extraction, and secondary recovery, to processing and refining, and ultimately to recycling.
- The MSP’s focus is to secure and utilize the minerals and metals supply chains most relevant for clean energy technologies.
- Example: Lithium, cobalt, nickel, manganese, graphite, 17 rare earth elements, and copper etc.
- Focus:
- Diversifying and stabilise the global supply chains
- Investment in those supply chains
- Promoting high environmental, social, and governance (ESG) standards in the mining, processing, and recycling sectors
- Increasing recycling of critical minerals.
- Projects in Pipeline: The MSP is collaborating on some 150-odd projects including fostering a critical minerals and metals cooperation forum for sharing of expertise, developing battery materials and jointly developing a minerals processing facility in South America.
- Significance:
- Building Resilience: The energy transition needs more production capacity for critical minerals which require decongestion of the supply chains and building its resilience.
- Minimise China’s Dominance: China controls close to 70% of the processing infrastructure in the world for critical minerals. The alliance is seen as primarily focused on evolving an alternative to China.
- Electric Vehicle Revolution: The Initiative will power the electric vehicle and battery revolution in the world through conscious and sustainable and equitable sourcing of these minerals which is crucial for greenify the transport and energy sector.
- Sustainable Critical Energy Minerals Supply Chains: Accelerate the development of diverse and sustainable critical energy minerals supply chains globally.
The Minerals Security Finance Network (MSFN)
- Members: US, Australia, Canada, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, India, Italy, Japan, the Republic of Korea, Norway, Sweden, the United Kingdom, and the European Union
- Implementing Agencies: This new partnership will bring together DFIs (development finance institutions) and ECAs (export credit agencies) from the Minerals Security Partnership (MSP) partner governments to create synergies, and increase impact.
- Aim: To strengthen cooperation and promote information exchange and co-financing among participating institutions to advance diverse, secure, and sustainable supply chains for critical minerals.
- Need: It was felt that any single institute by itself is unable to achieve the clean energy transition.The goal requires both the public sector and private sector to work together to deploy capital into new and existing markets in this sector.
|
About Critical Minerals
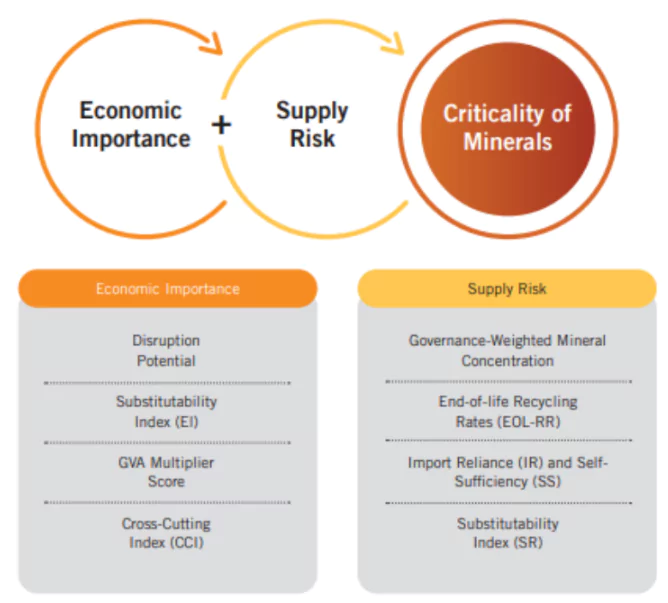
- Definition: These are the minerals which are essential for economic development and national security but the scarcity and limitation of its geographical availability leading to supply chain vulnerability and disruption constitute to its criticality.
 Major Critical Minerals: The Report of the Committee on Identification of Critical Minerals constituted by Ministry of Mines has identified 30 critical minerals,
Major Critical Minerals: The Report of the Committee on Identification of Critical Minerals constituted by Ministry of Mines has identified 30 critical minerals,
- Antimony, Beryllium, Bismuth, Cobalt, Copper, Gallium, Germanium, Graphite, Hafnium, Indium, Lithium, Molybdenum, Niobium, Nickel, PGE, Phosphorous, Potash, REE, Rhenium, Silicon, Strontium, Tantalum, Tellurium, Tin, Titanium, Tungsten, Vanadium, Zirconium, Selenium and Cadmium.
- Top Producers: According to the International Energy Agency, the major producers of critical minerals are China, Congo, Chile, Indonesia, South Africa, and Australia.
- China has global dominance in terms of processing.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
- Usage:
- Advanced Electronics: They are critical for making semiconductors and high-end electronics manufacturing.
- Clean Energy Technology: These minerals are an essential components in many clean energy technologies, from wind turbines and solar panels to electric vehicles.
- Transport and Communications: They are also used in manufacturing fighter jets, drones, and radio sets, Aircrafts and mainly power the transition to Electric Vehicles
- Diverse Sectors: To manufacture advanced technologies in diverse sectors such as mobile phones, tablets, electric vehicles, solar panels, wind turbines, fibre optic cables, and defence and medical applications.
- Battery and Storage Technology: These minerals are critical to develop the storage technology in terms of advancements in battery technology like Lithium-Ion.
 Components of Value Chain:
Components of Value Chain:
- Geoscience and Exploration
- Upstream: Mining and Extraction
- Midstream: Processing, Refining and Metallurgy
- Downstream: Component Manufacturing and Clean Digital Advanced Technology production
- Example: ZEV Manufacturing, Semiconductors, chips etc.
- Material Recovery and Recycling
Challenges
- New Source of Emissions: Energy intensive mining operations and processing activities will further lead to significant greenhouse gas emissions cancelling out the progress made by reducing fossil fuels.
- Environmental Degradation: Mining for these minerals in an unsustainable way will have the same adverse environmental impacts, including biodiversity loss and pollution.
- Human Rights Violation: The race for Critical minerals will lead to negative social impacts including human rights abuses such as child labour, indigenous people’s rights violation and displacement etc.
- Supply Chain Disruption: Scarcity in supply due to limited availability could slow down the energy transition or make it more expensive and unequal.
- Race for Control: Since these minerals will fuel the technologies of the future, It will lead to rising geopolitical tensions over their control, interference in markets, and strong political pressure to expand mining.
Way Forward
- Mineral Diplomacy: India must actively engage in bilateral and plurilateral arrangements for building assured and resilient critical mineral supply chains.
- Responsible Mining and Circularity: Ensure stability in supply by rethinking mobility, housing, and industrial systems while reducing demand through responsible sourcing by emphasizing on material efficiency, substitutes,and resource circulation is needed.
- Extended Producer Responsibility: The accountability of producers for the entire product lifecycle should be ensured by incorporating the concept of extended producer responsibility in a circular framework as a principle.
- Transparency and Trust: The lack of trust between producers and consumers, as well as within local communities should be bridged by disclosing information about extraction processes and mineral origins via real-time and robust information
- Regular Update of Assessment: The assessment of critical minerals for India needs to be updated every three years to keep pace with changing domestic and global scenarios.
- National Critical Minerals Strategy: A national critical minerals strategy for India, underpinned by the minerals identified in this study, can help focus on priority concerns in supply risks, domestic policy regimes, and sustainability.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
About Rare Earth (RE)

- Rare Earth (RE) are an essential part of many high-tech devices and comprises 17 elements which are classified as light RE elements (LREE) and heavy RE elements (HREE) including,
- The 15 Lanthanides: Atomic numbers 57 ( Lanthanum) to 71 in the periodic table
- Scandium (atomic number 21)
- Yttrium (39).
- Application In: Computer hard drives, cellular telephones, flat-screen monitors and televisions, and electric and hybrid vehicles.
- Availability: India has the world’s fifth-largest reserves of rare earth elements, nearly twice as much as Australia.
- LREEs available in India: Lanthanum, Cerium, Neodymium, Praseodymium and Samarium, etc.
- HREEs not Available in India: Dysprosium, Terbium, and Europium are not available in Indian deposits in extractable quantities.
|
![]() 26 Sep 2024
26 Sep 2024
 Major Critical Minerals: The Report of the Committee on Identification of Critical Minerals constituted by Ministry of Mines has identified 30 critical minerals,
Major Critical Minerals: The Report of the Committee on Identification of Critical Minerals constituted by Ministry of Mines has identified 30 critical minerals,
 Components of Value Chain:
Components of Value Chain: