Scientists are preparing for a clinical trial to test the safety and effectiveness of mitochondrial donation.
Mitochondrial donation Significance
- This procedure offers a cure for Mito disease
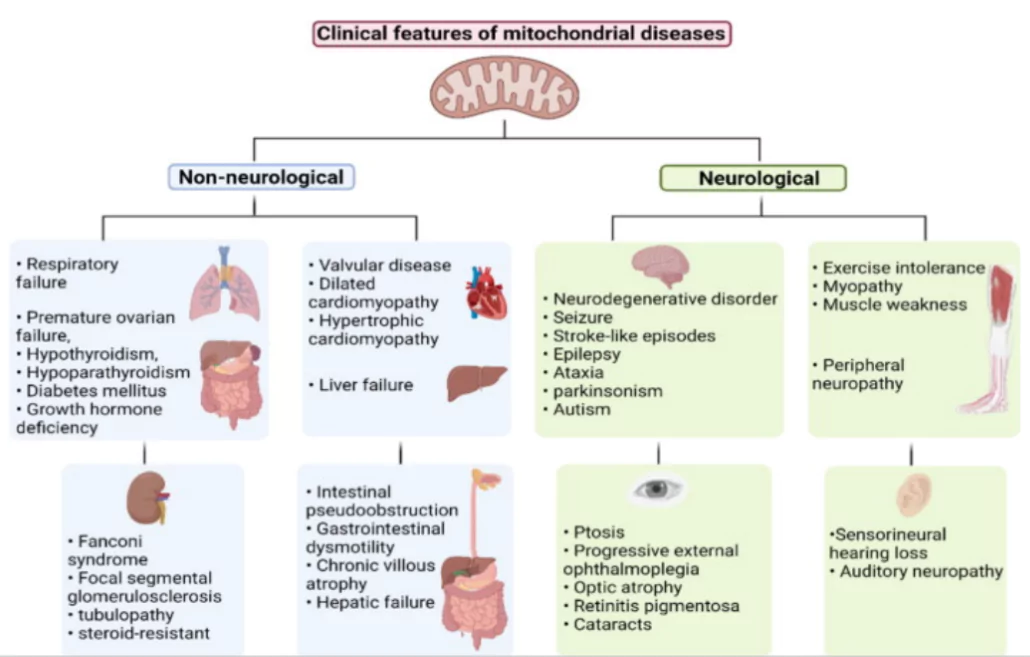
About Mitochondrial Disease
- Mitochondrial disease (or Mito) affects the mitochondria’s ability to produce energy for organs, leading to potential organ failure.
- Types: There are two types of Mito:
- Nuclear DNA Fault: Caused by faulty genes in nuclear DNA, inherited from either parent.
- Mitochondrial DNA Fault: Caused by faulty genes in mitochondrial DNA, inherited only from the mother. The severity can vary widely.
- Commonly Affected Organs: Heart, brain, and muscles, as they require a lot of energy.
- Childhood Impact: Mito in children often affects multiple organs, progresses quickly, and can be fatal.
- Prevalence: Around 1 in 5000 people suffer from genetic mitochondrial disease.
- Number, type of symptoms and organ systems cause misdiagnosis, leading to underestimation of prevalence of this disease.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Mitochondrial Donation
- Mitochondrial donation is a new IVF technique that helps people with faulty mitochondrial DNA have children who are genetically related to them without passing on the defective DNA.
-
Process
- Remove the nuclear DNA from an egg with faulty mitochondrial DNA.
- Insert the nuclear DNA into a donor egg with healthy mitochondrial DNA.
- Fertilize the egg with sperm, combining the nuclear DNA of both parents with healthy mitochondria from the donor.
-
Benefits: The child will have genetic material from three people—nuclear DNA from both parents and mitochondrial DNA from the donor.
- It will reduce or eliminate the risk of mitochondrial disease.
- Procedure of Mitochondrial Donation
- Preparation: Both the egg donor and the person with mitochondrial disease receive hormone injections to stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs.
- Egg Retrieval: Eggs are retrieved using an ultrasound-guided surgical procedure.
-
Challenges: One of the major hurdles in mitochondrial donation is finding suitable eggs. While frozen eggs might work for initial research and training, actual clinical trials require fresh eggs.
- There are two main challenges in acquiring these eggs:
- Limited availability: Not everyone opts to freeze their eggs, making readily available frozen eggs scarce.
- Need for fresh eggs: For the most effective procedures, fresh eggs are irreplaceable.
- Potential solutions to address this challenge:
- Egg donation programs: Encouraging people who have already undergone egg retrieval and have unused eggs to donate them.
- Volunteer donors: Recruiting individuals willing to undergo egg donation specifically to help those with mitochondrial diseases is another option.
- This could involve both those who know someone participating in the trials and those who are simply driven to help others have healthy children.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
Maeve’s Law on Mitochondrial Donation
- Legislation: The Mitochondrial Donation Law Reform Bill 2021 was passed by the Australian Senate in 2022 after three years of public consultation.
- Legalization: This law makes mitochondrial donation legal for research and clinical trials in Australia.
Regulations Under Maeve’s Law
- Permit Requirements: Facilities need a special permit to perform mitochondrial donation.
- Licensing:
-
- Initial licences will be issued for pre-clinical and clinical trial research and training.
- These licences ensure the safety and effectiveness of mitochondrial donation before it is used in regular clinical practice.
MitoHOPE Program
- Goals: The mitoHOPE program aims to refine the mitochondrial donation method and conduct a clinical trial to confirm its safety and effectiveness.
- Training:
- Embryologists will be trained in real-life clinical conditions.
- Existing techniques for mitochondrial donation will be improved through a preclinical research and training program.
- Requirements: A large number of human eggs are needed for this program.
|
![]() 12 Jul 2024
12 Jul 2024

