Recently the Finance Minister reported 5,892 cases under PMLA since 2015, but only 15 convictions, reflecting rising money laundering and weak enforcement.
What is Money Laundering?
- Definition: As per Section 3 of the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA) 2002, it involves concealing, possessing, acquiring, or using proceeds of crime and projecting them as untainted property.
- Types
- Traditional Laundering: Through businesses or banks to disguise illegal proceeds.
- Laundromats: Financial vehicles used to hide ownership, evade taxes, and move funds offshore, often operated by banks or service companies.
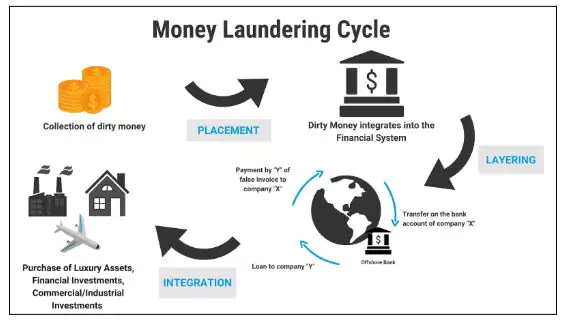
- Stages of Money Laundering
-
- Placement: Introducing illegal money into the financial system, often by breaking large cash amounts into smaller deposits (smurfing).
- Layering: Moving money through complex transactions and cross-border transfers to obscure its source.
- Integration: Bringing laundered money back into the economy through real estate, businesses, or asset formation.
Impact of Money Laundering
- Impact on National Security: The Supreme Court (P. Chidambaram vs ED, 2019) held that laundering undermines financial systems, sovereignty, and integrity, and fuels terror financing.
- Economic Instability: Expansion of illicit money disrupts monetary stability, triggering inflation and eroding trust in the economy.
- Trade Disruptions: According to FATF, laundering distorts fair competition and affects legitimate trading channels.
- Terror Financing: Illicit funds directly sustain extremist networks, making money laundering a critical threat to global and domestic security.
Provisions to Curb Money Laundering
Prevention of Money Laundering Act (2002)
- Burden of proof lies on the accused.
- Enforcement Case Information Report (ECIR) is sufficient to initiate proceedings; no FIR is required (Vir Bhadra Singh vs ED, 2017).
- Property can be attached even without a registered case (Vijay Madanlal Chaudhury vs Union of India, 2022).
- Focus on confiscation of property and punishment for offenders.
About Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA)
It is a bilateral treaty between two countries designed to:
- Avoid double taxation of the same income in both countries.
- Facilitate exchange of tax and financial information between tax authorities.
- Help prevent tax evasion and money laundering by improving transparency in cross-border financial flows.
|
International Mechanisms
- UN Political Declaration and Global Programme of Action (1990): Framework to prevent money laundering globally.
- Financial Action Task Force (FATF): Sets global standards on anti-money laundering (AML).
- Double Taxation Avoidance Agreements (DTAA): DTAA with 85 countries facilitate exchange of tax and financial information to prevent tax evasion and illicit transfers.
Challenges in Money Laundering Cases
- Low Conviction Rate: Only 15 convictions out of 5,892 cases indicate ineffective enforcement and investigation gaps.
- Rising Incidence: Increasing cases reflect failure to deter financial crimes.
- Misuse of Law: Authorities have allegedly used PMLA for political purposes, undermining trust in enforcement.
- Complexity of Transactions: Cross-border movements and digital methods make tracing time-consuming and resource-intensive.
- Impact on Economy: Leads to monetary instability, inflation, trade distortions, and links to terror financing.
Way Forward
- Strengthen Implementation: Follow FATF recommendations to ensure robust detection, reporting, and prosecution mechanisms.
- Build specialised investigation and forensic capacity to track complex financial flows.
- Prevent Misuse of Law: Ensure checks against politically motivated actions; apply PMLA strictly for genuine cases.
- Enhance International Cooperation: Fully utilise DTAA frameworks for real-time information sharing and coordinated investigations.
- Explore innovative cross-border tracking systems for digital and offshore transactions.
- Improve Conviction Rates: Establish dedicated financial courts for speedy trials.
- Increase capacity of ED and tax authorities to prepare stronger evidence.
- Focus on Terror Financing: Treat money laundering as a national security threat by integrating AML efforts with counter-terror frameworks.
Additional Reading: Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA)
![]() 6 Aug 2025
6 Aug 2025

