Context:
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
How dependent is India on monsoon rainfall?
- The monsoon has a direct impact on India’s economy. A successful monsoon season boosts farm production and income of both farmers and laborers.
- This in turn has an impact on rural household incomes, which then stimulates demand for goods and services, especially rural demand.
- Rainfall Deficit: The southwest monsoon season ended with rains that were ‘below normal‘. India saw a rainfall deficit of six percent in monsoon 2023 of the long-period average of 50 years.
- Six states viz. Assam, Manipur, Mizoram, Jharkhand, Bihar, and Kerala recorded major deficits.
- El Nino Impact: India is currently in an El Nino year which is generally associated with less intense rainfall than normal during the monsoon season for India.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
- Heavy Reliance on Monsoon: The Indian economy relies heavily on the Southwest monsoon since the country gets 75% of its rainfall during this period.
- A good or bad monsoon season can have a direct impact on the rural income and overall economic growth of the country.
- However, historical trends suggest that the equity market does not react linearly to the outcome of the monsoon.
Also Read: Onset’ Of The Monsoon
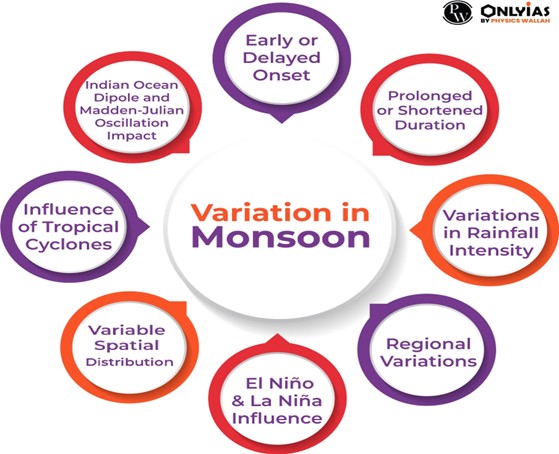
What are the major phenomena influencing Monsoon Rainfall?
- Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD): It involves fluctuations in sea surface temperatures (SST) across the Western Indian Ocean near the Arabian Sea and the eastern counterpart near Indonesia in the Indian Ocean.
- Positive IOD: When the western part of the Indian Ocean experiences higher SSTs compared to that over the eastern Indian Ocean, it signifies a positive IOD, which tends to be conducive for the stronger than normal Indian monsoon.
- Conversely, a negative IOD phase results in weaker than normal Indian monsoon.
- El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is one of the major drivers of the interannual variability of monsoon.
- ENSO refers to the large-scale ocean-atmosphere climate interaction linked to periodic variation in the winds and SSTs across the central and east-central Equatorial Pacific.
- Madden-Julian Oscillations (MJOs): The 30-60 days oscillations are the dominant component of the intra-seasonal variability in the tropical atmosphere.
- It can be characterised as an eastward moving ‘pulse’ of cloud and rainfall near the equator.
|
Enroll now for UPSC Online Coaching
Why are monsoon rainfall important for the Indian economy?
- Agriculture Dependency: India has a predominantly agrarian economy, contributing substantially to the country’s food security. Insufficient rainfall, particularly during the month of August, has significantly hindered the timely sowing of the majority of kharif crops.
- The all-India unemployment rate (UR) edged up to 8.1% in August 2023 from around 7% in June 2023 on account of higher UR in urban areas.
- Water Reservoirs and Irrigation: The monsoon season replenishes water reservoirs and helps in maintaining adequate water levels in rivers and lakes. Reliable monsoons reduce dependence on expensive irrigation methods and contribute to the sustainability of agriculture.
- Adequate monsoon rainfall ensures sufficient water levels in rivers and dams, facilitating hydropower generation.
- Rural Economy: Increased farm income contributes to higher rural spending, supporting various local businesses and services. States with low deficit or deficient rainfall have witnessed more demand for work under Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS).
- Inflation Control: A good monsoon season helps in maintaining stable food prices by ensuring an adequate supply of agricultural commodities.
- Due to deficit rainfall, headline inflation stood at 6.8% with food inflation at around 10% in August 2023.
- GDP Growth: A robust agricultural sector contributes to higher GDP, as it is a major component of the country’s economy. Conversely, poor monsoons can lead to agricultural distress and have a negative impact on economic growth.
How does monsoon rainfall affect the Indian economy and agriculture?
Enroll now for Online Course
- Agricultural Output: Insufficient rainfall can lead to crop failure which in turn, impacts farmers’ income, disrupts the supply of essential food items, and contributes to food inflation. The Indian economy suffers heavy losses due to floods and droughts almost every year.
- Impact on Rural Economy: Below normal monsoon conditions can lead to a slowdown in economic activities in rural areas, affecting various businesses and services that depend on agricultural income. For instance, about 800 million people live in villages and depend on agriculture, which accounts for about 15% of India’s gross domestic product (GDP) and a failed monsoon can have a rippling effect on the country’s growth and economy
- Pressure on Government Finances: The government may face increased financial pressure due to the need for relief measures to support affected farmers. Subsidies, loan waivers, and other financial assistance programs may be required to mitigate the economic impact on the agricultural sector.
- Trade Imbalance: A decline in agricultural production due to below normal monsoons can affect India’s export performance which can contribute to a trade imbalance and impact the country’s foreign exchange earnings.
- For instance, India’s imports of pulses such as tur (pigeon pea) and urad (black matpe) have more than doubled in the April-June quarter of 2023-23.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Relation between Monsoon Rainfall and Agriculture
- Farmers have been facing crop losses in many states, including Karnataka, Uttar Pradesh and Jharkhand due to the uneven monsoon.
- 8.68 lakh hectare crop area was affected by floods or heavy rainfall between April 1, 2023 and October 4, 2023.
- El Nino phenomenon: In August, lead to deficit in rainfall across India. This kharif season, sowing has been the weakest for pulses (8.6% lower than last year as on September 9).
|
Way Forward
- Groundwater Conservation: The Atal Bhujal Yojana is community-led groundwater management program helping improve rural livelihoods and build resilience in Indian states which have the highest rates of groundwater depletion.
- The “Paani Bachao, Paisa Kamao” (Save Water, Earn Money) scheme incentivizes farmers to reduce groundwater usage.
- For example, switching from rice to millets such as pearl millet & sorghum during the Kharif season and shifting from wheat to sorghum in the Rabi season could lower water consumption by 32%.
- Ensuring Supply: To check food inflation, the government needs to ensure domestic supplies of vegetables, pulses and other crops through imports.
- Recently, government resorted to imposing restrictions on the export of rice, wheat and sugar and took other regulatory measures because of the irregular nature of the monsoon.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Coaching
- Tackling Floods and Droughts: Climate change is increasing unpredictability in weather patterns and leading to more extreme weather events.
- Government had drawn up drought contingency plans for 571 districts with help from the Central Institute for Dryland Agriculture, similarly crop insurance through PM Fasal Bima Yojana can help farmers tide over potential crop losses.
- Research and Development: Water resources monitoring system is getting expanded to cover the entire country, including the Indus, Ganga, and Brahmaputra-Barak river basins.
- World Bank-supported hydrology projects have introduced new systems and technology that give an accurate picture of the water situation for a comprehensive knowledge base that can improve the overall management of water resources in the country.
- Artificial Rains: Artificial rain making techniques involving cloud seeding can be used for bringing rain clouds to rainfall deficit areas.
- For instance, Maharashtra government is considering cloud seeding to tackle deficient rainfall which could save kharif crops and also address depleted water levels in dams.
Also read: Interlinking of Rivers—Advantages, Challenges, and Solutions
Conclusion:
Monsoon rainfall is crucial for India’s economy, affecting farming, rural life, and economic growth. To address challenges, proactive steps like water conservation and advanced technologies are essential for sustainable growth.
| Attempt the PY Prelims Question
With reference to ‘Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD)’ sometimes mentioned in the news while forecasting
Indian monsoon, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2017)
1. IOD phenomenon is characterised by a difference in sea surface temperature between tropical Western Indian Ocean and tropical Eastern Pacific Ocean.
2. An IOD phenomenon can influence an El Nino’s impact on the monsoon.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b) |
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
![]() 14 Oct 2023
14 Oct 2023

