Context
Recently, a five-year-old girl suffering from primary amoebic meningoencephalitis (PAM),died in Kerala.
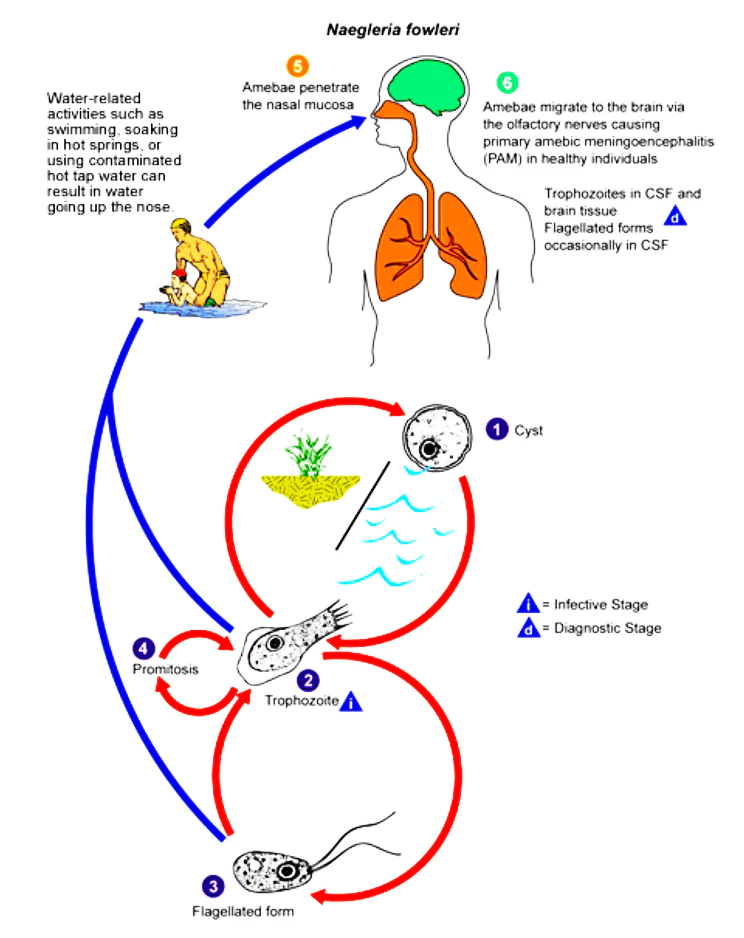
Naegleria fowleri
Naegleria fowleri is a free-living, single-celled amoeba that can lead to a rare brain infection called Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis (PAM).
- Type of Habitat: It inhabits warm freshwater and soil, infecting individuals when it enters the body through the nose.
- Growth Conditions : Higher temperatures of up to 115°F (46°C) are conducive to its growth and it can survive for short periods in warm environments.
- Non-Communicable: People cannot get infected with Naegleria fowleri from drinking water contaminated with the amoeba. PAM is also non-communicable.
- Forms of Naegleria fowleri:
- Cyst: Environmentally resistant, dormant form, Spherical shape, thick-walled.
- Trophozoite: Feeding and dividing form, Amoeboid shape with pseudopodia, Infective form in humans.
- Flagellate: Transitional form, Pear-shaped with two flagella, Non-feeding and temporary.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis (PEM)
- Symptoms of the Infection: Symptoms typically begin with headaches, fever, nausea, and vomiting. As the infection progresses, the individual may develop a stiff neck and exhibit confusion, seizures, hallucinations, and potentially lapse into a coma.
- Casualties: The majority of individuals affected by PAM succumb within 1 to 18 days from the onset of symptoms, often resulting in coma and eventual death approximately 5 days after symptoms appear.
- Treatment: Currently, no definitive treatment for the disease exists. It is managed using a combination of medications such as amphotericin B, azithromycin, fluconazole, rifampin, miltefosine, and dexamethasone.
Amoeba
Amoebas are classified as single-celled eukaryotic organisms, and are part of the Protista kingdom. They inhabit a range of aquatic and damp environments.
- Reproduction in Amoebas: Amoebas reproduce asexually through binary fission, dividing a cell into two identical daughter cells.
- Nutrition in Amoebas: Being heterotrophic, amoebas acquire nutrients by engulfing and digesting organic matter, bacteria, and other microorganisms through their pseudopodia.
- Diseases Caused by Amoeba: Certain types of amoebas, like Entamoeba histolytica, are parasitic and have the potential to induce illnesses in humans, such as amoebiasis.
- Role of Amoebas in Food chain: Amoebas play a crucial role in aquatic food webs, functioning as both predators and prey. They contribute significantly to nutrient cycling within their ecosystems.
![]() 24 May 2024
24 May 2024
