Dr. Ambarish Ghosh, a professor at IISc Bangalore, was recently awarded the 2025 New York Academy of Sciences and Tata Sons’ Transformation Prize for his work on magnetic nanorobots for targeted cancer therapy.
What Are Nanobots?
- Nanobots, short for nanorobots or nanomachines, are microscopic robots designed to operate at the nanoscale.
- Their size is typically measured in nanometers (one nanometer = one-billionth of a meter), meaning they are roughly the size of biological cells or large molecules.
- Function: They are programmable machines that can perform specific tasks at the molecular or cellular level.
- Materials: Often made from biocompatible substances like silica, DNA, metals (e.g., iron for magnetism), or even living cells (in “xenobots“).
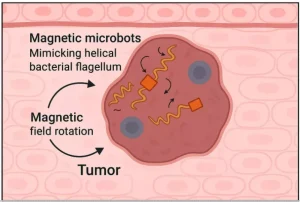
How They Work & Are Controlled?
- Nanobots are not autonomous, intelligent robots as seen in sci-fi.
- They are remotely controlled or pre-programmed to react to specific stimuli.
- Magnetic Fields: An external magnet rotates or guides a magnetic part of the bot.
- Chemical Reactions: The bot’s surface reacts with surrounding chemicals to generate movement. Enzymatic reactions on the bot’s surface can create propulsion.
- Biological Motors: Uses biological mechanisms (like ATP, the cell’s energy currency). DNA-based nanobots can “walk” along a track.
- Acoustic or Light Waves: Ultrasound or light pulses provide energy for movement. Microbubbles propelled by ultrasound waves.
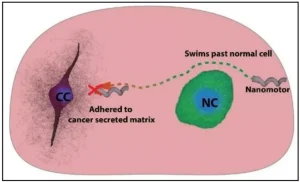
Potential Applications of Nanobots
- Targeted Drug Delivery: Deliver drugs directly to diseased cells (like cancer cells) while avoiding healthy ones.
- The nanobot can act as a “delivery truck,” coated with a cancer drug and steered magnetically to the tumor.
- Surgery & Cell Repair: Perform micro-surgeries inside the body, such as clearing clogged arteries, removing plaque, or repairing damaged tissue at the cellular level.
- Diagnostics & Imaging: Act as sensors to detect disease markers (like specific proteins or pH changes) or enhance imaging.
- Nanobots can be made to “light up” during an MRI, acting as beacons to pinpoint tiny or deep-set tumors.
- Disease Monitoring: Continuously monitor internal conditions (e.g., glucose levels for diabetics) and relay data externally.
- Other Fields:
- Environmental: Cleaning pollutants from water at the molecular level.
- Manufacturing: Building materials atom-by-atom (molecular manufacturing).
Challenges of Nanobots
- Engineering Challenges: Designing, manufacturing and controlling nanobots at atomic scales is extremely difficult due to limits in precision, power supply, communication and real-time navigation.
- Biocompatibility and toxicity: Nanobots may trigger immune responses, inflammation or cellular damage, and their safe degradation or removal from the body remains uncertain.
- Safety and reliability: Ensuring fail-safe functioning is challenging; malfunctioning nanobots are hard to track, deactivate or retrieve once released.
- Ethical and privacy concerns: Potential misuse for surveillance, human enhancement or biological harm raises serious ethical issues, including privacy of biological data.
- Regulatory and legal gaps: Lack of clear standards for testing, approval, liability and international control hinders large-scale deployment.
- High cost and accessibility: Advanced R&D and production costs limit affordability, risking unequal access and widening technological disparities.
Current Progress & Applications
- Cancer Types Tested: The technology has shown efficacy in lab tests against ovarian and breast cancer cells.
- Researchers are confident it can be adapted for other cancers.
- Dental Applications: Root canal infections are often caused by antibiotic-resistant bacteria, In early tests, nanobots have proven effective at targeting and destroying these bacteria.
- Future Potential: They may even help rebuild and remineralize teeth.
About the Tata Transformation Prize
- Established by: The New York Academy of Sciences and Tata Sons.
- Primary Goal: To advance innovation and support visionary Indian scientists developing breakthrough technologies to address India’s most significant societal challenges.
- Focus Areas: Food Security, Sustainability, and Healthcare.
- Award: Each winner receives ₹2 crore to advance their research and scale its real-world impact.
The 2025 Winners & Their Work
- Padubidri V. Shivaprasad for Food Security
- Research: Uses epigenetic engineering and small RNA modifications in rice to enhance stress tolerance and nutritional quality.
- Balasubramanian Gopal for Sustainability
- Research: Developed a green chemistry platform using bioengineered E. coli bacteria to produce key chemicals for pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and agriculture.
- Ambarish Ghosh for Healthcare
- Research: Developed magnetic nanorobots for cancer treatment.
|
![]() 26 Dec 2025
26 Dec 2025




