![]() 18 Nov 2025
18 Nov 2025
English
हिन्दी

NASA’s twin ESCAPADE spacecraft were launched aboard Blue Origin’s New Glenn rocket to study how solar wind shapes Mars’ magnetic and atmospheric environment.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books
Visit PW Store
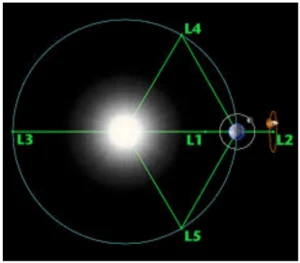 L1: Lies between Earth and Sun, enabling uninterrupted solar observation.
L1: Lies between Earth and Sun, enabling uninterrupted solar observation.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
