A National Mission to provide financial incentives to promote carbon capture, utilization and storage (CCUS) technologies aiming to achieve the net-zero goals is in consideration by the Union Government.
- The decision was announced on the sidelines of the 32nd annual general meeting of the American Chamber of Commerce in India (AMCHAM India) in New Delhi
- Responsible Ministry: The Union power ministry, NITI Aayog and the office of the principal scientific adviser to the Prime Minister’s Office (PMO) will form the core working group for the mission.
Features of the Mission
- Financial Mechanisms Proposed: The CCUS mission is proposed to include viability gap funding (VGF), carbon pricing and taxing mechanism, carbon trading and subsidies in terms of PLI to reduce the carbon footprint.
- The need for government support in the form of tax credits may be assessed on a case-by-case basis.
- Engagement: The government along with industry and academia will create a roadmap for developing an India-specific ecosystem and India specific CCUS technologies.
- Deployment: The mission would support the setting up of pilot plants that can capture 500 tonnes of CO2 per day.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage (CCUS)
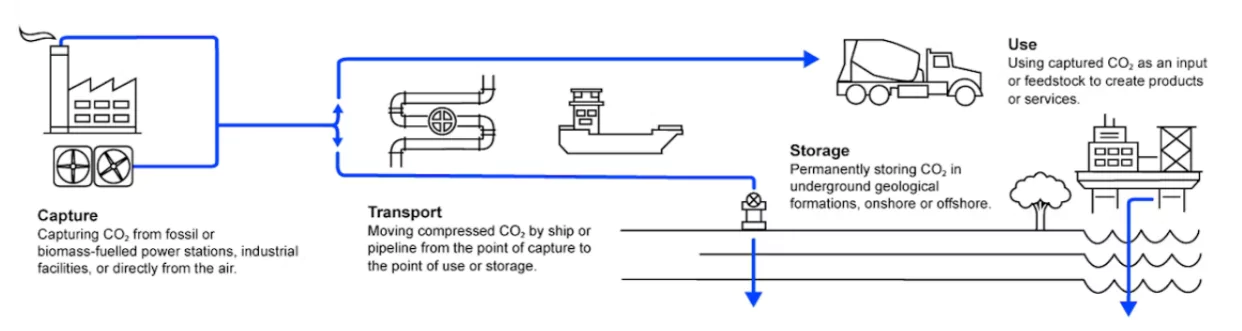
- About: CCUS involves 3 components ie.
- Carbon Capture: CO2 is captured from large point sources like power generation or industrial facilities that use either fossil fuels or biomass as fuel.
- Carbon Capture alone accounts for about 75% of the net CCUS cost.
- Utilisation: The captured carbon can be used on site or can be compressed and transported by pipeline, ship, rail or truck to be used in a range of applications off site
- Storage: C02 can also be stored for future use by injecting it into deep geological formations such as depleted oil and gas reservoirs or saline aquifers.
- Role of CCUS in Clean Energy Transitions:
- Easy Deployment: CCUS can be retrofitted to existing power and industrial plants, allowing for their continued operation.
- Emission Reduction in Very Polluting Industries: It can tackle emissions in hard-to-abate sectors, particularly heavy industries like cement, steel or chemicals.
- Decarbonisation: CCUS is an enabler of least-cost low-carbon hydrogen production, and offers the only known technology for decarbonising the hard-to-electrify and CO2-intensive sectors such as steel, cement, oil & gas, petrochemicals & chemicals, and fertilizers.
- Balancing CO2 concentration: Finally, CCUS can remove CO2 from the air to balance emissions that are unavoidable or technically difficult to abate.
- Technologies:
- Bioenergy with Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS): It involves capturing and permanently storing CO2 from processes where biomass is converted into fuels or directly burned to generate energy. Because plants absorb CO2 as they grow, this is a way of removing CO2 from the atmosphere.
- Direct Air Capture (DAC): It extracts CO2 directly from the atmosphere at any location, unlike carbon capture which is generally carried out at the point of emissions. The CO2 can be permanently stored in deep geological formations or used for a variety of applications.
- Carbon Capture and Utilisation: It refers to a range of applications through which CO2 is captured and used either directly or indirectly (i.e. transformed) in various products.
- CO2 is primarily used in the fertiliser industry and for enhanced oil recovery. New uses such as producing CO2-based synthetic fuels, chemicals and building aggregates are gaining momentum.
- Global Market Size: As of 2022, the global CCUS market size was $2.49 billion, and an annual growth rate of 13.3% is expected during 2022-2030.
- The CO2 capture capacity of about 361 million tonnes per annum (mtpa) is under development globally.
- Over 500 CCUS projects are in various stages of development across the CCUS value chain as per The International Energy Agency (IEA) with building momentum in recent years.
- Regional Potential: Region-wise CO2 storage potential in India during 2030-2050 would stand at,
- Western Regions: 388.9 gigatonnes
- Southern Regions: 80.58GT
- Eastern Regions: 76.3GT
- North-Eastern Regions: 47.2GT
- Northern Regions: 7.65GT
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
![]() 10 Aug 2024
10 Aug 2024
