Recently, NATO said it will boost its presence in the Baltic Sea after the suspected sabotage this week of an undersea power cable and four internet lines, while alliance member Estonia launched a naval operation to guard a parallel electricity link.
About Baltic Sea
- The Baltic Sea is a semi-enclosed inland sea located in Northern Europe.
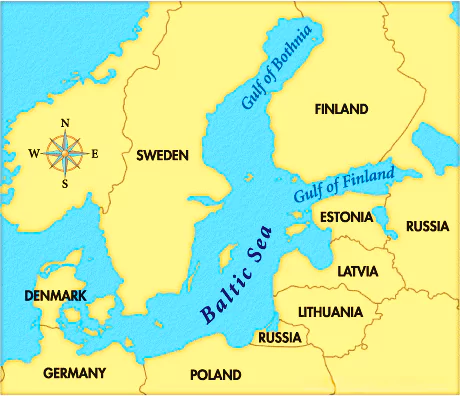 It is an arm of the North Atlantic Ocean, extending from Southern Denmark to the Arctic Circle.
It is an arm of the North Atlantic Ocean, extending from Southern Denmark to the Arctic Circle.- It separates the Scandinavian Peninsula (comprising Sweden, Norway, and the northwestern area of Finland) from the rest of continental Europe.
- Connections: It connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the Danish Straits.
- It is linked to the White Sea via the White Sea Canal and to the North Sea’s German Bight via the Kiel Canal.
- Geographical Features
- Gulfs:
- The Baltic Sea contains three major gulfs:
- Gulf of Bothnia.
- Gulf of Finland.
- Gulf of Riga.
- Brackish Water:
- The Baltic Sea is often cited as the world’s largest brackish inland water body.
- It has lower salinity due to:
- Inflow of freshwater from surrounding land.
- Its shallowness.
- Over 250 rivers and streams empty into the sea, with the Neva River being the largest.
- Islands: The Baltic Sea includes over 20 islands and archipelagos.
- The largest island is Gotland, located off the coast of Sweden.
- Surrounding Countries: The Baltic Sea is bordered by the following countries:
- Denmark, Germany, Poland, Lithuania, Latvia, Estonia, Russia, Finland, and Sweden.
- Baltic States: Group of independent countries bordering the Baltic Sea:
- Lithuania, Estonia, and Latvia.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
About NATO

- The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) is an intergovernmental military alliance.
- Established: NATO was established on April 4, 1949, with the signing of the North Atlantic Treaty in Washington, D.C. by 12 founding member countries from Europe and North America.
- Goal: To provide collective defence against potential aggression, particularly from the Soviet Union during the Cold War era.
- Members: The alliance currently consists of 32 member countries.
- Most recent additions were North Macedonia in 2020 and Finland in 2023 and Sweden in 2024.
- Headquarters: Brussels, Belgium.
- Objectives:
- Cooperation: To provide a unique link between these transatlantic countries, enabling them to consult and cooperate on political and military issues.
- Limiting threat: To counter the threat of erstwhile Soviet Union’s possible expansion attempts in Europe.
- Underlying Principle: Principle of Collective Defence: NATO is committed to the principle that an attack against one or several of its members is considered as an attack against all.
- Structure:
- Political Leadership: The North Atlantic Council (NAC) serves as NATO’s principal political decision-making body, composed of ambassadors from all member countries.
- Military Command Structure: NATO’s military command structure includes Strategic Commands (e.g., Allied Command Operations) responsible for operational planning and execution, as well as Regional Commands and Force Headquarters.
- Integrated Military Forces: NATO maintains integrated military forces, allowing member countries to contribute personnel and assets to collective defence efforts under NATO command.
Also Read: NATO
![]() 28 Dec 2024
28 Dec 2024

 It is an arm of the North Atlantic Ocean, extending from Southern Denmark to the Arctic Circle.
It is an arm of the North Atlantic Ocean, extending from Southern Denmark to the Arctic Circle.
