Context: This article is based on the news “How to read the NCRB 2022 report on crime in India” which was published in the Indian Express. The National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) released its annual report on crime in India for the year 2022.
| Relevancy for Prelims: NCRB Report 2022 On Crime in India, National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB), National Database of Sexual Offenders (NDSO), Crime and Criminal Tracking Network and System (CCTNS), Indian Penal Code (IPC), Code of Criminal Procedure (CrPC), and the Indian Evidence Act (IEA).
Relevancy for Mains: What steps can India take to improve its justice system? Is it important to upgrade the police, reform the judiciary, and ensure accurate crime data through NCRB for effective policymaking? |
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
2022 NCRB Report On Crime in India
- The NCRB report on crime in India is published by the NCRB presents data on reported crimes from across the country
- It includes statistics on offences ranging from financial and commercial crimes to crimes against women.
- The data for the NCRB report is collected by the State Crime Records Bureaux (SCRBx) from the District Crime Records Bureaux (DCRBx) and sent to NCRB at the end of every calendar year.
- The NCRB report contains comprehensive information on:
- Cases registered and their disposal and
- Persons arrested and their disposal.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
What are the key highlights from the NCRB 2022 report?
- Decline in Registration Cases: In 2022, 58,24,946 cognizable crimes comprising 35,61,379 Indian Penal Code (IPC) and 22,63,567 under Special and Local Laws (SLL) were registered.
- It shows a decline of 2,71,364 (4.5%) in registration of cases over 2021 (60,96,310 cases).
- The State/UT reporting the highest Charge-sheeting Rate under IPC Crimes are Kerala (96.0%), Puducherry (91.3%) and West Bengal (90.6%)
- Crime Rate: From 445.9 crimes reported per lakh people in 2021 to 422.2 crimes in 2022, the crime rate has decreased.
- Crime rate refers to the number of cases registered per lakh population.
- Cases of Murder: A total of 28,522 cases of murder were registered during 2022, showing a marginal decline of 2.6% over 2021(29,272 cases).
Enroll now for UPSC Online Coaching
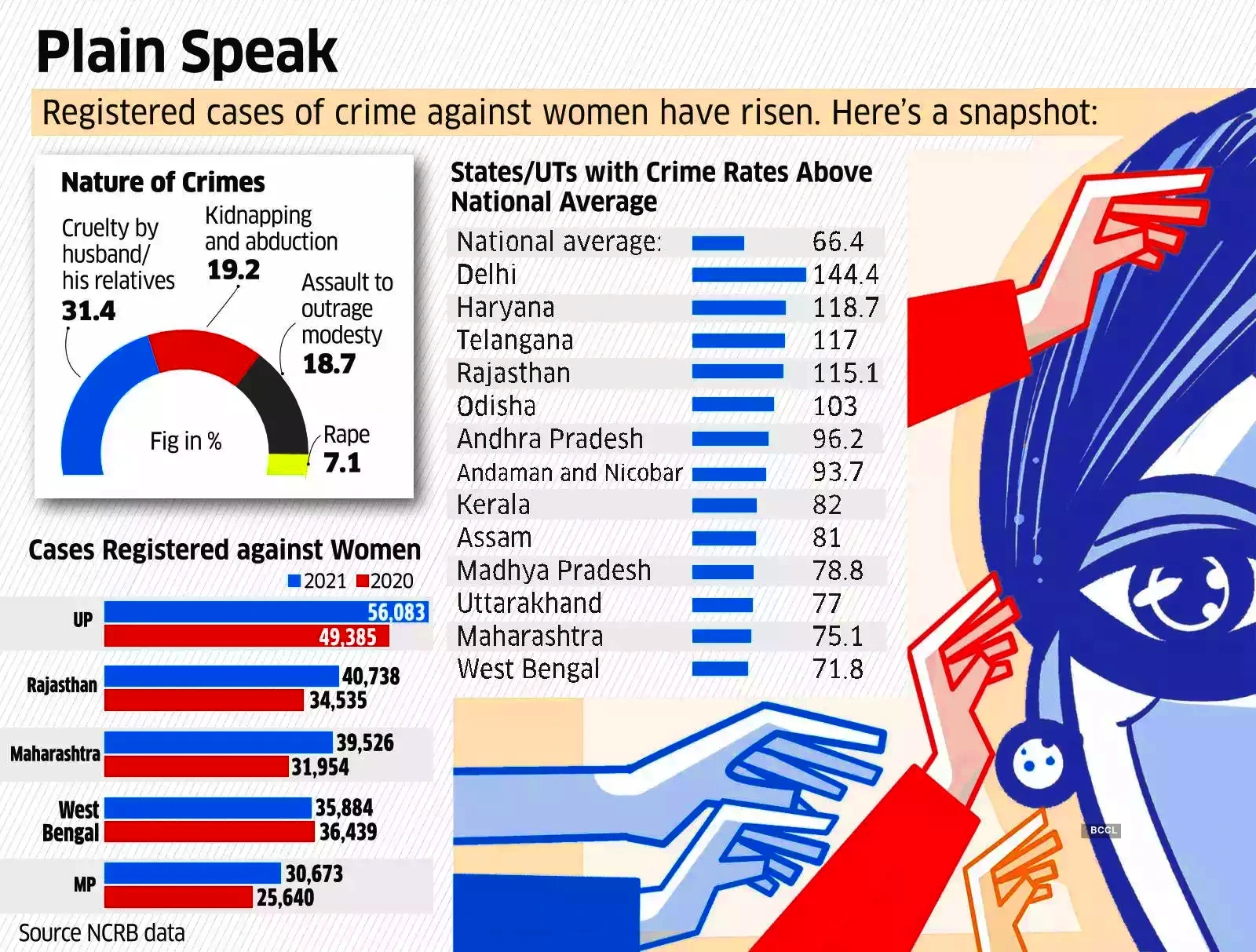
- Crime against Women: In 2022, 4,45,256 incidents of crime against women were reported. Compared to 2021(4,28,278 cases), there was a 4% increase in number.
- Major reason: Cruelty by Husband or His Relatives” accounted for the highest percentage of crimes against women (31.4%), followed by “Kidnapping & Abduction of Women” (19.2%) and “Assault on Women with Intent to Outrage her Modesty” (18.7%).
- State with maximum crime against women: With 14,247 cases, Delhi had the highest rate of crime against women at 144.4 against the country’s average of 66.4.
- Cybercrimes: Under it, 65,893 cases were registered showing an increase of 24.4% in registration over 2021 (52,974 cases).
- Reporting of Cyber Crime: It increased by 24.4 % compared to 2021 to 65,893 cases. Around 64.8% of registered cases were of fraud, followed by extortion (5.5%), and sexual exploitation (5.2%).
- Suicides: The number of suicides reported in 2022 increased by 4.2% over 2021.
- Major reason behind suicide: 54.9% of all suicides in the nation in 2022 were caused by “Family Problems (other than marriage-related problems)” (31.7%), “Marriage Related Problems” (4.8%), and “Illness” (18.4%). The suicide victims’ overall male to female ratio was 71.8:28.2.
- State with maximum suicides: Maximum suicides in the year were reported from Maharashtra (22,746), Tamil Nadu (19,834), Madhya Pradesh (15,386), Karnataka (13,606), Kerala (10,162), and Telangana (9,980).
- Occupational trend of suicides: 9.6% of the suicides were by self-employed or salaried professionals followed by unemployed persons comprising 9.2% of all suicides reported in India in 2022.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
-
- Among all suicides reported in the year, over 12,000 were of students.
- Kidnapping & Abduction: In 2022, 1,07,588 cases of kidnapping and abduction were reported, which represents a 5.8% increase from 1,01,707 occurrences in 2021.
- Crime against Children: In 2022, 1,07,588 cases of kidnapping and abduction were reported, which represents a 5.8% increase from 1,01,707 occurrences in 2021.
- Crime against Senior Citizens: 28,545 cases were registered for committing crimes against Senior Citizens (aged above 60 years), showing an increase of 9.3% from 2021.
- Crime/Atrocities against Scheduled Castes (SCs): There is a 13.1% rise in cases against SCs in 2021.
- Crime rate: Between 2021 and 2022, the recorded crime rate increased from 25.3 to 28.6.
- Crime/Atrocities against Scheduled Tribes (STs): Cases registered for committing crimes against Scheduled Tribes (STs) show an increase of 14.3% over 2021.
- Crime Rate: It registered an increase from 8.4 in 2021 to 9.6 in 2022.
- Economic Offences: These witness an increase of 11.1% in registration over 2021.
- Counterfeiting accounted for the greatest number of cases in 2022(1,70,901) followed by criminal breach of trust (21,814 instances) and counterfeiting (670 cases).
- Prevention of Corruption Act: State Anti-Corruption Bureau (ACBs) recorded 4,139 cases in 2022 compared to 3,745 cases in 2021, indicating a 10.5% rise.
- The Anti-Corruption Bureau is the main investigative unit of the Vigilance Department.
- Environment-Related Offences: 52,920 cases were registered under Environment-Related Offences as compared to 64,471 cases in 2021, showing a decrease of 17.9%.
- Crime Against Foreigners: 192 offenses were reported against foreigners (tourists and residents) in 2022 in contrast to 150 cases in 2021 indicating a 28.0% increase.
- Human Trafficking: 2,250 instances of human trafficking were reported in 2022 compared to 2,189 cases in 2021, indicating a 2.8% rise.
Also Read: Women Safety in India
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
About National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB):
- Origin: It was established in January 1986 based on the recommendations of the Tandon Committee.
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Home Affairs.
Also Read: Cyber Security and Rising Incidence of Cyber Crime
What are the functions of NCRB?
- Crime Data: It is mandated to compile and keep records of data on crime.
- Fingerprint Records: It also acts as a “national warehouse” for the fingerprint records of Indian and foreign criminals, and assists in locating interstate criminals through fingerprint searches.
- Implementation of (CCTNS) project: It is entrusted with monitoring, coordinating and implementing the Crime and Criminal Tracking Network and System (CCTNS) project.
- The CCTNS project connects about 15000 police stations and 6000 high offices of the country.
- Maintaining NDSO: It is also responsible for maintaining the National Database of Sexual Offenders (NDSO) and sharing it with the States/UTs on a regular basis.
- Monitoring Online Cyber Crime Information Portal: It oversees the technical and operational process of the Portal through which citizens can file complaints of child obscenity, rape, gang rape and collect evidence.
- Maintaining FICN: It maintains the Counterfeit Currency Information and Management System (FICN) and Integrated Monitoring Application on Terrorism.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Coaching
What are other key reports published by the NCRB?
- Crime in India
- Accidental Deaths and Suicides
- Prison Statistics
How are the data for NCRB reports compiled?
- Data from Police forces: The data is obtained from the police departments of 36 states and Union Territories.
- Data Verification: The data at the local police station level submitted by the State/UT police is verified by the district and state levels before being approved by the NCRB.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
What are the issues associated with the data provided by the NCRB?
- Adherence to Principal Offence Rule: As per this rule, the offence carrying the harshest penalty is taken into account out of all the offences listed in a single FIR.
- Under this, Murder with Rape being counted as “Murder” rather than “rape” leading to undercounting of the crime of rape.
- Data Inefficiencies at Local Level: The accuracy of the NCRB report is impacted by inefficiencies or gaps in data reported at the local level, as it is merely a compilation of data at local level.
- Lack of police personnel or vacancies in related positions at the local level makes data collection more difficult.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Way Forward/Reforms in Criminal Justice System:
- Modernisation of Police Forces: With the changing nature of crime, state-of-the-art technology and mutual coordination crime has become necessary for the police.
- Reforms in Judiciary: It should aim to reduce delays and arrears in the system and enhance accountability through structural changes and by setting performance standards and capacities. Measures needed are:
- Transparency in the appointment systems (Fair and Accountability)
- Reforming Investigation (Many Innocent people being wrongfully charged and punished.)
- Timely delivery of judgements
- Establishing National Judicial Infrastructure Authority of India (To improve Infrastructure for court systems )
- Better District Courts
- Prison Reforms: It should include the development of alternatives to imprisonment, the provision of education and job training programs, the implementation of mental health and substance abuse treatment programs.
- Welfare Scheme for Poor: Government interventions are needed to address the concerns of the poor in India.
- Poverty and crime have a complex and often contentious relationship.
- The cost of being unable to afford necessities, combined with the lack of opportunity for social and economic advancement, creates a breeding ground for criminal activities.
- Strengthen NCRB: States must utilise the NCRB’s data to create their annual police strategy, which should have a multifaceted and multipurpose use in crime control.
- Revamp of criminal laws: Indian Penal Code (IPC), Code of Criminal Procedure (CrPC), and the Indian Evidence Act (IEA) need overhaul as these laws were made to strengthen colonial rule,with the intention of giving punishment instead of justice.
Also Read: Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita (BNS), 2023
Enroll now for UPSC Online Coaching
Conclusion:
The 2022 NCRB report highlights India’s crime situation, indicating a decline in overall cases but an increase in certain areas. To improve the justice system, reforms such as modernizing police, judicial changes, prison reforms, and addressing socio-economic issues are essential.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
![]() 5 Dec 2023
5 Dec 2023


