Rekha Gupta, a first-time MLA from Shalimar Bagh, has been chosen as the new Chief Minister of Delhi.
Constitutional Provision for Delhi
First Schedule of Indian Constitution
- It lists the states and union territories and their corresponding territories.
- Provisions of Articles 1 to 4 of the Indian Constitution
Article 1: Name and Territory of the Union
- India, also called Bharat, is a Union of States.
- The States and Union Territories are specified in the First Schedule.
- India’s territory includes:
- State territories
- Union Territories
- Any acquired territories
Article 2: Admission or Establishment of New States
- Parliament has the power to admit or establish new states.
- The terms and conditions of such admission are decided by Parliament.
Article 3: Formation and Alteration of States
- Parliament can:
- Form new states by separation, merging, or adding territories.
- Alter state boundaries, names, and areas.
- The President’s recommendation is required before introducing such a bill.
- State legislature views must be sought, but their consent is not mandatory.
Article 4: Laws Related to Articles 2 and 3
- Laws under Articles 2 and 3 can amend the First and Fourth Schedules.
- Such laws do not count as a constitutional amendment under Article 368.
|
About Delhi Administration
- Delhi as a Union Territory: Delhi is classified as a Union Territory under the First Schedule of the Constitution of India.
- Administration of Union Territories: As per Article 239, a Union Territory is administered by the President through an Administrator appointed by the President.
- Creation of Local Legislatures and Council of Ministers: Article 239A allows for the creation of a local Legislature, a Council of Ministers, or both for certain Union Territories.
Special Status of Delhi: 69th Amendment Act, 1991
- Article 239AA was inserted into the Constitution through the 69th Amendment Act, 1991 to grant special status to Delhi.
- This amendment followed the recommendations of the S. Balakrishnan Committee, which examined the demand for full statehood for Delhi.
- After this amendment, Delhi is referred to as the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi.
- Designation of Administrator: The Administrator of Delhi, appointed under Article 239, is designated as the Lieutenant Governor (LG).
Structure of Governance in Delhi
- The NCT of Delhi consists of:
- An Administrator (Lieutenant Governor)
- A Legislative Assembly
Powers of the Delhi Legislative Assembly
- Authority to Make Laws: As per Article 239AA(3), the Delhi Legislative Assembly has the power to legislate on subjects listed in the State List and Concurrent List, with certain exceptions.
- Exceptions or the Restricted Subjects: The Delhi Assembly cannot make laws on the following subjects from the State List:
- Public Order (Entry 1)
- Police (Entry 2)
- Land (Entry 18)
Supremacy of Parliament
- Parliament retains the power to legislate for Delhi on any subject, including those within the jurisdiction of the Delhi Assembly.
- In case conflict between a Delhi law and a Parliamentary law, the Parliamentary law prevails, and the Delhi law becomes void.
- Exception for Presidential Assent: If a Delhi law is reserved for Presidential assent and approved by the President, it remains valid.
- However, Parliament can still amend, repeal, or override such a law at any time.
Provision for Strength of the Council of Ministers
- As per the 91st Constitutional Amendment Act, the minimum strength of the Council of Ministers in a State is 12, while the maximum strength is 15% of the total members of the Legislative Assembly.
- Article 164 lays down other provisions regarding Ministers.
- Article 164(1A) specifies that the total number of Ministers, including the Chief Minister, must not exceed 15% of the total strength of the Legislative Assembly of the State.
|
Council of Ministers
- Composition of Council of Ministers : Article 239AA(4) mandates the formation of a Council of Ministers, including the Chief Minister, with a strength not exceeding 10% of the total number of Legislative Assembly members.
- Function of the Council of Ministers: The Council of Ministers aids and advises the Lieutenant Governor on matters where the Delhi Assembly has legislative powers.
Appointment and Tenure of the Chief Minister and Ministers
- Appointment Authority: The Chief Minister of Delhi is appointed by the President of India under Article 239AA(5).
- The other Ministers are appointed by the President based on the advice of the Chief Minister.
- Tenure and Removal: The Chief Minister and the Council of Ministers hold office at the pleasure of the President.
Role of the Lieutenant Governor
- Discretionary Powers of the Lieutenant Governor: The Lieutenant Governor has the authority to act at his discretion in cases where law requires it.
- Dispute Resolution Between the LG and Ministers: If there is a difference of opinion between the Lieutenant Governor and the Council of Ministers, the LG can refer the matter to the President.
- Until the President takes a decision, the LG can take immediate action if the matter is urgent.
Limitations of the 69th Amendment Act
- Ambiguous Division of Powers: The Act does not clearly define the powers of the Lieutenant Governor (LG) and the Council of Ministers, leading to frequent disputes and confusion in governance.
- Overlapping Jurisdiction: The LG can refer any disagreement with the Council of Ministers to the President, often causing delays and administrative conflicts.
- Unclear Role of the LG: The Act does not explicitly define the LG’s role in daily administration, leading to frequent disagreements with the Delhi Government.
Supreme Court’s Suggestions (2018 Judgment)
- LG Must Act on Ministerial Advice: The LG is bound to act on the advice of the Council of Ministers except in matters where discretion is legally permitted.
- No Interference in Day-to-Day Administration: The LG cannot interfere in routine governance of the NCT.
- Emphasis on Cooperative Governance: The judgment promotes coordination between the LG and the Delhi Government, serving as a model for other Union Territories
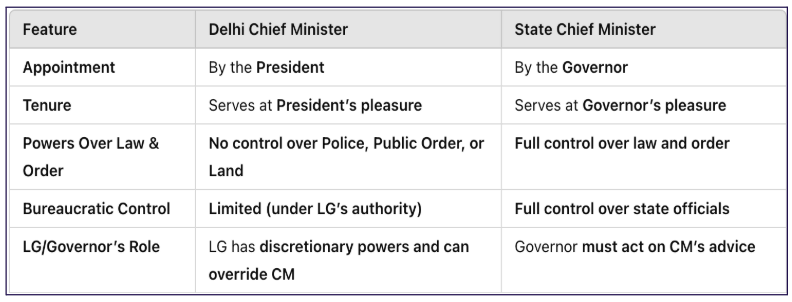
Delhi CM Vs Other State CM
![]() 20 Feb 2025
20 Feb 2025

