A study published in Scientific Reports in February 2024 estimated that 40% of bumblebee species in the Indian Himalaya could lose more than 90% of their habitat by 2050.
Reason for Declining Species of Bees
- It all happened due to the introduction of western honey bee colonies after which some disease completely decimated the indigenous pollinator populations.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
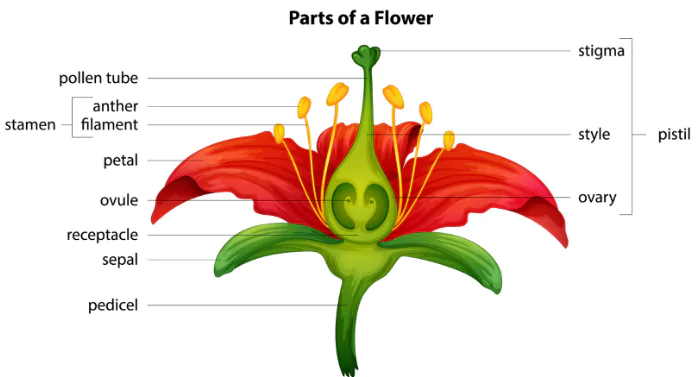
About Pollination
- It is a process in which pollen grains from male part of a flower (Anther) are transferred to the female part (stigma).
- Objective: The objective of pollination is the production of seeds which carry genetic material for creation of new plants.
- Pollination Vectors: Wind, Water, Birds, Insects (bees, butterflies, etc.), Bats, and Other animals that visit flowers.
 Pollinator
Pollinator-
- These are the animals or insects that help in moving pollen.
- It occurs when pollinators
- Collect pollen for its nutritional value (protein).
- Sip nectar from the flower.
About Insect Pollinators
- These are insects that assist in the transfer of pollen from one flower to another,
- It facilitates fertilization and seed production in plants.
- They play a crucial role in maintaining biodiversity and supporting agriculture.
Types of Insect Pollinators
- Bees:
- Honey Bees (Apis mellifera): Widely managed for honey production and crop pollination.
- Wild Bees: Includes bumblebees and solitary bees, often more efficient pollinators than managed honey bees.
- Wasps: Contribute to pollination, though less efficient than bees.
- Beetles: Known as “mess and soil” pollinators, they help in pollinating some flowering plants.
- Flies: Particularly hoverflies, which mimic bees and are significant pollinators for various crops.
- Moths and Butterflies: Pollinate flowers while feeding on nectar, often at night (moths) or during the day (butterflies).
Importance of Insect Pollinators
- Role of Insect Pollinators in Agriculture
-
- Over 75% of food crops, fruits, and flowering plants rely on pollinators like bees, wasps, butterflies, and beetles for successful yields.
- These pollinators are essential for global agricultural productivity and nutritional security.
Check Out UPSC Modules From PW Store
Threats to Pollinator Populations
- Pesticides and Pollution: Directly harm pollinators and their habitats.
- Climate Change: Disrupts ecosystems and reduces available resources.
- Infectious Diseases: Emerging as a new threat, worsened by habitat loss and reduced biodiversity.
- Economic Implications of Pollinator Decline
- A decline in pollinators could impact the agricultural economy globally, affecting food supply and livelihoods.
Impact of Pathogen Transmission on Pollinators
- Pathogen Spillover and Spillback
- Managed honey bees often carry pathogens like deformed wing virus and black queen virus.
- These pathogens are transmitted to wild pollinators when they share habitats or floral resources, a process called spillover.
- Pathogens may also mutate in wild pollinators and reinfect honey bees in more harmful forms (spillback).
- Findings from Swiss Research
- A study published in Nature Ecology and Evolution found:
- Pathogen loads in wild pollinators sharing habitats with managed honey bees were 10 times higher.
- Diverse habitats with abundant floral resources reduced pathogen transmission risks.
![]() 19 Nov 2024
19 Nov 2024


 Pollinator
Pollinator