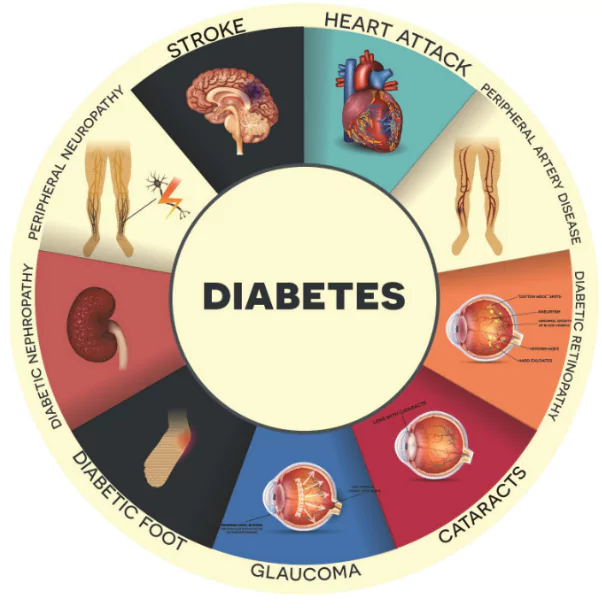
AIIMS software: Expanding Diabetic Care In Rural Area
|
- Recognizing the potential of telemedicine, AIIMS, Delhi, developed software to extend specialised diabetes care to rural primary healthcare centres (PHC).
Diabetes:
- About: Diabetes is a Non-Communicable Disease (NCD) characterised by insufficient insulin production or ineffective use of insulin, leading to high blood sugar levels.
Software Solution:
- Involvement of local healthcare professionals: The AIIMS software addresses these issues by allowing local healthcare professionals to input patient data on risk factors such as blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar.
- The attending physician remains crucial, needing to tailor the software’s advice to the patient’s lifestyle for optimal care.
- Treatment Recommendations: The Software processes the data to suggest appropriate treatments, helping to streamline diagnosis and management of diabetes.
- Integration with National Health Programs: The software’s effectiveness could be enhanced by integrating it with national health initiatives, such as the National Health Programme for Non-Communicable Diseases and the Ayushman Bharat Digital Health Mission.
- This would improve data sharing and collaboration among medical experts.
|
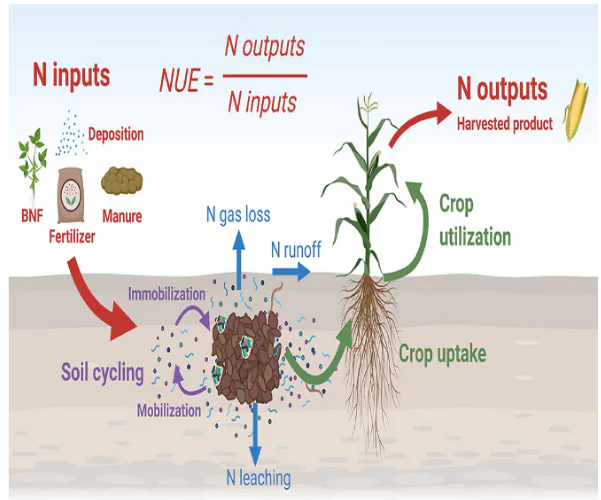
Nitrogen-Use Efficiency (NUE)
|
- The study, published in the Journal of Plant Growth Regulation, reveals that Indian scientists have identified significant natural variations in nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) among different rice varieties.
- High NUE varieties like Khira and CR Dhan 301 are long-duration crops, whereas Dhala Heera offers high NUE with a shorter growth duration
Nitrogen Use Efficiency (NUE): NUE is defined as the ratio of the amount of nitrogen effectively utilised by crops to the amount of nitrogen applied.
Significance of NUE in Agriculture:
- Optimising Crop Yields: Efficient nitrogen use is vital for maximising crop yields.
- Economic Impact of Poor NUE: Poor NUE leads to significant nitrogen fertiliser wastage, with costs estimated at Rs 1 lakh crore annually in India and over $170 billion globally.
- Environmental Consequences: Inefficient nitrogen management contributes to greenhouse gas emissions (e.g., nitrous oxide) and water body eutrophication, which harms aquatic ecosystems.
- Benefits of Enhanced NUE: Increasing NUE can enhance productivity and profitability for farmers by reducing fertiliser costs and minimising environmental impacts.
Global Commitments:
- India is a signatory to the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (2022), which mandates countries to halve their nutrient waste from all sources by 2030.
|
World Craft City Tag

|
Recently, Srinagar was officially named a World Craft City by the World Crafts Council (WCC), recognizing the city’s rich tradition in crafting, joining three other Indian cities (Jaipur, Malappuram and Mysore) and 60 cities globally.
Other Indian cities
- Jaipur – Known for Block printing, blue pottery, and hub for Gemstone Jewelry.
- Malappuram – Famous for ancient stone carving techniques in temples.
- Mysore – Famous for its exquisite silk sarees, Sandalwood Carvings, and traditional Mysore paintings
About World Crafts Council International (WCC)
- It is a Non-profit, non-governmental organization
- Establishment: Founded on June 12, 1964.
- Headquarters: Kuwait.
Mission and Goals
- Empowerment: Aims to support artisans and enhance their skills.
- Cultural Diversity: Celebrates and promotes global cultural diversity through traditional crafts.
- Sustainable Development: Contributes to sustainable development by advancing global craftsmanship.
- Affiliation and Status
- Maintains Consultative Status with UNESCO, emphasizing its role in the global cultural landscape.
|
|
Coal India eyes lithium in Chile
|
State-run Coal India (CIL) is exploring the possibility of extracting lithium from salt flats in Chile.
Global Lithium Reserves
- Major Reserves: Chile holds about half of the world’s viable lithium reserves and is the second-largest producer globally.
- Market Share: Chile contributes around 36% to the global lithium trade.
Importance of Lithium for India
- Key Component in Batteries: Lithium is a crucial element in lithium-ion batteries, which power electric vehicles (EVs) and renewable energy storage systems.
- Energy Transition: As India shifts towards cleaner energy sources and aims to reduce its carbon footprint, lithium becomes increasingly important for the country’s energy independence.
- Electric Vehicle Push: The growing demand for electric vehicles in India necessitates a reliable supply of lithium for battery manufacturing.
|
Standardised Precipitation Index SPI
|
The Indian Meteorological Department has analysed trends for precipitation and drought like conditions over India using ‘Standardised Precipitation Index’ (SPI).
Key Analysis of the Index
- Dry Conditions: The year 2021 witnessed extremely dry and severely dry conditions over the Eastern and NorthEastern parts of country (Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Meghalaya, Nagaland, Manipur, Mizoram, Tripura, Sub Himalayan West Bengal, Sikkim, eastern Uttar Pradesh) plus Himachal Pradesh and Jammu & Kashmir
- Extreme Rainfall and Flooding Event: The Frequency of extreme rainfall event is increasing in some parts of India, including the peninsular, east, northeast, and some parts of central India
- Flood Affected: The number of States affected by major floods increased from 08 States in 2017 to 15 in 2021 as per a study by the National Remote Sensing Centre.
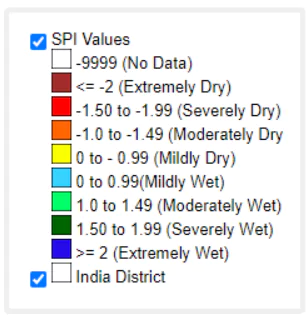
About Standardised Precipitation Index (SPI)
- It is a tool which was developed by McKee in 1993 to define and monitor drought primarily.
- It can also be used to determine periods of anomalously wet events
- Probability: SPI is probabilistic index it has a straight- forward relation to occurrence frequencies
- Example: Extreme droughts (SPI ≤ -2), are expected to occur with a chance of 2.3%
- Aim: To allow an analyst to determine the rarity of a drought event at a given time scale (temporal resolution) of interest for any region with historic data.
- Process: For each time step, precipitation of the preceding t (time scale) months is accumulated.
- The time series is first fitted with a model distribution to the data (for precipitation series, the Gamma distribution is typically used)
- Subsequently it is transformed to values of the standard normal distribution for each calendar month separately
- The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) recommends, that all national meteorological and hydrological services should use the SPI for monitoring of dry spells
- Advantages:
- Adaptability to change: The possibility to compute SPI for different time scales (t) allows for an adaptation of the index to slowly or fast evolving environmental or societal systems.
- Easy Interpretation: SPI is straightforward to interpret as negative (positive) values are directly related to a shortage (surplus) of water availability at a given location relative to the normal conditions.
- Normalised: Because the SPI is normalized, wetter and drier climates can be represented in the same way; thus, wet periods can also be monitored using the SPI.
|
INS Tabar

|
INS Tabar has arrived at St. Petersburg, Russia on a four day visit to participate in 328th Russian Navy Day Parade celebrations.
- INS Tabar conducted the Maritime Partnership Exercise (MPX) with the Russian Navy Ship Soobrazitelny.
- Maritime Partnership Exercise (MPX): The Exercise involved a series of complex naval manoeuvers, including communication drills, Search & Rescue tactics and Replenishment at Sea serials.
About INS Tabar
- It is the 3rd of the Talwar class Frigate of the Indian Navy. The other 2 being being INS Talwar and INS Trishul
- The frigate was commissioned on 19 April 2004 in Kaliningrad, Russia
- INS Tabar is assigned to the Indian Navy’s Western Naval Command
- Displacement: INS Tabar has a displacement of 4,035 tons.
- Range: INS Tabar’s maximum range is 4,850 nautical miles (8,980 km; 5,580 mi) at 14 knots
- Weapons: INS Tabar is the third Indian warship to incorporate an eight cell KBSM 3S-14NE Vertical Launcher
- It is the first to upload the new Indian/Russian designed missile, the supersonic BrahMos PJ-10 ASCM (anti-sub/ship/surface cruise missile).
|
![]() 6 Aug 2024
6 Aug 2024