Mahaparinirvan Diwas
Context: The President, Vice President, Prime Minister and other national leaders paid homage to Dr. B.R. Ambedkar on the 70th Mahaparinirvan Diwas at the Parliament complex.
About Mahaparinirvan Diwas
- Mahaparinirvan Diwas is observed annually on 6 December to commemorate the death anniversary of Dr. Bhimrao Ramji Ambedkar, the chief architect of the Indian Constitution.
- Historical Significance: The day signifies remembrance of Ambedkar’s lifelong struggle for social justice, equality, and empowerment of marginalized communities.
- Legacy: The observance highlights Ambedkar’s enduring influence on India’s democratic ethos and inspires citizens to uphold dignity, fraternity, and inclusive nation-building.
About ‘Mahaparinirvan’
- Buddhist Roots: The term Mahaparinirvan originates from Buddhist scriptures, referring to the attainment of nirvana after death, marking complete liberation from the cycle of birth and rebirth.
- Ambedkar’s Buddhist Association: Dr. Ambedkar embraced Buddhism in 1956, viewing it as a path to personal and social liberation from caste oppression and inequality.
- Philosophical Influence: Ambedkar was deeply influenced by Buddha’s teachings on rationality, compassion, and moral responsibility, shaping his work as a reformer and thinker
20th UNESCO Intangible Cultural Heritage Committee Session
Context: India is hosting the 20th UNESCO Intangible Cultural Heritage Committee session in New Delhi.
About UNESCO Intangible Cultural Heritage Committee Summit
- The Intergovernmental Committee for Safeguarding Intangible Cultural Heritage implements UNESCO’s 2003 Convention and oversees global efforts to protect living cultural traditions.
- The Intergovernmental Committee of the 2003 Convention was adopted by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) in 2003 and entered into force in 2006.
- Venue: The 20th session (20.COM) is being held from 8–13 December 2025 at the Red Fort in New Delhi.
- The 19th summit (19.COM) took place in Asunción, Paraguay.
- Participants: The Committee consists of 24 State Party representatives elected for four-year terms with equitable geographical representation.
- India’s Role: India, a member of the Committee for the 2022–2026 cycle, has nominated Diwali for the Representative List during the 20th session.
- Functions: The Committee examines nominations for the Representative and Urgent Safeguarding Lists, manages the ICH Fund, approves international assistance, and develops operational guidelines for the Convention’s implementation.
About Intangible Cultural Heritage (ICH)
- Intangible cultural heritage comprises practices, expressions, knowledge, and skills that communities recognize as part of their cultural identity and transmit across generations.
Key Characteristics
- ICH must be community-recognized, transmitted over time, and contribute to identity, continuity, and respect for cultural diversity.
- UNESCO-Inscribed ICH of India: India has 15 UNESCO Intangible Cultural Heritage (ICH) elements, including:
- Ramlila (North India, 2008), Kutiyattam (Kerala, 2008), Vedic Chanting (Pan-India, 2008), Mudiyettu (Kerala, 2010), Chhau Dance (Jharkhand, Odisha, West Bengal, 2010), Kalbelia (Rajasthan, 2010), Ladakh Buddhist Chanting (Ladakh, 2012), Sankirtana (Manipur, 2013), Thathera Craft (Punjab, 2014), Yoga (India, 2016), Nowruz (Parsi, India, 2016), Kumbh Mela (India, 2017), Durga Puja (Kolkata, 2021), and Garba (Gujarat, 2023)
Shingles Vaccine
Context: A new long-term study from Wales finds that the shingles vaccine (Zostavax) significantly reduces death from dementia.
About Shingles
- Shingles is a viral infection that produces painful rashes, often appearing as a single band of blisters on one side of the torso along the path of an affected nerve.
- Cause of the Infection
-
- It is caused by the varicella-zoster virus, the same virus responsible for chickenpox.
- After a person recovers from chickenpox, the virus remains dormant in nerve cells and can reactivate later in life when immunity weakens.
- Transmission: People who have never had chickenpox can become infected if they come into direct contact with the fluid from shingles blisters or inhale virus particles released into the air.
- Vaccine Recommendation: The shingles vaccine, which prevents reactivation of the virus, is mainly recommended for adults above 50 years and for immunocompromised individuals such as those living with HIV.
- Types of Vaccines:
- Zostavax: Uses a live, weakened virus,
- Shingrix: Uses recombinant technology with non-infectious viral components.
Key Findings of the Study
- Zostavax Vaccine administered to dementia patients resulted in 30% lower risk of dying from dementia during a 9-year follow-up period.
- In an earlier study, it was found that older adults who received the Zostavax vaccine were 20% less likely to develop dementia compared to those who didn’t receive the vaccine.
About Dementia
- Dementia is a general term for a decline in cognitive function, including memory, thinking, judgment, and reasoning, that is severe enough to interfere with a person’s daily life and activities.
- It is not a specific disease but a syndrome associated with various underlying conditions
- Types of Dementia:
-
- Alzheimer’s Disease: The most common form of dementia, characterized by the buildup of amyloid plaques and tau tangles in the brain, leading to gradual memory loss and cognitive decline.
- Vascular Dementia: Caused by reduced blood flow to the brain, often after a stroke, leading to cognitive impairment.
- Lewy Body Dementia: Characterized by abnormal protein deposits called Lewy bodies in the brain, causing movement problems, hallucinations, and cognitive decline.
- Frontotemporal Dementia (FTD): Involves the progressive degeneration of the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain, affecting personality, behavior, and language.
Africa Heading for a Continental Breakup
Context: Researchers have predicted that Africa is undergoing a geological transformation that may eventually split the continent into two separate landmasses, creating a new ocean basin in the next 5 to 10 million years.
Key Findings
- Continental Separation: The ongoing separation of Africa is progressing from northeast to south, with intense volcanic and seismic activity.
- Impact: Upon completion, the continent will likely split into:
- Western landmass: Includes Egypt, Algeria, Nigeria, Ghana, Namibia.
- Eastern landmass: Includes Somalia, Kenya, Tanzania, Mozambique, and parts of Ethiopia.
- Scientific Foundation:
- The separation aligns with plate tectonics, where Earth’s continents are not fixed and have continuously shifted over millions of years.
- The East African Rift, a key rift system over 4,000 miles long, marks the primary zone of separation, where the crust is weakening and pulling apart.
- Afar Region: Scientists have forecasted that Africa’s Afar region may become Earth’s next ocean basin due to tectonic activities.
- Location: The Afar region lies in the northeastern part of Ethiopia, where the Red Sea converges with the Gulf of Aden.
- Features: The northern portion of the Afar region is dominated by the Afar or Danakil depression, a desert scrubland area featuring shallow salty lakes and a series of active volcanoes.
- The Awash River valley marks the southern boundary of the region.
- Significance: The Afar region is a unique tectonic triple junction, where the Red Sea, Gulf of Aden, and East African Rift meet.
EARTH Summit 2025
Context: Union Home & Cooperation Minister Amit Shah inaugurated the EARTH Summit 2025 at Gandhinagar and launched multiple digital initiatives under Sahakar Sarathi.
About Earth Summit 2025
- The EARTH Summits are designed to enhance the rural economy and establish a national policy framework, which will be finalized at the third summit in Delhi in 2026.
- Organised by: The summit is jointly organized by the National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) and the Internet and Mobile Association of India (IAMAI).
- Initiatives Launched: ver 13 new digital services launched under the Sahakar Sarathi platform. These include –
- Digi-KCC
- Campaign Sarathi, Website Sarathi
- Cooperative Governance Index
- ePACS
- Grain Storage Application
- Shiksha Sarathi
- Sarathi Technology Forum
- Technology Integration: NABARD’s Sahakar Sarathi platform aims to unify all cooperative banks under one technological framework.
- It is an Integrated digital system for recovery, disbursement, KYC, legal documentation, appraisal.
- Gujarat Model: The model of “Cooperation Among Cooperatives,” which has generated significant low-cost deposits by integrating cooperative banks within the cooperative system, is set to be replicated nationwide.
Hepatitis B
Context: Recently, U.S. vaccine advisers delayed a vote on a proposal to end routine hepatitis-B vaccination for children, limiting it to infants of Hepatitis-B-positive mothers, seeking more time for review.
About Hepatitis B
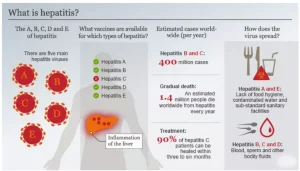
- It is a contagious disease caused by the Hepatitis B virus.
- Transmission: It is transmitted through flat, exhausted wounds and contact with an infectious body’s blood, saliva, or secretions.
- It can also be transmitted via needlestick injury, tattooing and piercing.
- Symptoms: Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection may cause stomach pain, tiredness, and jaundice, though many remain asymptomatic.
- In most adults, it resolves naturally, but in over 90% of infants and up to 50% of young children, it becomes chronic, potentially leading to liver failure and the need for transplant, with recurrent disease, as there is no cure.
- Severeness: The World Health Organization estimates that 254 million people worldwide were living with chronic hepatitis B infection in 2022, with 1.2 million new infections each year.
- Treatment:
- Acute Hepatitis B: Most cases resolve on their own with supportive care; no antiviral treatment required.
- Chronic Hepatitis B: Managed with antiviral medications like tenofovir and entecavir. Regular monitoring is essential to prevent liver damage.
- Prevention:
-
- Vaccination: A safe and highly effective 3-4 dose vaccine that provides long-term protection.
- Universal Precautions: Safe medical practices, needle exchange programs, and safe sex reduce transmission.
- Birth Dose: Infants born to infected mothers should receive the first dose of the vaccine within 24 hours to prevent mother-to-child transmission.
Exercise Harimau Shakti
Context: Recently, India and Malaysia launched the 5th Harimau Shakti exercise.
About Exercise Harimau Shakti
- Harimau Shakti is a bilateral military exercise between India and Malaysia aimed at improving joint operational capabilities in counter-terrorism and peacekeeping environments.
- It is held annually alternatively in India and Malaysia.
- First Edition of the exercise happened in 2012 in Malaysia.
- 2025 Participants:
- India: Troops primarily from the Dogra Regiment of the Indian Army.
- Malaysia: Personnel from the 25th Battalion of the Royal Malaysian Army.
- Venue: Mahajan Field Firing Range, Rajasthan.
- Focus Areas
- Interoperability: In sub-conventional operations under the UN Chapter VII mandate.
- Counter-terrorist training: Cordon-and-search, search-and-destroy missions, room intervention drills.
- Heliborne operations: Securing helipads and casualty evacuation in hostile terrain.
- Combat skills: Army Martial Arts Routine (AMAR), combat reflex shooting, and joint physical conditioning including yoga.
- Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) harmonisation: Enhancing joint response mechanisms and reducing operational risks.
![]() 6 Dec 2025
6 Dec 2025

