NO2 Emissions: Stanford study
Context: A study by Stanford University studies Impact of Coal Power Plant Emissions on Crop Losses in India.
About NO2 Emissions
- Nitrogen dioxide (NO₂) is a gas released into the air mainly from burning fossil fuels like coal, oil, Characteristics of NO2
- Reactive Gas: It is a reactive gas that easily interacts with other substances in the air.
- Part of NOx: It belongs to a group of gases known as nitrogen oxides (NOx)
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Key Findings of the Study
- Prevention of crop losses: The study found that eliminating nitrogen dioxide (NO₂) emissions from coal-fired power plants in India could prevent crop losses worth nearly $1 billion annually.
- NO₂ emissions from these plants reduce wheat and rice yields by 10% or more in many areas.
- Economic Impact
- Potential Benefits: Eliminating coal emissions during key growing seasons (January-February and September-October) could:
- Increase rice output value by approximately $420 million per year.
- Increase wheat output value by $400 million per year.
- State-Wise Impact of Coal Emissions
- NO₂ pollution from coal power plants varies across states:
- Chhattisgarh: Coal plants contribute 13-19% of NO₂ pollution.
- Uttar Pradesh: Coal plants contribute only 3-5% of NO₂ pollution.
- Other NO₂ sources include vehicles and industries.
- Long-Term Crop Losses
- In states like West Bengal, Madhya Pradesh, and Uttar Pradesh, crop yield losses exceed 10% annually.
- This is equal to six years of average annual yield growth (2011-2020).
International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA)
Context: Recently, the Environment Ministry announced that the Framework Agreement on the establishment of the International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA) has officially come into force.
About International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA)
- Launched by: Launched by the Prime Minister in 2023 at an event commemorating 50 years of Project Tiger in India.
- Objective: To reach out to 97 range countries covering the natural habitats of the seven big cats.
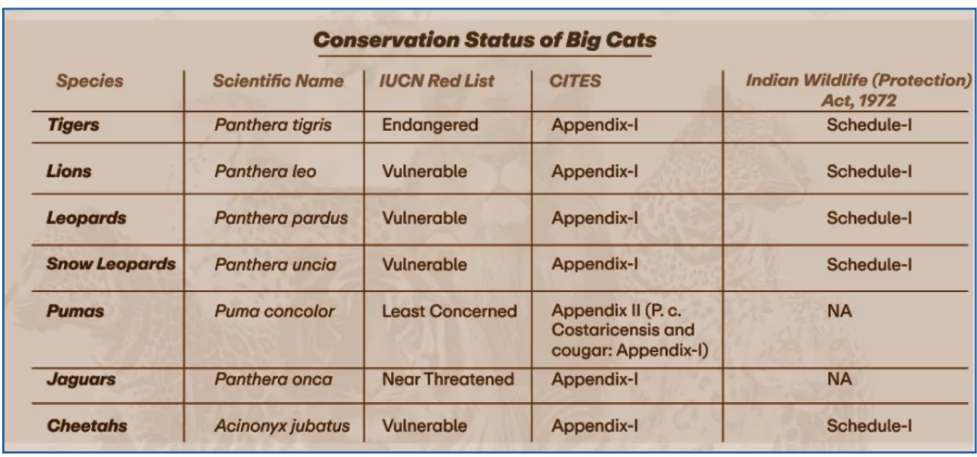
- Seven cats include tiger, lion, leopard, snow leopard, cheetah, jaguar, and puma
- Among the seven big cats, five Big Cats; tiger, lion, leopard, snow leopard and cheetah are found in India, excluding puma and jaguar.
- Twenty-four (24) countries (including India) have consented to be members of IBCA.
- All UN member countries are eligible for becoming a member of IBCA.
- IBCA governance: Governed by a General Assembly made up of all member nations, an elected member nations Council, and a Secretariat.
- Funding of IBCA: IBCA has secured Government of India’s initial support of Rs. 150 crore for five years (2023-24 to 2027-28)
- Headquarters: India
Jevons Paradox
Context: Microsoft CEO Satya Nadella recently referenced the Jevons Paradox in relation to AI, emphasizing that increased efficiency and accessibility of AI could drive a significant rise in demand.
About Jevons Paradox
- The Jevons Paradox states that technological advancements that enhance efficiency or reduce the cost of using a resource often lead to an increase in its overall consumption.
- This concept was introduced by economist William Stanley Jevons in 1865.
- Key Principle: As technological advancements improve the efficiency of resource utilization, the total consumption of that resource tends to increase rather than decrease.
- Explanation
- Intuitive Assumption: When a technology enhances efficiency, it is expected to lower overall resource consumption.
- Jevons’ Argument: Increased efficiency reduces the effective cost of using the resource, which in turn boosts demand. As a result, total consumption may rise instead of decline.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Examples of Jevons Paradox
- Coal and Steam Engines: In his 1865 book The Coal Question, Jevons observed that improved steam engine efficiency led to increased coal consumption, contrary to expectations of a decline.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): As AI models become more efficient and affordable, their adoption increases, leading to higher energy consumption in data centers.
- Energy Efficiency in Transportation : The introduction of fuel-efficient vehicles lowers per-mile fuel costs, encouraging people to drive more, which ultimately results in higher overall fuel consumption.
Exercise Ekuverin
Context: The 13th edition of the joint military exercise ‘Ekuverin’ between the Indian Army and the Maldives National Defence Force has commenced in the Maldives.
About Exercise Ekuverin
- Meaning: The term ‘Ekuverin’ means ‘Friends’ in the Dhivehi language.
- Dhivehi is an Indo-European language spoken in Maldives and Indian UT Lakshadweep.
- Aim & Objectives: To enhance interoperability in counter-insurgency and counter-terrorism operations.
- It also includes joint humanitarian assistance and disaster relief operations.
Other Exercises Between India and Maldives
- Exercise Ekatha: An annual exercise between the navies of India and the Maldives.
- Dosti Trilateral Exercise: A biennial trilateral coast guard exercise involving India, the Maldives, and Sri Lanka.
4.3 GW Solar Manufacturing Unit Inaugurated
Context: The Chief Minister of Tamil Nadu has recently inaugurated a 4.3 GW solar cell and module manufacturing facility in Tirunelveli, Tamil Nadu.
About The Facility
- The solar cell and module manufacturing plant is India’s largest single-location solar manufacturing facility
- Technology: The plant is equipped with cutting-edge TOPCon and Mono Perc technologies and will also manufacture some of the raw materials for module manufacturing.
- Project By: The Facility is developed by TP Solar Ltd (Tata Power’s Solar manufacturing arm & a subsidiary of Tata Power renewable Energy Limited)
- Objective: The facility would produce photovoltaic cells and modules for solar power generating units having an annual capacity of 4 GW.
- Significance:
- Support India’s Solar Industry: The facility will deliver enhanced efficiency and long-term reliability in solar plants and rooftop projects for residential, commercial and industrial purposes
- Creating Local Employment: The facility will pay a crucial role in community development by creating job opportunities, with 80% of the workforce comprising women.
- Build Capacity: It will strengthens India’s solar manufacturing capabilities by reinforcing the supply chain
- Goal of Net Zero: The Facility will pave the way to achieve India’s goal of solar power capacity of 500 GW and Net Zero by 2070.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
National Fellowship scheme
Context: OBC and Scheduled caste research scholars have reported delays in receiving their grants under the National Fellowship.
About National Fellowship Scheme for Scheduled Caste Students
- It is a Central Sector Scheme.
- launched : In the financial year 2005-06.
- Objective: To provide higher education opportunities for SC students pursuing M.Phil. and Ph.D. degrees in Sciences, Humanities, and Social Sciences.
- Implementing Agency
- Central Nodal Agency (CNA): Since October 1, 2022, the National Scheduled Castes Finance and Development Corporation (NSFDC) for implementing the scheme.
- Earlier, the scheme was managed by the University Grants Commission (UGC).
- NSFDC’s Role:
- Establishing guidelines and procedures for implementation.
- Selecting beneficiaries for the fellowship.
- Disbursing fellowship funds to the selected candidates.
Executions with Nitrogen Gas
Context: Recently, Alabama put a man(Demetrius Frazier, a 52-year-old inmate,) to death for a 1991 murder in the nation”s 4th execution using nitrogen gas.
Execution Method: Nitrogen Gas
- Alabama became the first state to introduce execution by nitrogen gas in 2024.
- This method uses pure nitrogen to make the culprit unconsciousness
- Nitrogen-filled face masks are used over the mouth and nose of the culprit.
- It causes disconnection of oxygen flow, causing death of a person.
- It can cause seizure-like movements.
- This technique can kill a person in a few minutes.
India Becomes the World’s 2nd Largest Mobile Manufacturer
Context: India has emerged as the world’s 2nd largest mobile manufacturing country, marking a significant transformation in its electronics manufacturing sector.
- Currently the country produces 99.2% of mobile phones sold domestically.
- China remains the world’s largest manufacturer of mobile phones.
Current Status of Mobile Manufacturing in India
- Rise in Domestic Production: In 2014-15, only 26% of mobile phones sold in India were manufactured locally, with the majority being imported.
- Near-Complete Localization: By 2025, 99.2% of mobile phones sold in India are now made domestically, reducing reliance on imports.
- Shift Towards Self-Reliance: This growth highlights India’s transition from an import-dependent nation to a global hub for mobile manufacturing.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Major Reasons for India’s Growth in Mobile Manufacturing
- Government Initiatives and Policy Support
- Make in India (2014): Encouraged domestic manufacturing and reduced dependency on imports.
- Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme (2020): Offered financial incentives to
- Increased Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): FDI in: 100% FDI allowed in electronics manufacturing under the automatic route attracted global players.
- Rising Domestic Demand for Smartphones: Expanding internet penetration and affordable data boosted smartphone adoption.
- Tariff and Import Duty Policies: Increased customs duties on imported mobile phones and components encouraged local production.
- Geopolitical and Market Factors: US-China trade tensions pushed global manufacturers to diversify production to India.
-
- Companies like Apple and Foxconn expanded operations due to supply chain shifts.
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
![]() 7 Feb 2025
7 Feb 2025


