Mpemba Effect
Context: Indian scientists have developed the first supercomputer-powered simulation to capture the long-existing paradox of Mpemba Effect.
About the Mpemba Effect
- The Mpemba Effect is the counterintuitive phenomenon where hot water freezes faster than cold water under certain conditions.
- Historical Background: Named after Erasto Mpemba, a Tanzanian student who reported the effect in 1963.
- Although the name is recent, the phenomenon was noted by Aristotle, and later by Francis Bacon and René Descartes.
- Proposed Scientific Explanations: Possible reasons include evaporation reducing mass, convection currents, dissolved gases, and supercooling differences—no single explanation fits all cases.
- Conditions: The effect depends on factors like container shape, environment, initial temperatures, water purity, and freezer conditions.
Applications of the Mpemba Effect
- Faster Freezing in Food Processing: Helps in rapid freezing techniques to reduce ice crystal size, preserving texture, taste, and nutritional quality of food.
- Cryopreservation & Material Science: Insights aid in controlled solidification of liquids, useful in preserving biological samples and studying phase transitions in materials.
- Improved Cooling & Refrigeration Systems: Understanding the effect can help optimize cooling cycles, potentially improving energy efficiency in industrial refrigeration.
- Climate & Environmental Studies: Provides clues to ice formation in natural systems, such as cloud physics, lake freezing, and polar climate processes.
- Scientific Modelling & Education: Used as a benchmark phenomenon to test thermodynamic models and promote critical thinking in physics education.
Greenland
Context: Recently, the US President stated that the US needs Greenland for Security purposes, prompting strong objections from Denmark and Greenland.
Why Greenland Matters Strategically to the U.S.?
- Strategic Geography: Greenland’s location between North America and Europe makes it a critical node in the Arctic security architecture, hosting key elements of the U.S. ballistic missile defence early-warning system.
- Resource & Geopolitical Value: The island holds significant reserves of rare earths and minerals, aligning with U.S. efforts to reduce dependence on China and strengthening its importance amid rising Arctic geopolitics and great-power competition.
About Greenland
- It is the world’s largest island, lying in the North Atlantic Ocean.
- The Greenlandic people call their homeland Kalaallit Nunaat (Country of the Greenlanders).
- Capital: Nuuk
- Highest Point: Gunnbjorn’s Fjeld
- Location: It is located in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northeastern coast of Canada.
- It is bounded on the north by the Arctic Ocean; on the west by Smith Sound, Baffin Bay and the Davis Strait; and on the east by the Arctic and North Atlantic oceans.
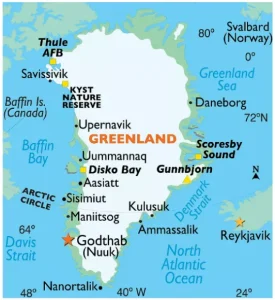 It is the world’s largest (non-continent) island.
It is the world’s largest (non-continent) island.- It shares its maritime borders with Canada, Iceland and Norway.
- It is positioned both in the Northern and Western hemispheres of the Earth.
- Physical Feature: It is noted for its vast tundra and immense glaciers.
- One of the largest glaciers is the Peterman.
- Greenland’s major physical feature is its massive ice sheet, which is second only to Antarctica’s in size and covers over four-fifths of Greenland’s total land area.
- In Greenland, the sun does not set from May 25 to July 25 and July is the only month when the temperature reaches above freezing.
- Greenland Sea: It is an outlying portion of the Arctic Ocean, which lies south of the Arctic Basin proper and borders Greenland (west), Svalbard (east), the main Arctic Ocean (north), and the Norwegian Sea and Iceland (south).
- National Park: Northeast Greenland National Park is the world’s largest national park.
- Administration of Greenland: Greenland is an autonomous territory within the Kingdom of Denmark (alongside Denmark proper and the Faroe Islands).
- Its administrative structure is defined by the Self-Government Act of 2009, which transitioned the island from “Home Rule” to a more independent “Self-Rule” status.
- It has its self-government and its own Parliament (Inatsisartut).
W Ursae Majoris Stars
Context: A new study of special “stellar twins” known as W Ursae Majoris–type contact binaries is providing groundbreaking insights into how binary star systems evolve .
About the W Ursae Majoris Stars
- Extreme Proximity: W UMa stars are contact binaries—two stars so close they orbit each other while physically touching.
- Shape and Atmosphere: They share a single, common outer atmosphere, forming a peanut or dumbbell-like structure.
- Stellar Laboratories: Their close interaction allows astronomers to calculate fundamental stellar parameters like mass, radius, temperature, with high precision.
- This makes them ideal for testing stellar evolution models and understanding how stars age.
- Mass Transfer & Orbital Changes: Material (mass transfer) flows between the two stars, altering their evolution.
- Their orbits show period changes and slight shifts due to gravitational interactions and mass exchange.
- Strong Magnetic Activity & Star Spots: These stars exhibit strong magnetic activity, leading to dark star spots (like sunspots).
About the Binary Stars
- Definition: A binary star system consists of two stars gravitationally bound and orbiting a common center of mass.
- Binary and multi-star systems are incredibly common, they are the dominant configuration in our galaxy, outnumbering single stars like our Sun.
Global Minimum Tax
Context: OECD/G20 Inclusive Framework on Base Erosion and Profit Shifting (BEPS) agreed on a side-by-side arrangement for coordinated implementation of global minimum tax rules.
About Global Minimum Tax
- The Global Minimum Tax, based on Global Anti-Base Erosion (GloBE) Model Rules, ensures large multinational enterprises pay a minimum tax in every jurisdiction of operation.
- Key Features
-
- Prescribes a 15% minimum effective corporate tax rate under BEPS Pillar Two.
- Targets profit shifting to low- or no-tax jurisdictions through interest, royalty and similar deductible payments.
- Applies to large multinational enterprise (MNE) groups with cross-border operations.
- Includes simplification measures and safe harbours to reduce compliance burdens.
- Exception: US-based multinational corporations are effectively exempted from the 15% global minimum tax under the side-by-side arrangement.
- The US argued for exemption citing its domestic minimum corporate tax (15%) and its international tax regime taxing foreign profits at 12.6–14%.
- Other countries are restricted from imposing top-up taxes on US MNEs’ undertaxed foreign profits.
Significance of the Global Minimum Tax
- Simplified and Predictable Tax Regime: Introduces simplification measures and safe harbours, reducing compliance burden for multinational enterprises and administrative complexity for tax authorities.
- Fair Treatment and Level Playing Field: Ensures uniform application through evidence-based stocktake mechanisms and aligned tax incentives across Inclusive Framework members.
- Protection of National Tax Bases: Strengthens qualified domestic minimum top-up taxes, helping countries—especially developing economies—safeguard revenues from base erosion.
- Curbing Harmful Tax Competition: Places a global floor under corporate tax rates, limits profit shifting, and aligns taxation with real economic activity.
Organisation for Economic Co-operation & Development (OECD)
- OECD is an intergovernmental body promoting economic cooperation and global policy standards.
- BEPS Leadership: Leads OECD/G20 Inclusive Framework to curb multinational tax avoidance.
- OECD was officially established in 1961, succeeding the Organisation for European Economic Co-operation (OEEC) (founded 1948) and is headquartered in Paris, France.
- Membership: 147 countries and jurisdictions, including India.
- Two-Pillar Solution:
- Pillar One reallocates taxing rights
- Pillar Two introduces global minimum tax.
BEPS: Base Erosion and Profit Shifting (BEPS) refers to tax avoidance strategies used by multinational enterprises (MNEs) to shift profits from high-tax countries to low- or no-tax jurisdictions, thereby eroding the tax base of countries where real economic activity occurs.
India’s First Urban Night Safari: Kukrail Forest Area
Context: Uttar Pradesh announced India’s first urban night safari at Lucknow’s Kukrail Forest Area, integrating wildlife conservation, eco-tourism and controlled nocturnal wildlife viewing within city limits.
India’s First Urban Night Safari
- Introduction: India’s first urban night safari is being developed at Kukrail Forest Area,Lucknow, UP, inspired by the Singapore Night Safari and adapted to Indian ecological conditions.
- Nodal Body: Uttar Pradesh Eco-Tourism Board.
- Key Features
- Nocturnal wildlife viewing: Structured evening safaris along designated routes to observe animal behaviour after dark.
- Low-impact infrastructure: Controlled lighting, restricted access and eco-friendly design to minimise wildlife disturbance.
- Upgraded conservation centres: Modernisation of crocodile, gharial and turtle rehabilitation facilities.
- Visitor amenities: Nature trails, bamboo huts, children’s park, open gym and interpretation centres.
- Significance
- Urban conservation model: Demonstrates coexistence of wildlife conservation and city-based recreation.
- Environmental awareness: Promotes education on nocturnal ecosystems for families and students.
- Economic benefits: Generates local employment and positions Lucknow as a new eco-tourism hub.
About Kukrail Forest Area
- Kukrail Forest Area is an ecologically important green buffer zone on the outskirts of Lucknow with established wildlife conservation facilities.
- Location: Situated along the Kukrail River in northern Lucknow, providing a natural ecological shield for the city.
- Key Features
-
- Existing crocodile, gharial and turtle conservation and breeding centres.
- Forested riverine ecosystem suitable for controlled ecotourism activities.
- Designated nature trails and protected zones to regulate human movement.
- Flora: Dominated by riverine forest vegetation, bamboo species and native trees supporting urban biodiversity.
- Fauna: Home to reptiles like crocodiles and gharials, freshwater turtles, birds, and other small forest and wetland species.
- Gharial (Gavialis gangeticus) is Critically Endangered on the IUCN Red List, due to habitat loss, river modification, and fishing-related threats.
- Crocodile (Mugger / Crocodylus palustris) is Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List, mainly threatened by habitat degradation and human–crocodile conflict.
The Kukrail Urban Night Safari represents an innovative, sustainable model of urban wildlife tourism, blending conservation, education and leisure within a metropolitan setting.
Wolf Supermoon
Context: The Wolf Supermoon of January 2026 reached peak brightness on 2 January, drawing attention to the combined cultural and astronomical significance of full moons.
About Wolf Supermoon
- A Wolf Supermoon is a popular term describing a January first full moon that occurs when the Moon is near its closest point to Earth.
- Cultural Significance: The name is associated with winter stories of wolves being heard more frequently, though it carries no special astronomical effect.
- Moon’s Orbital Position: The Moon follows an elliptical orbit around Earth, bringing it closer at perigee and farther away at apogee.
- A supermoon occurs when a full moon coincides with or occurs near perigee, making it appear slightly larger and brighter.
- Brightness and Size: During a Wolf Supermoon, the Moon appears marginally bigger and brighter than an average full moon, though the difference is subtle.
- Moon Illusion: The Moon may seem much larger near the horizon due to a psychological effect known as the moon illusion, not actual size change.
Other Types of Moons
- Blue Moon: A Blue Moon refers to either the second full moon occurring within a single calendar month or, less commonly, the third full moon in a season with four full moons, without any change in lunar colour.
- Black Moon: A Black Moon is the second new moon in a calendar month, during which the Moon’s Earth-facing side remains completely dark and invisible.
- Blood Moon: A Blood Moon occurs during a total lunar eclipse when Earth’s atmosphere scatters sunlight, giving the eclipsed Moon a red or reddish-brown appearance.
Suryastra Multi-Calibre Rocket Launcher System
Context: Recently, the Indian Army signed a ₹293-crore emergency procurement contract with NIBE Limited to induct the indigenous Suryastra long-range rocket launcher system.
Suryastra Multi-Calibre Rocket Launcher System
- Suryastra is India’s first indigenous universal multi-calibre long-range rocket launcher, designed for precision surface-to-surface strikes up to 300 km.
- Manufacturer: National Industrial and Business Enterprises (NIBE) Limited
- Technology Partner: Elbit Systems (Israel)
- Technology Base: Adapted from Israel’s PULS under a Technology Collaboration Agreement (July 2025)
- Key Features
- Extended Strike Range: Capable of engaging targets at 150 km and 300 km, enabling tactical deep-strike operations.
- Universal Launcher Capability: Can fire multiple rocket calibres (122 mm, 160 mm, 306 mm) and compatible tactical missiles from a single platform.
- High Precision: Demonstrated a Circular Error Probable (CEP) of less than 5 metres, allowing accurate, targeted strikes.
- Operational Flexibility: Supports multi-target engagement at different ranges and is deployable on 4×4, 6×6 and 8×8 wheeled chassis.
- Significance
- Enhanced deterrence: Strengthens India’s conventional strike capability against adversaries through long-range, precision firepower.
- Force multiplier: Represents a major advancement over existing Pinaka systems in both range and accuracy.
- Atmanirbhar Bharat: Reduces dependence on imported long-range artillery and boosts indigenous defence manufacturing.
Suryastra marks a significant leap in India’s rocket artillery capabilities, combining precision, range and flexibility to enhance the Indian Army’s deep-strike and joint-firepower operations.
![]() 7 Jan 2026
7 Jan 2026

 It is the world’s largest (non-continent) island.
It is the world’s largest (non-continent) island.