International Medical Device Regulators Forum (IMDRF)

|
Context: India becomes an affiliate member of International Medical Device Regulators Forum ( IMDRF).
About IMDRF:
- Nature of Grouping: It is a voluntary group comprising medical device regulators from various countries.
- Establishment: The IMDRF was formed in 2011.
- Goal of IMDRF: To accelerate international medical device regulatory harmonisation and convergence.
- Foundation of GHTF: The IMDRF builds upon the foundational work of the Global Harmonization Task Force on Medical Devices (GHTF), which previously worked on aligning medical device regulations globally.
- Current Members: The IMDRF includes regulatory authorities from the U.S., Australia, Canada, the European Union, Japan, the United Kingdom, Brazil, Russia, China, South Korea, Singapore, and the World Health Organization (WHO).
India’s Path to Membership: In 2024, the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO), under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare applied for IMDRF affiliate membership, which was approved at the 26th session in September 2024, Seattle, USA.
Benefits of IMDRF Affiliate Membership
- Harmonisation and Reduction in Regulatory Compliance: India’s membership aligns its medical device regulations with global standards, reducing regulatory complexities globally and improving public health protection.
- Participation in Open Sessions: India can now participate in open sessions to exchange information, discuss regulatory strategies, and adopt IMDRF documents for its domestic framework.
- Enhanced Domestic Competitiveness: CDSCO’s regulatory framework will be strengthened, enabling it to handle emerging technical challenges.
- Boosting “Brand India”: The membership will also help Indian medical device manufacturers meet global regulatory requirements, boosting their presence in international markets.
|
Tourism Development Index 2024 (TTDI)
|
Context: Recently, the Travel and Tourism Development Index (TTDI) 2024 was released.
Key Findings from the 2024 TTDI Report
- Published by: World Economic Forum (WEF).
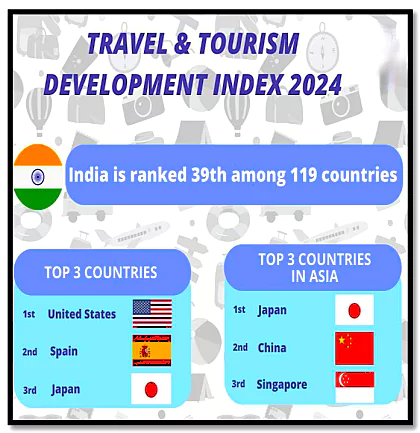
- TTDI Rank 2024: India is ranked 39th out of 119 countries in (TTDI) 2024 by the World Economic Forum (WEF).
- Previous Rank: In the 2021 index, India was ranked 54th, but after a revision in WEF’s methodology, India’s rank for 2021 was adjusted to 38th.
- Areas of Improvement: India’s scores improved in three key areas:
- Prioritization of Travel & Tourism
- Safety & Security
- Health & Hygiene
- Domestic Tourist Visits (DTVs)
-
- 2023 Data: India recorded 2,509.63 million DTVs (provisional) compared to 1,731.01 million in 2022.
- Job Creation: In the 2022-23 period, tourism created 76.17 million direct and indirect jobs, up from 70.04 million in 2021-22.
Initiatives to Boost Foreign tourist arrivals (FTAs)
- Promotional Steps:
- Focus on adventure and niche tourism.
- Simplified e-visa processes.
- A 24/7 multilingual helpline for tourists.
- Launch of Paryatan Didi and Paryatan Mitra: Introduced on World Tourism Day 2024 to enhance tourist experiences in India.
|
Chenchus Tribe

|
Context: The Chenchus of Penukumadugu, traditionally hunter-gatherers, who lived in the dense Nallamala forests of Andhra Pradesh face dwindling employment opportunities under MGNREGA.
About Chenchus Tribe
- The Chenchus are a small, migratory tribal community.
- Predominantly found in Andhra Pradesh and Odisha,
- These are among the 12 Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) in Andhra Pradesh.
Lifestyle and Occupation
- The Chenchus traditionally depend on hunting and gathering for sustenance rather than agriculture.
- They are known for their skills in bamboo cutting and honey collection..
- They mainly cultivate tobacco, maize, and millet but rely heavily on natural resources for their diet.
- Many Chenchus have moved towards agricultural and forest work due to the influence of non-tribal communities
Demographics and Language
- The Chenchus numbered approximately 59,000 at the beginning of the 21st century.
- They predominantly speak Telugu, a Dravidian language, and have distinct dialects such as Chenchucoolam and Chenswar.
- Their physical characteristics include being shorter in stature, with a flat nose and wavy black hair.
- Social Structure and Family
-
- Chenchu families are typically small.
- Men and women enjoy equal status.
- They practice exogamous marriages, allowing individuals to choose their partners freely.
|
![]() 7 Oct 2024
7 Oct 2024