SAMPANN Portal
Context: Recently, the Controller General of Communication Accounts expanded SAMPANN Portal coverage and integrated pension documents with DigiLocker for Department of Telecommunications pensioners.
About SAMPANN Portal
- SAMPANN (System for Accounting and Management of Pension) is an integrated, online pension processing and payment system for Department of Telecommunications pensioners.
- Launched on 29 December 2018
- Implemented by the Controller General of Communication Accounts (CGCA) Under the Department of Telecommunications, Ministry of Communications
Key Features
- Single-window pension management: Integrates pension processing, sanction, authorisation and payment on one digital platform.
- Direct Benefit Transfer: Ensures timely, direct credit of pension into pensioners’ bank accounts without intermediaries.
- Online grievance redressal: Enables pensioners to lodge and track grievances digitally, reducing paperwork.
- Real-time tracking: Allows pensioners to monitor pension status, arrears and revisions from home.
- DigiLocker integration: Provides digital access to Pension Payment Orders, Gratuity Orders, commutation orders and Form 16.
Significance
- Enhanced efficiency: Speeds up settlement of pension cases and improves reconciliation and auditing processes.
- Transparency and accountability: Digital tracking and records reduce errors and enhance trust in pension administration.
- Ease for pensioners: Eliminates physical visits and simplifies document management through paperless access.
- Digital governance: Supports the Government’s vision of e-governance and secure, long-term digital preservation of pension records.
Sudan Crisis
Context: In January 2026, intensified fighting between Sudan’s army and the Rapid Support Forces displaced thousands from South Kordofan, forcing cross-border flight.
About the Crisis in Sudan
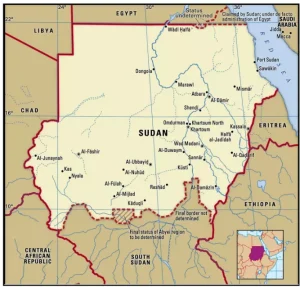
- Renewed clashes in South and West Kordofan have followed the Rapid Support Forces’ expansion into oil-producing regions, including the capture of Heglig, Sudan’s largest oil field.
- The conflict, ongoing since April 2023, has triggered mass displacement, food insecurity, and cross-border refugee movements into South Sudan, worsening an already severe humanitarian crisis.
About Sudan
- Sudan is a northeastern African country, the third-largest in Africa, with its capital Khartoum located at the confluence of the Blue Nile and White Nile.
- Location: It lies between North Africa and Sub-Saharan Africa, with a coastline along the Red Sea and extending southward toward tropical regions.
- Borders: Sudan shares borders with Egypt, Libya, Chad, Central African Republic, South Sudan, Ethiopia, and Eritrea.
- Geography
-
- Mountains: The highest point is Jabal Marrah, located in the western Darfur region.
- Rivers: The country is drained by the Nile River system.
- Relief: Sudan is dominated by vast plains and plateaus, with limited highland regions.
- Vegetation: Northern Sudan is largely desert and semi-arid grassland, transitioning southward into savannah and forest zones.
- Climate: Predominantly hot and arid, with increasing rainfall toward the southern regions.
Sudan’s strategic geography and resource-rich regions continue to shape both its economic importance and conflict dynamics.
Doomsday Glacier
Context: A recent scientific study highlights accelerating fracturing in the Thwaites Glacier, indicating possible future collapse of Antarctic ice sheets.
Key Concerns Regarding the Doomsday Glacier
- Accelerated ice fracturing: The annual length of fractures in the Thwaites Eastern Ice Shelf has more than doubled between 2002 and 2022, weakening structural stability.
- It has increased from 165.2 +/- 6.6 km in 2002 to 335.5 +/- 13.4 km in 2022,
- Rising sea levels: Complete melting of the glacier could raise global sea levels by around 65 centimetres, threatening coastal regions worldwide.
- Climate tipping risk: Destabilisation of the glacier may trigger irreversible changes in the West Antarctic Ice Sheet, causing cascading climate impacts.
About the Doomsday Glacier (Thwaites Glacier)
- The Thwaites Glacier is one of the most rapidly changing ice–ocean systems on Earth and plays a crucial role in regulating global sea levels.
- The Thwaites Glacier is called the “Doomsday Glacier” because its potential, rapid collapse could significantly accelerate global sea-level rise, posing a catastrophic threat to coastal regions worldwide
- Location: Situated in West Antarctica, draining ice from the West Antarctic Ice Sheet into the Amundsen Sea.
- Its eastern extension forms the Thwaites Eastern Ice Shelf, which floats on the ocean surface.
- Key Features
- Massive size and impact: Its collapse alone could significantly destabilise the entire West Antarctic Ice Sheet.
- Pinning point dependence: The ice shelf is anchored to an undersea ridge that slows ice flow; weakening of this pinning point accelerates ice discharge.
- Two-stage fracture pattern: Fractures first develop parallel to ice flow, followed by perpendicular cracks, leading to rapid ice shelf disintegration.
PANKHUDI Portal
Context: The Ministry of Women and Child Development (MWCD) has launched PANKHUDI, an integrated Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) and partnership facilitation portal
Key Features of the Portal
- Single-Window Digital Platform: PANKHUDI serves as a one-stop platform for NGOs, corporates, NRIs, and government agencies involved in women and child development activities.
- Streamlining Contributions: The portal enables stakeholders to register contributions, identify initiatives, submit proposals, and track the progress of their contributions through clear approval workflows.
- Non-Cash Contributions: To ensure financial transparency and accountability, all contributions are accepted only through non-cash modes.
- Focus on Key Areas: The portal supports initiatives in areas such as nutrition, health, Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE), women’s safety, and empowerment.
- Supporting Flagship Missions: PANKHUDI strengthens the implementation of flagship initiatives like Mission Saksham Anganwadi and Poshan 2.0 aimed at improving nutritional outcomes for women and children.
- The portal also supports Mission Vatsalya, focused on child welfare and protection, and Mission Shakti, which works on women’s empowerment and safety.
Benefits of the Portal
- Increased Efficiency and Accountability: By providing a common digital interface, the portal enhances coordination and monitoring, ensuring greater accountability for all involved in women and child development initiatives.
- Infrastructure Enhancement: PANKHUDI is expected to improve services and infrastructure in over 14 lakh Anganwadi Centres, 5,000 Child Care Institutions, and 800 One Stop Centres (OSCs), ultimately improving ease of living for millions of citizens.
![]() 9 Jan 2026
9 Jan 2026


