Project ICE-CRUNCH
Context: The Indo-Swiss Joint Research Project “ICE-CRUNCH (Ice nucleating particles and cloud condensation nuclei properties in the North-Western Himalayas) has been recently launched.
- The first ever “Himalayan High Altitude Atmospheric and Climate Research Centre” has also been inaugurated.
About Project “ICE-CRUNCH
- It is a collaborative study between Indian scientists and researchers from ETH Zürich, Switzerland
- Aim: The project aims at exploring the properties of ice nucleating particles and cloud condensation nuclei in the region.
- Significance: To understand the role of aerosols in cloud microphysics and their broader implications on climate systems and precipitation in the Himalayan region.
About the Himalayan High Altitude Atmospheric and Climate Research Centre
- The centre will serve as a crucial gateway for cutting-edge climate research in the north-western Himalayas.
- Location: The centre has been launched in the higher hill reaches of Nathatop, Jammu and Kashmir.
- Collaboration: The centre is established in partnership with the, Ministry of Science & Technology, the Government of Jammu and Kashmir, the Central University of Jammu and the Swiss National Science Foundation
- Objective: To study atmospheric processes in free tropospheric conditions, a key requirement for understanding cloud formation, weather patterns, and aerosol interactions.
- Affiliated To: The Centre will be affiliated with the World Meteorological Organization’s (WMO) Global Atmospheric Watch (GAW) Programme.
PM-POSHAN Scheme
Context: The Central Government has increased the material cost for midday meals by 9.5% under the PM-POSHAN scheme.
- This will lead to an extra cost of ₹954 crore for the Centre in the 2025–26 financial year.
About PM-Poshan Scheme
- The PM POSHAN Scheme (earlier called the Mid-Day Meal Scheme) was approved from 2021-22 to 2025-26.
- Implemented by the Ministry of Education.
- It provides one hot cooked meal to students in:
- Bal Vatika (pre-primary)
- Classes 1 to 8
- Covers around 11.80 crore children in 11.20 lakh government and government-aided schools.
- Implemented across all states/UTs, without discrimination based on gender or social class.
- Main Objectives
- Fight hunger and improve education for schoolchildren.
Improve nutritional status of students in government and aided schools.
- Motivate children, especially from poor and disadvantaged families, to:
- Attend school regularly.
- Focus better on studies.
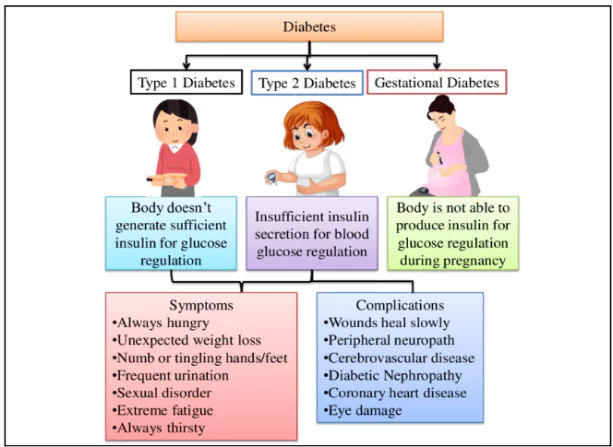
Gestational Diabetes
Context: The World Health Organization (WHO) has chosen the theme: Healthy Beginnings, Hopeful Futures for World Health Day on April 7, 2025.
The theme emphasizes preventing diseases like diabetes starting in the womb, ensuring better health for mothers and children.
About GDM
- It refers to Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GSM).
- GDM is a type of diabetes that occurs during pregnancy and increases the risk of:
- Type 2 diabetes in mothers.
- Metabolic disorders in children.
- Caused by: hormonal changes and increased insulin resistance.
- It impairs the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar effectively.
- Diagnosis Time: GDM is usually identified between 24 to 28 weeks of pregnancy.
- Why Early Screening is Important?
- Current Problem: GDM is usually detected late (in the 2nd trimester), by which time the baby is already affected.
- Need for Early Action: Experts now recommend glucose testing by the 8th week of pregnancy.
- Reason: High blood sugar in the 1st trimester can affect the baby’s metabolism and increase risk of future diseases.
About Diabetes
- It is a chronic disease.
- In this disease, the body does not produce enough insulin.
India Skills Accelerator
Context: The Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE), in collaboration with the World Economic Forum (WEF) is deliberating to launch the “India Skills Accelerator”
About The India Skills Accelerator
- The India Skills Accelerator will function as a national public-private collaboration platform
- It is designed to enable cross-sectoral efforts in unlocking innovative ideas and driving systemic progress on complex challenges that demand a multi-stakeholder approach.
- Aim: The Accelerator aims to catalyze change across three critical levels.
- By improving awareness and shifting mindsets around future skills needs
- By increasing collaboration and knowledge sharing among stakeholders
- To commit upgrading institutional structures and policy frameworks to support a more adaptive and responsive skilling ecosystem.
- Progress Measure: The progress will be tracked through WEF’s Global Learning Network (enabling peer learning and global benchmarking).
- The accelerator will also get insights from the World Economic Forum’s Future of Jobs 2025 report.
Nilgiri Tahr
Context: Kerala and Tamil Nadu will conduct a synchronised census of the Nilgiri Tahr from April 24 to 27, 2025.
Census Coverage and methods
- Kerala: 89 census blocks across 20 forest divisions, from Thiruvananthapuram to Wayanad.
- Tamil Nadu: 176 census blocks in Nilgiri Tahr habitats.
- The census will cover both protected areas and non-protected zones in the Western Ghats.
- Scientific Techniques: Camera traps will be used to capture images of the animals.
- Pellet samples (droppings) will be collected for genetic studies and analysis of population distribution.
- The initiative commemorates the 50th anniversary of the Eravikulam National Park, which is home to the largest population of this endangered species.
About the Nilgiri Tahr
- Nilgiri Tahr is an endangered species and the sole Caprinae species found in the tropical mountains of southern India.
- It is also the state animal of Tamil Nadu.
- The adult males of Nilgiri Tahr species develop a light grey area or “saddle” on their backs and are called “Saddlebacks”.
- It is known for its ability to climb steep and rocky terrains.
- Protection Status: Nilgiri Tahr is a vulnerable species listed on the IUCN Red List.
-
- Nilgiri Tahr has been listed under Schedule 1 of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
- Habitat: Endemic to the Western Ghats, primarily in the high-altitude grasslands of southern India.
Project Nilgiri Tahr
- Project Nilgiri Tahr is a conservation initiative launched by the Tamil Nadu government.
- It aims to protect the endangered Nilgiri Tahr, through surveys, reintroduction efforts, and addressing threats to its habitat.
- The project was launched in 2022 and is to be implemented from 2022 to 2027.
Vitamin D Crisis In India: ICRIER Report
Context: According to the ICRIER report titled ‘Roadmap to Address Vitamin D Deficiency in India’, one in five Indians suffer from Vitamin D deficiency.
About Vitamin D
- Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin crucial for calcium absorption, bone health, muscle strength, immunity and mental well-being.
- It is known as the “sunshine vitamin” because the body produces it when exposed to sunlight.
- Its deficiency is linked to fatigue, muscle weakness, depression, cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes and cancers.
Key Findings of the ICRIER Report
- Deficiency of Vitamin D prevalent Across Age Groups:
- Children (0–10 years): 46% suffer from rickets.
- Elderly (60+ years): 80–90% are at risk of osteoporosis, fractures, and long-term disability.
- Highest deficiency in Eastern India: Around 39% population affected.
- Gender Disparity: Indian women across all age brackets are more vulnerable to Vitamin D deficiency than men.
- Factors Responsible for Deficiency::
- Prevalence in India: Limited sun exposure due to indoor lifestyles, pollution, and skin pigmentation reducing UVB absorption, clothing preference.
- Dietary gaps: Low intake of Vitamin D-rich foods like fish, eggs, and dairy—especially among vegetarians and the lactose intolerant.
- Cost and Accessibility Barriers: Expensive tests and costly supplements (₹48–₹130 for 10 tablets) hinder affordable diagnosis and treatment.
- Regulatory gaps: Only the animal-based form (D3) is price-regulated under the National Pharmaceutical Pricing Authority (NPPA). Plant-based D2 remains unregulated and expensive.
About Indian Council for Research on International Economic Relations (ICRIER): It is a policy-oriented think tank that conducts research and advocacy on various issues to accelerate India’s development.
New Homes for One-Horned Rhinos
Context: India is stepping up its efforts to secure the future of the endangered one-horned rhinoceros by establishing new conservation centers across several states.
- The move aims to reduce the burden on existing habitats and improve the species’ genetic health through translocation programs.
- The new action plan is prepared by the Wildlife Institute of India in collaboration with rhino experts and forest departments.
Donor Sites
- Kaziranga National Park: Kaziranga National Park in Assam, has been identified as the primary donor site for translocation.
- Kaziranga is home to the world’s largest population of one-horned rhinos (2,613 as per the 2022 census),
- Pobitora Wildlife Sanctuary, Assam: Pobitora, with 107 rhinos in just 16 sq km, has the highest rhino density globally.
- Translocation from this sanctuary is critical to reduce risks like territorial aggression, inbreeding, disease outbreaks, and human-wildlife conflicts.
- Jaldapara and Gorumara, West Bengal: These parks will receive rhinos from Assam and also serve as donor sites themselves.
New Conservation Centers
- Dibru-Saikhowa National Park (Assam): Targeted to reintroduce five rhinos over 13 years.
- D’Ering Memorial Wildlife Sanctuary (Arunachal Pradesh): Proposed for five rhinos in the same time frame.
- Valmiki Tiger Reserve (Bihar): Prepared to receive relocated rhinos.
- Uttar Pradesh Sites: Dudhwa National Park, Pilibhit Tiger Reserve, and Katarniaghat Wildlife Sanctuary are listed for potential rhino reintroduction.
- Surai Range (Uttarakhand): Identified as a future rhino habitat.
About the One-Horned Rhino
- The one-horned rhinoceros, also known as the Indian rhinoceros (Rhinoceros unicornis), is a large herbivorous mammal native to the Indian subcontinent.
- Once widespread across the Indo-Gangetic plains, their numbers drastically declined due to poaching, habitat loss, and human encroachment.
- Today there are around 4,000 one horned rhinos currently surviving in the wild, found only in India and Nepal.
- Primary Habitat: Floodplain grasslands, swamps, and forests in the Terai region.
- Conservation Status: Listed as Vulnerable by the IUCN Red List.
![]() 11 Apr 2025
11 Apr 2025


