Manas National Park
Context: Manas National Park in Assam, India, saw its tiger population triple from 2011 to 2019.
- In 2021, 44 adult tigers were recorded.
- Population density: 1.06 tigers per 100 sq. km in 2011–12 to 3.64 tigers per 100 sq. km in 2018–19.
- Potential: 8 tigers per 100 sq. km.
About Manas National Park
- Location: Foothills of Himalayas in Assam.
- Key Characteristics: A unique distinction of being a Natural World Heritage Site, a Tiger Reserve, an Elephant Reserve, a Biosphere Reserve and an Important Bird Area.
- It is one of the first reserves included in the tiger reserve network under project tiger in 1973.
- It forms part of a large tiger conservation landscape which includes Buxa-Nameri-Pakke-Namdapha tiger reserves and protected areas of Bhutan and Myanmar.
- Habitat: Semi-evergreen and Mixed deciduous forests, scrub forests, old plantations (in buffer areas), interspersed with grasslands and riparian vegetation (in core area).
- Flora: Sal (Shorea robusta).
- Fauna: Hispid Hare, Pigmy Hog, Golden Langur, Indian Rhinoceros, Asiatic Buffalo etc.
- River: The name of the park originates from the Manas River, which is named after the serpent goddess Manasa.
- The Manas River is a major tributary of Brahmaputra River, which passes through the Manas National Park.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Exercise AUSTRAHIND
Context: The 3rd edition of Exercise AUSTRAHIND, a joint military exercise between India and Australia, began on November 8, 2024, at the Foreign Training Node in Pune, Maharashtra.
- This annual exercise alternates between India and Australia, with the previous edition held in Australia in December 2023.
- Objectives:
- To strengthen military cooperation by enhancing interoperability for joint sub-conventional operations in semi-urban and semi-desert environments, in line with Chapter VII of the UN mandate.
- Focus areas include joint planning, high physical fitness standards, and tactical drills for effective joint operations.
- Significance:
- The exercise promotes an exchange of tactical knowledge and operational best practices between Indian and Australian forces.
- It also fosters camaraderie and professional understanding, contributing to stronger defense ties between India and Australia.
Agrivoltaic Farming
Context: At the seventh session of the International Solar Alliance (ISA) in New Delhi, a visit was organized to a farm site in Najafgarh to demonstrate the agrivoltaic model in action.
- Delegates observed how India integrates solar panels with traditional farming practices, illustrating a sustainable approach that maximizes land productivity.
About Agri Voltaic Farming
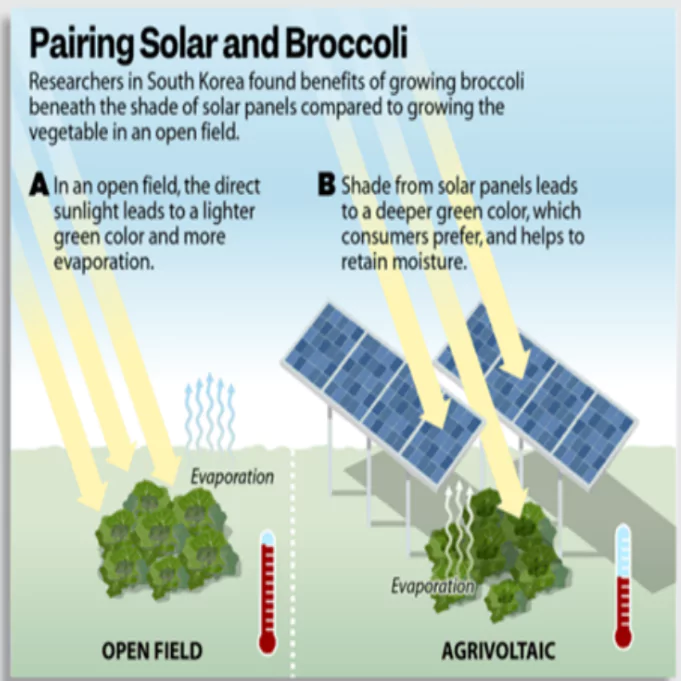
- Definition: Agrivoltaic farming is the simultaneous use of land for both agricultural activities and solar energy generation.
- Concept: This system allows solar panels to be installed above or near crops, enabling efficient land use by generating renewable energy while continuing crop cultivation on the same land.
- Benefits of Agrivoltaic Systems
- Enhanced Land Use Efficiency: By combining solar energy production with agriculture, agrivoltaic systems make more effective use of available land.
- Energy Security and Sustainability: provide a renewable energy source that supports agricultural productivity, reducing dependence on conventional power sources.
- Support for Rural Economies: help generating additional income through solar energy production while continuing crop cultivation.
- Potential for Global Application: a model for countries aiming to improve both food security and energy access sustainably, especially in regions where arable land is limited.
Allulose
Context: South Korea has become a top testing ground for the sweetener allulose, a potential rival to sugar substitutes like Stevia.
- Both large food corporations and influencers in South Korea endorse allulose, leading to increasing demand and wider accessibility.
Allulose: A low-calorie sweetener found naturally in fruits like figs and kiwis; chemically similar to sugar but with 70% of its sweetness and almost zero calories.
Health Benefits and Risks
- Potential Health Benefits: Shown to aid in weight control and beneficial for individuals with diabetes due to its ability to reduce blood glucose response when combined with sugars like sucrose.
- Health Concerns: Experts recommend further research to confirm long-term safety. Side effects, such as gastrointestinal discomfort, can occur if consumed in large quantities.
- WHO Position: The World Health Organization advises against the use of non-sugar sweeteners for weight control due to potential long-term health risks, although it has not issued a specific stance on allulose.
About Stevia
- Source: Derived from the leaves of the Stevia rebaudiana plant, native to South America.
- Active Compounds: The sweetness of stevia comes from naturally occurring chemicals in the leaves known as steviol glycosides, which give it a highly concentrated sweetness.
- Sweetness Profile and Nutritional Value
- Sweetness Intensity: Approximately 200 to 400 times sweeter than table sugar, allowing for much smaller quantities to achieve desired sweetness levels.
- Caloric and Nutritional Content: Classified as a non-nutritive sweetener, meaning it contains no calories, carbohydrates, or artificial additives, making it suitable for low-calorie diets.
- Popularity and Usage
- Global Use: Stevia has gained popularity worldwide as a natural alternative to artificial sweeteners, particularly among consumers seeking low-calorie, plant-based options.
- Common Applications: Used in a variety of products, from beverages and baked goods to snacks, due to its intense sweetness and lack of calories.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Review of mechanism to curb fake news post court verdict
Context: The Parliamentary Panel on Communications and Information Technology, is calling for a review of mechanisms to curb fake news.
More on the news
- On November 21, the panel will meet with the News Broadcasters and Digital Association, the Editors Guild of India, and the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting for discussions.
Background on IT Rules Amendment, 2021
- Amended IT Rules: In April 2022, the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology introduced amendments to the IT Rules, 2021, through the IT (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Amendment Rules, 2023.
- Scope Expansion: Rule 3(1)(b)(v) of the IT rules 2021 was amended to include “fake news” related specifically to “government business.”
What is fake news, misinformation, and disinformation?
- These are fabricated information which aim to mislead narrative or facts.
- Misinformation is created without having the intent of malicious content.
- Disinformation is created with malicious intent like deceiving.
About Fast Check Unit
- Purpose and Role
- Verification: The FCU checks the accuracy of information related to government policies, programs, and announcements.
- Countering Misinformation: It monitors and combats false or misleading information about government activities.
- Public Engagement
- Providing Reliable Information: The FCU shares verified and trustworthy information with the public through social media and other communication channels.
- Complaint Resolution
- Handling Complaints: It accepts and addresses reports of fake news through WhatsApp, email, and a dedicated web portal.
Legal Challenges and Court Rulings
- Challenge by Editors Guild and Kunal Kamra: The Editors Guild of India, along with stand-up comedian Kunal Kamra, challenged the constitutionality of the amendment, raising concerns over freedom of speech and press.
- Supreme Court Intervention: After the government’s notification of the FCU on March 20, the Supreme Court stayed the implementation the next day, pending the Bombay High Court’s review.
- Bombay High Court Ruling: On September 21, 2023, the Bombay High Court struck down the amended rule, deeming it “unconstitutional.”
Role of the Parliamentary Panel on Communications and Information Technology
- Regulation and Oversight: The panel monitors and guides rules related to communication and information technology, making sure they are effectively managed.
- Policy Review: It examines and reviews policies and amendments related to online content and fake news, ensuring they are suitable and effective.
- Engaging Stakeholders: The panel invites media groups and government representatives to discuss and provide input on issues related to digital content regulations.
- Recommending Changes: The panel suggests changes to laws for better control over digital content and to manage fake news more effectively.
- Raising Public Awareness: It works to educate the public about responsible online behavior and the effects of fake news on society.
|
![]() 11 Nov 2024
11 Nov 2024

