Cauvery Panel

|
- The Cauvery panel asks Karnataka to ensure flow of water for Tamil Nadu.
Cauvery Panel:
- Cauvery Water Dispute: The allocation of Cauvery water has been a longstanding issue between Tamil Nadu and Karnataka, rooted in agreements from 1892 and 1924 between the former Madras Presidency and the Princely State of Mysore.
- Establishment of Cauvery Water Disputes Tribunal: In 1990, the Union government established the Cauvery Water Disputes Tribunal, which issued its ruling in 2007.
- However, the decision did not resolve the dispute, prompting both Tamil Nadu and Karnataka to file petitions seeking a review of the verdict.
Cauvery Delta:
- Cauvery River Basin: The Cauvery river basin, covering 81,155 km2, is among South India’s largest. It is shared by Karnataka (42.23%), Kerala (3.53%), Puducherry (0.2%), and Tamil Nadu (54.04%), with Karnataka and Tamil Nadu having the largest shares.
- Cauvery River: The Cauvery river, which travels approximately 800 kilometres, empties into the Bay of Bengal.
|
Vizhinjam International seaport in Kerala

|
- The Vizhinjam International Seaport in Kerala receives its inaugural container vessel.
Vizhinjam International Seaport:
- About: Vizhinjam Seaport in Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala, is India’s first Deepwater Container Transshipment Port, representing an ambitious project of the Kerala government.
- Development Model: The port is currently under development in a landlord model with a Public-Private Partnership component, following a Design, Build, Finance, Operate, and Transfer (DBFOT) basis.
- Under this model, the port authority serves as a regulatory body and landlord, while private companies (specifically Adani Vizhinjam Port Pvt Ltd in this instance) handle port operations, particularly cargo handling.
- Versatile Functionality: The port is equipped to manage container transshipment, multi-purpose, and break-bulk cargo. Situated strategically just ten nautical miles from the international shipping route.
- Efficient Operations: With minimal littoral drift and low maintenance dredging needs, the port ensures reduced operational costs.
Transshipment Hub:
- About: Transshipment hubs are ports that serve as intermediate points for cargo transfer between originating and destination ports.
- Approximately 75% of India’s transshipment cargo is processed at ports located outside the country. The majority of this cargo, over 85%, is handled by the Ports of Colombo, Singapore, and Klang.
Steps to develop transshipment hubs in India:
- Cochin Port: The Cochin Port Authority (CoPA) has established the International Container Transshipment Terminal in Cochin.
- Great Nicobar: Galathea Bay in Great Nicobar Island, part of the Andaman & Nicobar Islands, has been earmarked for the development of an International Container Transshipment Port.
|
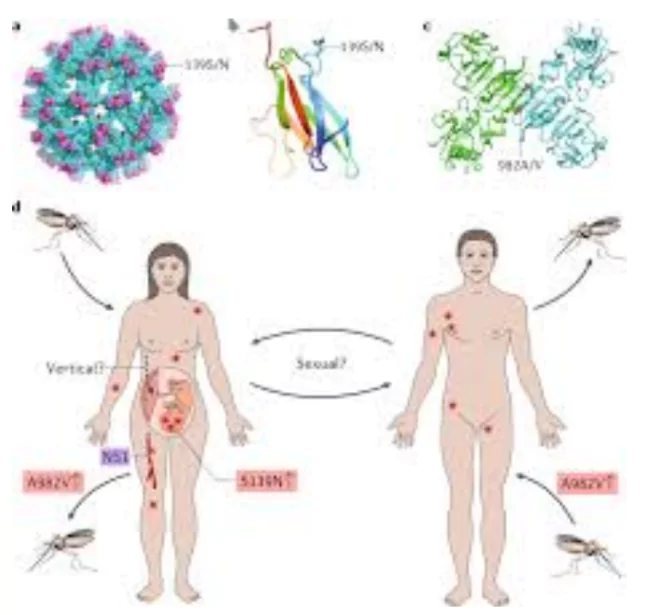
Zika Virus
|
- At least 15 cases, including eight pregnant women, of Zika have been discovered so far in Pune, Maharashtra.
Zika Virus:
- About: It is a virus transmitted by mosquitoes, initially identified in Uganda in 1947 in a Rhesus macaque monkey. Subsequently, evidence of infection and disease in humans emerged in other African countries during the 1950s.
- Transmission: Zika virus spreads through bites of infected Aedes mosquitoes, which also transmit dengue, chikungunya, and yellow fever.
- Zika virus can be sexually transmitted between humans.
- Infected mothers can transmit the virus to their newborns during childbirth.
- Symptoms: Zika virus often causes no symptoms in infected individuals.
- Symptoms of Zika virus infection are similar to other arbovirus diseases like dengue, including fever, skin rashes, conjunctivitis, muscle and joint pain, malaise, and headache.
- Zika virus infection during pregnancy can lead to babies being born with microcephaly.
- Diagnosis: Through blood tests conducted in a laboratory
- Treatment: No specific treatment or vaccine exists for Zika virus infection or disease.
- Those with symptoms such as rash, fever, or joint pain should rest, stay hydrated, and manage symptoms with antipyretics and/or analgesics.
- Prevention: Prevention and control of Zika virus rely on reducing mosquito breeding sites.
- To reduce mosquito-human contact, use insect repellent, wear light-coloured clothing, use screens on windows and doors, and sleep under mosquito nets.
|
MeDevIS Platform
|
- The World Health Organization (WHO) recently launched the MeDevIS platform.
MeDevIS:
- About: The MeDevIS platform is the first global open access clearinghouse for information on medical devices.
- Handling Non-Standard Device Names: Replaces traditional paper-based literature searches across multiple publications, particularly when dealing with non-standard device names, which can increase complexity.
- Features: This platform assists governments, regulators, and users in choosing, acquiring, and utilising medical devices for diagnosing, testing, and treating various health conditions.
- MeDevIS encompasses 2301 types of medical devices, addressing health concerns such as reproductive health, noncommunicable diseases, and infectious diseases like COVID-19.
- Aim: To simplify the naming of medical devices.
- References: MeDevIS includes two international naming systems for medical devices.
- European Medical Device Nomenclature (EMDN) is predominantly used in European countries
- Global Medical Device Nomenclature (GMDN) is used in Australia, Canada, the USA, and other member countries.
|
Veerangana Durgavati Tiger Reserve

|
- Madhya Pradesh launches probe into alleged irregularities poaching in new tiger reserve
Veerangana Durgavati Tiger Reserve:
- About: The reserve stretches across Sagar, Damoh, and Narsinghpur districts in Madhya Pradesh.
- It includes parts of the Nauradehi Wildlife Sanctuary and Durgavati Wildlife Sanctuary.
- Named after Rani Durgavati, the queen of the Gondi people, it is the seventh tiger reserve established in Madhya Pradesh.
- Features: A green corridor is planned to connect the Panna Tiger Reserve with Durgavati, enabling tigers to move freely between the reserves.
- The reserve encompasses areas within the Narmada and Yamuna River basins.
- The historic Singorgarh Fort lies within the reserve’s boundaries.
- Fauna: Teak, Saja, Dhaora, Ber, and Amla.
- Flora: Tigers, leopards, wolves, jackals, Indian foxes, striped hyenas, Nilgai, Chinkara, Chital, Sambhar, Black Buck, Barking deer, Common Langur, and Rhesus Macaque, White-Rumped and Indian Vultures can be found.
|
![]() 12 Jul 2024
12 Jul 2024