Tato-II Hydro Electric Project
Context: Recently, the Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA), chaired by the PM approved the construction of the 700 MW Tato-II Hydro Electric Project (HEP) in Shi Yomi district of Arunachal Pradesh.
About Tato-II Hydro Electric Project
- The Tato-II Hydro Electric Project is a run-of-river project on the Siyom River.
- Part of a cluster with Tato-I, Heo, Naying, and Hirong projects.
- Fits into the revival of 13 stalled hydro projects in the state.
- A Run-of-River project is a type of hydroelectric generation where water from a river is diverted through a channel or penstock to a powerhouse, without creating a large reservoir.
- It relies on the natural flow and elevation drop of the river.
- Implementing Agency: North Eastern Electric Power Corporation (NEEPCO) under Neepco Arunachal Hydro Power Corporation (Central PSU partnership).
- Planned Capacity: 700 MW.
- Purpose: Boost power supply in Northeast India and aid in stabilizing the National Power Grid.
- Power Allocation: Arunachal Pradesh will receive 12% free power from the project, along with an additional 1% earmarked for the Local Area Development Fund (LADF).
- LADF is a dedicated fund created by project developers (usually large infrastructure or hydropower companies) to finance socio-economic development in areas affected by the project.
About Siyom River
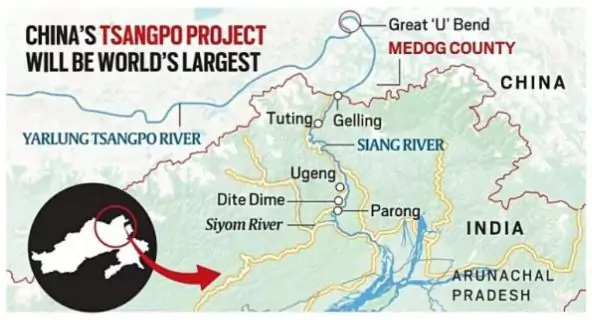
- A tributary of the Brahmaputra River in Arunachal Pradesh.
- Origin: Near the Mishmi Hills, close to the China-India border in the northeastern extremity of Arunachal Pradesh.
- Course: Flows southwards through West Siang district, then passes through important towns like Along (Aalo) and joins the Brahmaputra River (called Siang in Arunachal Pradesh) near Pasighat.
- Tributaries and Features: Receives water from numerous small streams originating from the Himalayan slopes such as Taying River, Tuting River & Mipi River
- The river basin is characterized by steep valleys, gorges, and rich biodiversity.
India–Singapore Green & Digital Maritime Corridor (GDMC)
Context: Recently the India–Singapore Green & Digital Maritime Corridor (GDMC) was highlighted at the Mumbai Dialogue 2025, ahead of India Maritime Week 2025 (27–31 October).
About Green & Digital Maritime Corridor (GDMC)
- Refers: A specific shipping route where countries collaborate to decarbonize and digitalize maritime operations.
- Decarbonization: Promotes low- or zero-carbon fuels (green hydrogen, ammonia) and development of bunkering infrastructure at ports to reduce GHG emissions.
- Digitalization: Adoption of electronic documentation, real-time tracking, and data exchange, resulting in faster port turnaround, reduced operational costs, and improved safety.
- Aligned with: The International Maritime Organization (IMO) goals to reduce carbon emissions from shipping
About India–Singapore GDMC
- It has emerged as a key area of bilateral cooperation, with a recent high-level “Leaders’ Dialogue” in Mumbai laying the groundwork for its future development.
- Bilateral Maritime Cooperation: Strengthens trade, investment, and technology exchange between India and Singapore.
- Includes defense cooperation, e.g., SIMBEX (Singapore–India Maritime Bilateral Exercise).
- Strategic and Policy Alignment: Acts as a precursor to India Maritime Week 2025, showcasing joint projects in green shipping and digitalisation.
- Supports Maritime Amrit Kaal Vision 2047 and Harit Sagar Guidelines for sustainable maritime operations.
- Complementarity with Other Corridors: Complements India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEEC) and International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC).
- Significance of GDMC:
- Sustainable Trade & Green Shipping: Promotes low-carbon maritime trade between India and Singapore.
- Efficiency & Safety: Enhances maritime efficiency, operational reliability, and safety through digital technologies.
- Strategic Connectivity: Strengthens India’s maritime presence in the Indo-Pacific and supports blue economy initiatives.
- Policy & Global Leadership: Reinforces India’s Act East Policy and global maritime leadership ambitions.
- Technology & Skill Development: Provides a platform for technology transfer, innovation, and maritime skill development.
INS Himgiri
Context: The Indian Navy is set to commission INS Himgiri at Visakhapatnam.
About Himgri
- Himigri is third ship of Nilgiri Class (Project 17A); first P17A of its class built by Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers (GRSE), Kolkata.
- It is designed by the Warship Design Bureau (WDB) and overseen by the Warship Overseeing Team (Kolkata).
Features of Himigri
- Multi-Mission Platform: Equipped for anti-air, anti-surface, and anti-submarine warfare.
- Strike & Defence Systems: Features BrahMos cruise missiles (anti-ship and land-attack) and Barak 8 surface-to-air missiles.
- Surveillance & Combat Systems: Integrated with AESA radar and advanced combat management systems.
- Propulsion System: Uses combined diesel and gas turbine propulsion for operational flexibility.
- Crew Capacity & Aviation: Accommodates 225 personnel and supports full helicopter operations.
INS Udaygiri
Context: The Indian Navy will commission INS Udaygiri at Visakhapatnam.
About INS Udaygiri
- INS Udaygiri is the second ship of the Project 17A stealth frigates, built by Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited (MDL), Mumbai.
- It is the modern avatar of the erstwhile INS Udaygiri, decommissioned in 2007, and is the 100th ship designed by the Navy’s Warship Design Bureau.
Features of INS Udaygiri
- Enhanced Stealth Capability: The ship incorporates advanced stealth measures to reduce radar, thermal, and acoustic signatures, making it harder to detect in hostile environments.
- State-of-the-Art Systems: It is equipped with advanced weapons, modern sensors, and cutting-edge warfare technologies to counter emerging maritime threats.
- Multi-Mission Operational Role: INS Udaygiri can engage both conventional and non-conventional threats, enabling operations across the full spectrum of maritime warfare.
About Project 17A (P-17A) Frigates
- Project 17A is the advanced follow-on to the Project 17 (Shivalik-class) frigates, featuring enhanced stealth, upgraded sensors, modern weapons, and an integrated platform management system.
- Some key ships under this project include INS Nilgiri, INS Udayagiri, and INS Taragiri.
18th International Olympiad on Astronomy and Astrophysics
Context: Recently, the Indian Prime Minister addressed the 18th International Olympiad on Astronomy and Astrophysics.
About 18th International Olympiad on Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Organisers: Homi Bhabha Centre for Science Education (HBCSE), under Tata Institute of Fundamental Research (TIFR), with support from the Prime Minister’s Office and the Department of Atomic Energy.
- Host Country: India (Mumbai)
- Participants: Over 300 high school students and 140 mentors from 64 countries
- Largest IOAA Edition: Reflects international collaboration and shared learning.
Key Highlights from the Address
- India’s Historical and Scientific Legacy:
- India’s Astronomical Tradition: Long-standing culture of sky observation, curiosity, and innovation.
- Aryabhatta (5th Century): Invented zero and first stated that Earth rotates on its axis.
- India’s Contemporary Astronomy and Space Science Achievements:
- Indian Astronomical Observatories:
- Ladakh Observatory: Situated at 4,500 metres, ideal for high-altitude observations.
- Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope (GMRT), Pune: One of the world’s most sensitive radio telescopes, decoding pulsars, quasars, and galaxies.
- Global Mega-science Contributions: Participation in Square Kilometre Array and LIGO-India.
- Space Missions:
- Chandrayaan-3: First successful landing near Moon’s South Pole.
- Aditya-L1 Solar Observatory: Monitors solar flares, storms, and Sun’s activity.
- Group Captain Shubhanshu Shukla: Indian mission to International Space Station.
- Nurturing Scientific Curiosity and STEM Education:
- Atal Tinkering Labs: 10+ million students learning STEM through hands-on experimentation.
- One Nation One Subscription: Free access to reputed international journals for students and researchers.
- Women in STEM: India is a leading country in women participation in science.
- Research Investments: Billions of dollars invested in India’s scientific ecosystem.
- Encouragement for Young Explorers: Invitation to young scientists worldwide to study, research, and collaborate in India.
- Application of Space Science for Humanity:
- Better weather forecasts for farmers.
- Prediction of natural disasters.
- Monitoring forest fires and melting glaciers.
- Improving communication in remote areas.
UNDP Equator Initiative Award
Context: Recently, the Bibi Fatima Self-Help Group (SHG) from Teertha village in the Dharwad district of Karnataka has been awarded the prestigious UNDP Equator Initiative Award.
About UNDP Equator Initiative Award
- Often called the “Nobel Prize for Biodiversity Conservation”.
- Presented under the Equator Initiative of UNDP.
- Recognises community-led efforts to reduce poverty through biodiversity conservation.
- Frequency: Biennial
- Prize Money: $10,000
- 2025 Theme: Women and Youth Leadership for Nature-Based Climate Action
- Eligibility Criteria: Initiative/action must exist for ≥3 years.
- Nominee:
- Local community-based group in rural area (supported by UNDP) OR
- Indigenous Peoples’ community in rural areas anywhere.
- Actions must be nature-based and deliver benefits related to ≥2 SDGs.
- Significance:
- Highlights local solutions to climate change and biodiversity loss.
- Promotes women and youth leadership.
- Connects traditional knowledge with sustainable development.
- Offers global recognition and a platform for sharing best practices.
About Equator Initiative
- Launched by UNDP in 2002 to support indigenous peoples and local communities conserving biodiversity while reducing poverty.
- Promotes women & youth leadership, knowledge sharing, and capacity building.
National Anubhav Awards
Context: Recently, the Department of Pension & Pensioners’ Welfare (DoPPW) announced the celebrations for the 10th anniversary of National Anubhav Awards.
About the National Anubhav Awards
- Launched in: 2015 by the Department of Pension & Pensioners’ Welfare (DoPPW) under the Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances and Pensions.
- Purpose: Document the administrative history of India through the personal memoirs of retired employees.
- Awards Scheme: Honors the contribution of retired employees by recognizing their memoirs published on the Anubhav Portal.
Key Features of the National Anubhav Awards
- Eligibility: Employees who are retiring within the next 8 months or have retired within the last 3 years.
- Write-ups submitted by employees are evaluated for Anubhav Awards or Anubhav Jury Awards.
- Write-ups must be published on the Anubhav Portal between 1 April 2024 and 31 March 2025.
- Awards:
- In 2015: Initially 5 National Anubhav Awards and 10 Anubhav Jury Awards.
- In 2023: Expanded participation base by including employees from 12 Public Sector Banks and Central Public Sector Enterprises (CPSEs).
- In 2024: Introduction of marking system to enhance objectivity in the assessment process.
Easter Island
Context: Recently, a study warns that sea level rise could submerge Easter Island’s iconic moai statues by 2080.
About Easter Island
- Location: Easter Island is located in the Southeastern Pacific Ocean, a territory of Chile.
- It forms part of the Polynesian Triangle, which also includes Hawaii and New Zealand.
- This region is traditionally home to the Polynesian people.
- Also known as: Rapa Nui (its indigenous name)
- UNESCO Designation: Rapa Nui National Park that protects most of the island, is a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- Geography: Volcanic island with rocky, lava-covered terrain.
- Climate: Tropical rainforest climate.
The Moai Statues
- The moai statues, carved by the Rapa Nui people between 1250–1500 CE, are central to the island’s cultural identity.
- The statues, crafted from volcanic rock, were created to honor the islanders’ ancestors.
- Found mostly around the island’s perimeter, the moai statues stand on stone platforms known as ahu, which are ceremonial sites.

![]() 13 Aug 2025
13 Aug 2025


