Exercise AL NAJAH V
|
Context: The Indian Army contingent has departed for the 5th edition of Exercise AL NAJAH, which will take place from 13th to 26th September 2024 at the Rabkoot Training Area in Salalah, Oman.
About Exercise AL NAJAH:
- Conducting between: AL NAJAH is a Joint Military exercise between India and Oman.
- This is the fifth edition of the exercise.
- Purpose: Exercise AL NAJAH,aims to strengthen the joint military capabilities of both the nations in executing counter-terrorism operations under Chapter VII of the United Nations Charter.
- Operational Environment: This year the exercise will be based on operations in a desert environment.
- Biennial Schedule: Exercise AL NAJAH has been held biennially since 2015.
- Previous Edition Location: The last edition was conducted at Mahajan, Rajasthan.
- Significance of this Exercise: It will allow both sides to exchange best practices in tactics, techniques and procedures for joint operations.
- It will foster interoperability, goodwill and camaraderie between the two armies.
- Additionally, the joint exercise will strengthen bilateral defence cooperation between the two friendly nations.
Other exercises between India and Oman:
- Navy exercise: Naseem-Al-Bahr
- Air Force: Eastern Bridge
|
Industrial output grew 4.8% in July

|
Context: India’s industrial output grew 4.8% in July, the second-slowest pace in the financial year 2024-25, from an upgraded 4.7% rise in June, even as mining and electricity growth slowed, and non-consumer durables’ production slipped by a sharp 4.4%, marking the third contraction in four months.
About Industrial Production Index (IIP)
- The IIP is a composite indicator that measures the short-term changes in the production volume of various industrial products over a given period.
- It tracks changes in the production volumes of different industries, including manufacturing, mining, and electricity generation.
- The IIP series in India has been revised from time to time by reviewing the coverage of items and industries and by improving to reflect adequately, the industrial growth and structure.
- When the index was commenced in India, the base year adopted was 1937 and this was revised successively to 1946, 1951, 1956, 1960, 1970, 1980-81, 1993-94, 2004-05 and recently to 2011-12
- Currently, the base year of IIP is 2011-12:
- Headline PMI (0 to 100): A numerical representation of the overall business activity.
- PMI Above 50: Indicates an expansion compared to the previous month. The higher the number above 50, the more significant the expansion.
- PMI Under 50: Represents a contraction. The lower the number below 50, the more significant the contraction.
- PMI at 50: Indicates no change in business activity.
- Weightage of Different Sectors: It consists of 839 items with the highest share of Manufacturing items i.e 809.
- Mining(29): 14.37 %
- Manufacturing (809): 77.63 %
- Electricity(1): 7.99 %
- Eight Core Sectors
- Comprising 40.27% of the weight of items included in the Index of Industrial Production.
- The eight core sector industries in decreasing order of their weightage: Refinery Products > Electricity > Steel > Coal > Crude Oil > Natural Gas > Cement > Fertilizers.
|
ONDC launches Saarthi reference app
|
Context: Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC) recently launched Saarthi, a reference application designed to assist businesses in creating their own customised buyer-side apps, co-developed with Bhashini.
About Saarthi
- Saarthi is a reference application developed by ONDC to help businesses create customized buyer-side apps with multilingual capabilities.
- Collaboration: Developed in collaboration with Bhashini, an AI-driven language translation tool.
- Language Support:
-
- Initially supports 5 languages: Hindi, English, Marathi, Bangla, Tamil.
- Plans to expand to 22 languages offered by Bhashini.
About Open Network Digital Commerce (ONDC)
- Open Network Digital Commerce (ONDC) is an interoperable network based on the BeckN protocol that anyone can piggyback on.
- The ONDC entity, a not-for-profit company incorporated under Section 8 of the Companies Act 2013, manages and operates the ONDC Network.
- It is responsible for building and maintaining the underlying infrastructure (common registries and protocols) and defining the rules of engagement and code of conduct for the Network Participants through the ONDC Network Policy and the ONDC Network Participant Agreement.
- Seamless operations: It seeks to break down silos in digital commerce by enabling platforms of varying configurations (big or small) to connect and operate seamlessly on it.
- Network Participants: It comprises different entities called Network Participants, including Buyer Applications, Seller Applications, and Gateways that perform the search and discovery function
- Open network model: The government wants to change the fundamental structure of the e-commerce market from the current platform-centric model to an open network model.
About Bhashini:
- Bhashini is a National Language Technology Mission (NLTM) that provides language technology solutions to make digital services and products accessible to all Indians in their native languages.
- Bhashini’s services include:
- Translation: Bhashini uses artificial intelligence to translate services into 22 Indian languages in real time.
- Voice-based access: Bhashini provides voice-based access to digital services and the internet.
- Content creation: Bhashini helps create content in Indian languages.
- Education and health: Bhashini provides services for education and health.
- Bhashini was launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi in July 2022. The name Bhashini stands for Bhasha Interface for India.
|
PM addresses second International Conference on Green Hydrogen

|
Context: Recently, the Prime Minister, Shri Narendra Modi addressed the International Conference on Green Hydrogen via video message.
About International Conference on Green Hydrogen:
- The Government of India has organised an International Conference on Green Hydrogen (ICGH-2024) on 11-13 September 2024 at Bharat Mandapam, New Delhi.
- Purpose: To discuss the recent advances and upcoming technologies across the entire Green Hydrogen value chain.
- Participants: Global scientific community and industry experts.
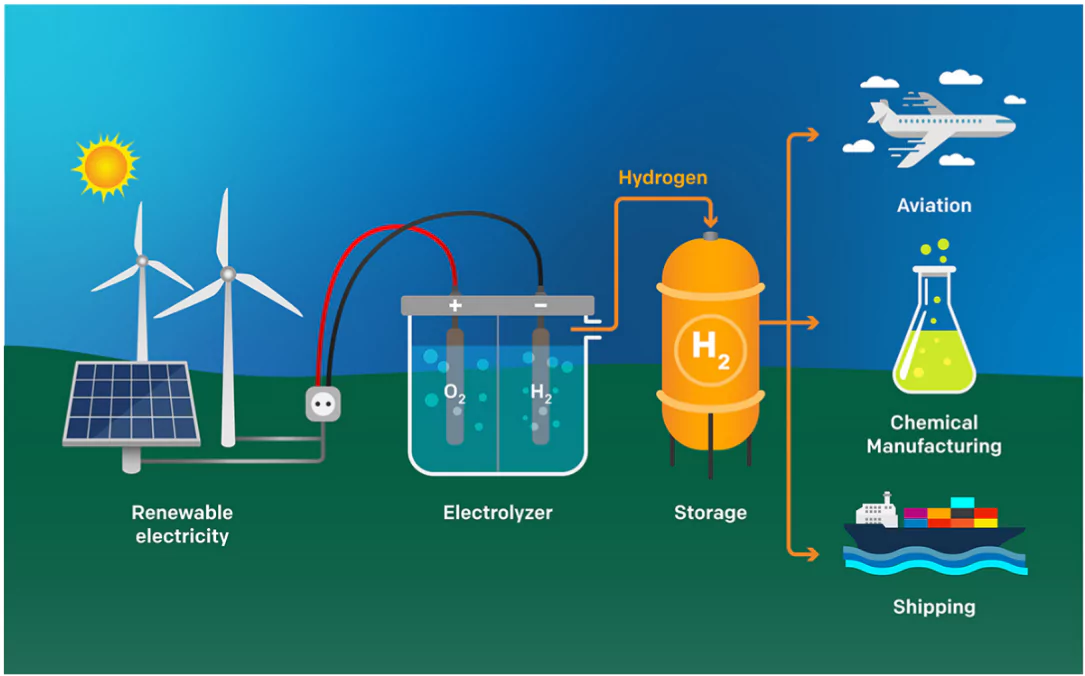
About Green Hydrogen:
- It is produced by electrolysis of water using renewable energy (like Solar, Wind) and has a lower carbon footprint.
- Electricity splits water into hydrogen and oxygen.
- By Products: Water, Water Vapor.
National Green Hydrogen Mission:
- The Union Cabinet has approved the National Green Hydrogen Mission in Jan 2023.
- Budget Outlay: Rs. 19,744 crore, for various components.
- Aims: To make India a global hub for the production, utilization, and export of green hydrogen and its derivatives. Sets export targets from 2027 onwards.
- Central PSUs like NTPC Ltd, NLC India Ltd. etc expected to establish capacity to generate green hydrogen at commercial scale.
- Proposes viability gap funding, loans, grants etc to support pilot projects in green hydrogen storage, fuel cell technology, applications in mobility etc.
- Institutes governing framework for standards, regulations, testing protocols related to production, storage, transportation of green hydrogen.
- Implementation: Ministry of New & Renewable Energy
- Sub Schemes under the National Green Hydrogen Mission:
- Strategic Interventions for Green Hydrogen Transition Programme (SIGHT): It will fund the domestic manufacturing of electrolysers and produce green hydrogen.
- Aims to support 4GW of domestic electrolyser manufacturing capacity and assist production of 1 million tonnes of green hydrogen by 2030.
- Green Hydrogen Hubs: States and regions capable of supporting large scale production and/or utilization of hydrogen will be identified and developed as Green Hydrogen Hubs.
|
Salt Pans

|
Context: The Centre approved transferring 256 acres of Mumbai’s salt pan land to Dharavi Redevelopment Project Pvt Ltd (DRPPL) for building rental houses for slum dwellers.
About Salt Pan Lands:
- They are parcels of low-lying lands where seawater flows in at certain times, and leaves behind salt and other minerals.
- Formation: These naturally occurring expanses of land which are covered with salt and minerals are formed where large water bodies evaporate over thousands of years.
- Ecological Sensitivity: According to the Coastal Regulation Zone (CRZ) notification of 2011, the salt pans fall under CRZ-1B category, where no economic activity is allowed with the exception of salt extraction and natural gas exploration.
- Scale: In all, 5,378 acres of land in Mumbai have been designated as salt pan lands.
- Usage: They can be used for water collection and salt production. They can also support huge biodiversity.
Significance of Salt Pan Lands:
- Flood Prevention: Salt pans act as natural flood buffers by collecting rainwater and tidal flows, preventing flooding in areas like Vikhroli, Kanjurmarg, and Bhandup.
- Climate Resilience: They mitigated the impact of the 2005 Mumbai deluge, reducing damage in the eastern suburbs.
- Environmental Protection: Salt pans, along with mangroves, prevent urban flooding and support biodiversity, hosting various bird and insect species.
- Sustainability Concerns: Development over salt pans risks increased flooding and disregards the ecological balance and conservation needs of the city.
|
Inflation Under 4%
|
Context: India’s retail inflation stayed under the RBI’s median target of 4% for the second successive month in August.
Consumer Price Index (CPI) – Retail Inflation:
- Refers → Measures change in the retail price in the prices of commodities of both goods and services with reference to a base year
- Measured by → National Statistics Office, Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation
- Types:
- CPI for Industrial Workers (CPI-IW) → By the Labour Bureau
- CPI for Rural Laborers and Agricultural Laborers (CPI-AL&RL) → By the Labour Bureau
- CPI for Urban Non-Manual Employees (CPI-UNME) → Discontinued
- New CPI → CPI (Rural), CPI (Urban) and CPI (Combined)
- Base Year → 2012
- Compiled and Published by → The Central Statistical Organisation (CSO)
Wholesale Price Index (WPI):
- Refers → Measures the average change for bulk sale before the retail level
- Base Year → 2011-12
- Compiled and Released by → Office of Economic Advisor, Ministry of Commerce and Industry
- Released on a monthly basis
- Weights → Each covered commodity in the WPI basket
- Based on the value of production adjusted for net imports
About Base Effect:
- Refers → Comparison of impact of the rise in price level in corresponding period of the previous year
- Impact → Smaller rise in the Price Index → High rate of Current inflation and vice versa
|
Ozone pollution slows tropical forest growth by halting carbon absorption

|
Context: A Study, published in Nature Geoscience, reveals ozone pollution is hindering tropical forest growth.
About the study on ozone pollution and tropical forests:
- Impact: Tropical forests lose nearly 300 million tonnes of carbon absorption each year due to ozone.
- Ozone Effect: Ground-level ozone reduces new tropical forest growth by 5.1% annually.
- Cause: Ozone is formed by pollutants from urbanization, industrialization, fossil fuel burning, and fires.
- Consequences: Rising ozone levels will worsen the impact on forest restoration and climate change mitigation.
- Findings: Ozone pollution has prevented 290 million tonnes of carbon capture annually since 2000.
- Call for Action: Greater environmental protection can reduce ground-level ozone, improve air quality, and enhance carbon uptake in forests, aiding climate change mitigation.
Ozone
- About: Ozone is a variant of oxygen composed of three oxygen atoms.
- Location: It occurs both in the Earth’s upper atmosphere and at ground level.
- Good or Bad Ozone: Ozone can be good or bad, depending on where it is found.
- Stratospheric Ozone: In the stratosphere, it forms a layer that protects us from the sun’s ultraviolet rays.
Ground Level Ozone
- Definition: Ground-level ozone is a colourless and highly irritating gas that forms near the Earth’s surface, typically within two miles above the ground.
- It is also known as surface-level ozone or tropospheric ozone.
- It is a secondary, short-lived pollutant.
- Formation Process: The formation involves Nitrogen Oxides (NOx), Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs), and carbon monoxide from sources like vehicles, power plants, and factories.
- Reaction Mechanism: Ground-level or tropospheric ozone is created by chemical reactions between NOx gases (oxides of nitrogen produced by combustion) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
- The combination of these chemicals in the presence of sunlight form ozone.
|
![]() 13 Sep 2024
13 Sep 2024
