Indian Leopard

|
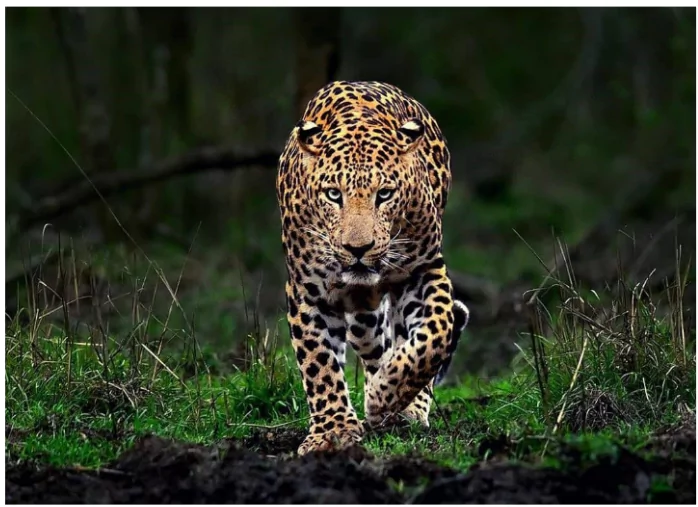
- The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) examines the conservation status of the Indian leopard and highlights several key details regarding its population patterns.
Key Highlights:
- Decline in Population: The IUCN assessment reports a nearly 24.5% decline in the Indian leopard (Panthera pardus fusca) population over the last three generations, primarily due to habitat loss, fragmentation, poaching, and human-leopard conflicts.
- Conservation Status: The Indian leopard is classified as Near Threatened on the IUCN Red List, indicating it is close to becoming endangered or vulnerable due to significant population declines.
- CITES: Appendix I
- Wildlife Protection Act 1972: Schedule I
Leopards:
- About: The leopard (Panthera pardus) is a large cat closely related to lions, tigers, and jaguars.
- Leopards vary significantly in size and markings, typically weighing between 50 and 90 kg and measuring about 210 cm in length, excluding the tail.
- Features: Leopards typically have a yellowish coat above and a white underside, adorned with rosettes of dark spots lacking central spots like those seen on jaguars.
- These solitary animals inhabit bush and forest environments, primarily active at night but occasionally visible during the day.
- Diet: Their diet encompasses a wide range of prey, from small rodents to antelopes, deer, and even dogs and baboons in Africa. Leopards are skilled climbers and often stash their kills in tree branches.
- Breeding Season: Leopard breeding is non-seasonal, with females giving birth to two to four cubs after a gestation period of approximately three months.
|
Forest Advisory Committee (FAC)
|
- The Forest Advisory Committee (FAC) of the Union Environment Ministry has reprimanded the Odisha government for building walls, without approval, in forest land
Forest Advisory Committee (FAC):
- About: The FAC (Forest Advisory Committee) is a statutory body led by the Director General of Forests at the Ministry of Environment, Forests, and Climate Change (MoEFCC).
- Mandate: Under the Forest Conservation Act of 1980, the Central government introduced the Forest Conservation (Amendment) Rules of 2004, wherein sections 3 and 4 outline the responsibilities of the FAC (Forest Advisory Committee).
- Referral: The Central Government refers every proposal that involves over 40 hectares of forest land, excluding those related to linear projects, along with site inspection reports, to the Forest Advisory Committee (FAC).
- Recommendation: FAC also has the authority to recommend conditions or restrictions on the utilization of forest land for non-forest purposes.
- Approval:After reviewing the FAC’s advice, the Central Government either approves the proposal with suitable mitigative measures or rejects it.
- Role: The role of FAC is purely advisory.
|
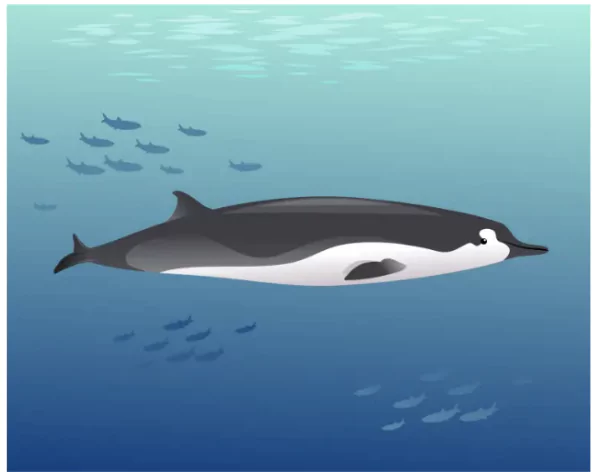
Spade Toothed Tale
|
- The discovery of a beaked whale on a beach in New Zealand provides a unique opportunity for scientists to study the elusive spade-toothed whale.
Spade-toothed whale:
- About: The spade-toothed whale (Mesoplodon traversii) is the least known and rarest species of whale.
- Discovery site: The species was initially identified from a partial jaw discovered on Pitt Island, New Zealand, in 1872. In 2010, two specimens were found stranded on Opape Beach, also in New Zealand.
- Specimens: The sole complete specimens known are a 5.3-meter adult female and her 3.5-meter male calf.
- The adult female had a spindle-shaped body with a dark grey or black dorsal side and a white underside, featuring a light thoracic patch, along with dark eye patches, rostrum, and flippers.
- Conservation Status: The spade-toothed whale is included in the Memorandum of Understanding for the Conservation of Cetaceans and Their Habitats in the Pacific Islands Region (Pacific Cetaceans MOU).
- Its conservation status on the IUCN Red List is categorized as “Data Deficient (DD)” due to limited information and uncertain data.
|
Bhojshala Complex

|
- The existing structure at the Bhojshala complex was constructed using remains of a temple that existed earlier at the site.
Bhojshala complex:
- About: Located in the Dhar district of Madhya Pradesh, this site was established in 1034 AD and was built by Raja Bhoj of the Parmar Dynasty (1000–1055 AD).
- Features: It served as a university where the statue of Vagdevi (Mata Saraswati) was installed.
- History: Bhojshala faced its first attack by Alauddin Khilji in 1305 AD. In 1514 AD, Mehmudshah Khilji II attempted to convert Bhojshala into a dargah.
- He encroached upon land outside the Saraswati Temple and constructed the ‘Kamal Moulana’ Makbara.
- ASI: In 1952, the Central Government transferred Bhojshala to the Archaeological Survey of India.
- Architecture: The complex features a spacious open courtyard surrounded by a verandah adorned with pillars. Located to the west of this verandah is a prayer hall.
- The intricately carved pillars and the beautifully adorned ceiling of the prayer hall were sourced from Bhojshala.
- Inscriptions at the complex:Two Prakrit hymns on the Karmavatar of Vishnu engraved in the rocks.
- Two Sarpabandha pillar inscriptions from the 11th-12th century, detailing Sanskrit grammar and alphabet.
- Two Sanskrit texts in Anustubha verse, one praising Raja Bhoj’s successors and the other crediting Udayaditya for installing the pillars.
|
One Scientist-One Product initiative.
|
- The Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) is preparing to introduce its ‘One Scientist-One Product‘ initiative.
One Scientist-One Product initiative:
- Aim: To promote advancements in agriculture and animal husbandry research.
- Launch of New Crop Varieties: This initiative will coincide with the introduction of 323 new varieties across 56 crops, encompassing cereals, oilseeds, forage crops, and sugarcane, during an event in Delhi commemorating ICAR’s 96th foundation day.
- Enhanced Crop Varieties: Out of these, 289 are developed to withstand climate challenges, while 27 are enhanced with additional nutrients.
- Development: According to the Director-General of ICAR, each of the organization’s 5,521 scientists will embark on developing a product, technology, model, concept, or significant publication.
- Scientists will outline their projects at the start of each year, with quarterly reviews conducted at the institute level and semi-annual reviews at headquarters.
|
Trade Deficit
|
- India’s June merchandise exports rose by 2.55% to $35.2 billion, while imports increased by 5% to $56.2 billion, widening the trade deficit by 9.4%.
Trade Deficit:
- About: A trade deficit occurs when a country’s imports exceed the value of its exports. It is a measure of international trade known as a negative balance of trade.
- Calculation: The deficit is calculated by subtracting the total value of a country‘s exports from the total value of its imports.
Factors Influencing Trade Deficits:
- Economic growth: A growing economy can lead to increased consumer spending on imports, contributing to a trade deficit.
- Government spending: Higher government expenditures can reduce national savings and potentially widen the trade deficit.
- Exchange rate fluctuations: Changes in currency strength affect the cost of imports and exports, influencing trade deficit levels.
- Production limitations: Some goods are cheaper or more efficiently produced abroad, necessitating imports despite domestic capabilities.
- Trade policies: Removing trade barriers, like tariffs, can alter trade patterns, impacting the balance of trade with various trading partners.
|
NaBFID
|
- The government wants to increase the capital base of the National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development, or NaBFID, to *1 trillion through support from banks
NaBFID
- About: Established in 2021 through an Act of Parliament known as The National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development Act, 2021, it operates as a specialised Development Finance Institution in India.
- Objectives: Its objectives include bridging gaps in long-term non-recourse finance for infrastructure development, enhancing the development of bond and derivatives markets in India, and fostering sustainable economic growth.
- Regulation: Regulated and supervised by the RBI, it operates as an All India Financial Institution (AIFI).
|
![]() 16 Jul 2024
16 Jul 2024