2,000-year-old Buddhist Site Found in Haryana
Context: Recently, IT Kanpur, using Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR), has discovered signs of ancient Buddhist stupas and structural remains in Haryana’s Yamuna Nagar district.
Key Highlights
- Evidence of a Buddhist Stupa: Technology: GPR revealed circular structures, old walls, and rooms 6–7 feet deep, suggesting a 2,000-year-old Buddhist site.
About Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR)
- A non-invasive geophysical method that uses radar pulses to image the subsurface. It’s like an X-ray for the ground, allowing scientists and engineers to “see” what’s buried beneath without digging.
|
- Sites of Discovery:
- Topra Kalan: Strong GPR signals indicated a buried semi-circular structure, likely a stupa, near an ancient temple.
- ‘Jarasandha ka Qila’: A mound here also showed signs of a circular structure, consistent with another stupa.
- Historical Significance:
- The site may date back to the Buddhist era or possibly the Mahabharata period, as per local oral traditions.
- These findings offer vital clues into ancient trade routes, religious networks, and cultural exchanges across the subcontinent.
- If similar structures are uncovered, it could point to a broader spread and influence of this ancient civilization.
Key Buddhist Sites
- Lumbini, Nepal: Recognized as Buddha’s birthplace, it is closely linked to Indian Buddhist sites.
- Bodh Gaya, Bihar: The site of Buddha’s enlightenment under the Bodhi tree.
- Mahabodhi Temple, Bodh Gaya: Site of Buddha’s enlightenment, a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 2002.
- Vaishali, Bihar: Where Buddha gave his final sermon and announced his Parinirvana.
- Rajgir and Nalanda, Bihar: Renowned centers of Buddhist learning and ancient monasteries.
- Sarnath, Uttar Pradesh: The location where Buddha delivered his first sermon.
- Kushinagar, Uttar Pradesh: The place of Buddha’s Mahaparinirvana (final passing away).
- Sanchi, Madhya Pradesh: Home to ancient stupas and Buddhist monuments, showcasing Buddhist architecture and heritage.
- McLeod Ganj, Dharamshala, Himachal Pradesh: Houses the Dalai Lama and the Tibetan Government-in-Exile, serving as a key Tibetan Buddhist hub.
- Ellora Caves, Maharashtra: A UNESCO World Heritage Site, showcasing rock-cut temples from Buddhist, Hindu, and Jain traditions.
- Ajanta Caves: Known for ancient Buddhist monasteries and murals depicting the life of Buddha.
Prithvi-II & Agni-I Ballistic Missiles
Context: Short-Range Ballistic Missiles Prithvi-II and Agni-I were successfully test-fired on July 17, 2025, from Chandipur, Odisha.
- The tests, conducted by the Strategic Forces Command, validated all operational and technical parameters.
- The tests mark a boost to India’s nuclear and air defence capabilities.
About Prithvi-II Ballistic Missile
- Type: Short-range, single-stage, liquid-fueled surface-to-surface ballistic missile.
- Developed By: Defence Research & Development Organization (DRDO) under the Integrated Guided Missile Development Program (IGMDP).
- Range: Approximately 250-350 km.
- Payload: Capable of carrying 500 kg to 1000 kg warheads, including both conventional and nuclear options.
- User: Primarily developed for the Indian Air Force, inducted into the Strategic Forces Command in 2003.
- Features: Designed with measures to deceive anti-ballistic missiles and has improved navigation.
About Agni-I Ballistic Missile
- Type: Short to medium-range, single-stage, solid-fueled ballistic missile.
- Developed By: DRDO, designed to fill the range gap between the Prithvi-II and longer-range Agni missiles, particularly after the Kargil War.
- Range: 700-1200 km, capable of reaching up to 1200 km with lighter payloads.
- Payload: Can carry a 1000 kg payload, including conventional and nuclear warheads.
- Mobility: Road and rail mobile, offering greater survivability.
- User: Used by the Strategic Forces Command of the Indian Army.
- Future: An upgraded two-stage variant, Agni-1P, is being developed with enhanced accuracy and reliability, potentially replacing older Agni-1 and Agni-2 missiles.
Tawke Oilfield, Iraq
Context: Recent drone strikes in Iraq’s Kurdistan region have disrupted oil output, with the Tawke oilfield (operated by Norway’s DNO) hit on 17th July 2025.
About Tawke Oilfield
- Location: An onshore operation situated in the Zakho Administration area of Duhok Province, within the Kurdistan Region of northern Iraq.
- The Kurdistan Region refers to areas inhabited by ethnic Kurds, primarily in Iraq, Iran, Syria, and Turkey.
- Operated by: The Norwegian oil and gas company DNO.
- Strategic Importance: A significant oil production site.
- The Tawke Oilfield produced an average of 78,615 barrels of oil per day in 2024.
Iraq
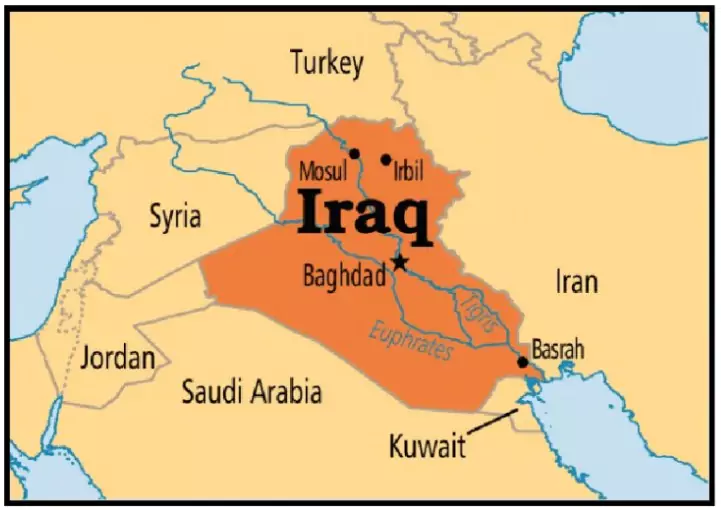
- Location: Iraq is located in Western Asia
- Borders: Iraq shares borders with several countries:
- Turkey to the north
- Iran to the east
- The Persian Gulf and Kuwait to the southeast
- Saudi Arabia to the south
- Jordan to the southwest
- Syria to the west
Three-person in vitro fertilization (IVF) Technique
Context: In a remarkable breakthrough, scientists in the UK used a three-person in vitro fertilization (IVF) technique to bring to life eight children and spared them from genetic mitochondrial disease.
About Three-person in vitro fertilization (IVF) or Mitochondrial Replacement Therapy (MRT)
- Refers: A technique to prevent mothers from passing on severe mitochondrial diseases to their children.
- Purpose: Prevents inherited mitochondrial diseases, which affect organs like the brain and heart and are passed exclusively by the mother.
- Genetic Composition: Despite being termed a “three-parent” baby, over 99.9% of the DNA is inherited from the biological parents.
How Does It Work?
- Maternal Spindle Transfer (MST): The nucleus (parent’s main DNA) from the mother’s unfertilized egg is transferred into a donor’s healthy, enucleated (nucleus-removed) egg.
- This reconstructed egg is then fertilized by the father’s sperm and implanted.
- Pronuclear Transfer (PNT): Both the mother’s and donor’s eggs are fertilized by the father’s sperm.
- The pronuclei (early nuclei) from the parents’ fertilized egg are transferred into the donor’s enucleated fertilized egg.
- This new embryo is then implanted.
Key Considerations
- Minimal Donor DNA: The donor contributes only a tiny fraction of DNA from the mitochondria, not influencing traits like appearance.
- Germline Modification: It’s considered germline modification because the mitochondrial DNA is inheritable, especially by female offspring.
- Regulation: Highly regulated and legal in a few countries (e.g., UK since 2015).
- Three-person IVF is not explicitly legal or regulated in India.
- While the Assisted Reproductive Technology (Regulation) Act, 2021 exists, no specific law permits MRT for clinical use, keeping it in a regulatory grey area—unlike countries like the UK, where it is formally allowed.
- Success: As of July 2025, eight healthy babies have reportedly been born in the UK using this method, free of mitochondrial disease.
About Mitochondrial Diseases
- Mitochondria are often called the “powerhouses” of cells because they generate energy. If the mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) is mutated, it can lead to a range of severe and often fatal conditions affecting organs with high energy demands, such as the brain, muscles, heart, and liver.
- These diseases are exclusively inherited from the mother.
- Common examples include MELAS (Mitochondrial Encephalomyopathy, Lactic Acidosis, and Stroke-like episodes), MERRF (Myoclonic Epilepsy with Ragged Red Fibers), LHON (Leber Hereditary Optic Neuropathy), and Leigh syndrome.
|
Central Adoption Resource Authority (CARA)
Context: The Central Adoption Resource Authority (CARA) has issued comprehensive directions to strengthen and institutionalise structured counselling services throughout the adoption process.
Key Aspects of the New Directives
- Mandatory Counselling: Counselling is now a critical and mandatory component at pre-adoption, during adoption, and post-adoption stages.
- Qualified Counsellors: State adoption boards must designate or empanel qualified professionals (child psychology, mental health, social work backgrounds) at district and state levels.
- Stakeholder Support: Aims to reinforce psychosocial support for prospective adoptive parents, adopted children (especially older ones), and biological parents.
- Specific Situations: Post-adoption counselling is required for root searches, non-adjustment issues, or potential adoption disruptions.
- Legal Backing: Directions are issued under the Juvenile Justice Act, 2015 (amended 2021) and Adoption Regulations, 2022.
About CARA
- Institutional Identity: CARA is India’s apex statutory body for adoption, under the Ministry of Women & Child Development.
- Status: Established in 1990 as autonomous; gained statutory status via JJ Act 2015.
- Role: The nodal body that monitors and regulates both in-country and inter-country adoptions of orphan, abandoned, and surrendered children.
- International Role: Designated Central Authority for inter-country adoptions under the Hague Convention (1993).
- Framework: Operates under the JJ Act 2015, and is linked to Child Care Institutions (CCIs).
OECD-FAO Agricultural Outlook 2025-2034
Context: Recently, the Agricultural Outlook 2025-2034 was released by a joint report from the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) and the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO).
- It provides a comprehensive assessment of the ten-year prospects for agricultural commodities (including fish) and their markets at national, regional, and global levels.
Key Global Trends (by 2034)
- Cereal Use Shift: Only 40% for direct human consumption; 27% for biofuel/industrial (up from 23%), and 33% for animal feed.
- Biofuel Boom: 0.9% annual growth, led by India, Brazil, Indonesia, heavily relying on food-based feedstocks.
- Production Growth: 1.1% annually (mostly yield gains). India and Southeast Asia will drive 39% of cereal consumption growth.
- Animal Products: Rising demand, particularly in middle-income nations, leading to increased meat/dairy production (17%) and 6% rise in agricultural greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.
- Cotton: India set to overtake China as top producer.
India’s Agri-Marketing Challenges & Solutions
- Challenges:
- Weak Infrastructure: ₹92,000 crore in post-harvest losses due to inadequate cold storage/transport.
- Fragmented Markets: No national integrated market; Agricultural Produce Market Committees (APMCs) regulated by states.
- Agricultural marketing is a State subject, regulated by State-specific APMC Acts, under which APMCs are established.
- Limited Access: Small farmers struggle with market access and low prices.
- Government Steps:
- National Agriculture Market (e-NAM): Online platform for price transparency and wider reach.
- 10,000 Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs) Scheme: Strengthens market linkages for small farmers.
- Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF): Provides financial aid and interest subvention to support post-harvest infrastructure like warehouses and cold chains.
- Agricultural Marketing Infrastructure (AMI): Focuses on enhancing rural storage capacity through godown/warehouse construction.
Senegal
Context: Recently, France formally handed back its last military bases in Senegal, leaving Paris with no permanent camps in either West or Central Africa.
- The French withdrawal comes as the Sahel region faces a growing jihadist conflict across Mali, Burkina Faso and Niger that is threatening Gulf of Guinea nations to the south.
About Senegal
- Capital: Dakar
- Form of Government: Presidential Republic.
- Location: Westernmost part of Africa, bordering Mauritania, Mali, Guinea, and Guinea-Bissau.
- Located in the Northern and Western hemispheres of the Earth.
- It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the west.
- Geography: Dominated by the Sahara desert, with the Senegal River as a major drainage system.
- Climate: Dry, hot, and windy, with desertification being a concern.
- Historical Context: Gained independence in 1960 from France.
![]() 18 Jul 2025
18 Jul 2025


