Bureau of Port Security (BoPS)
Context: The Union Government has approved the establishment of a statutory Bureau of Port Security to strengthen India’s maritime security architecture.
About Bureau of Port Security (BoPS)
- BoPS is a newly constituted statutory body, modelled on the Bureau of Civil Aviation Security, to regulate and coordinate port security in India.
- Nodal Ministry: The BoPS functions under the Ministry of Ports, Shipping and Waterways (MoPSW).
- Objective: To create a robust, risk-based, and future-ready port security framework ensuring compliance with international maritime security standards.
- Structure of BoPS
-
- The BoPS is established under Section 13 of the Merchant Shipping Act, 2025, giving it statutory authority.
- It will be headed by a Director General of IPS rank to ensure strong regulatory enforcement.
- During the initial one-year transition period, the Director General (DG) of Shipping will hold additional charge as DG for BoPS.
Role of Bureau of Port Security
- Regulatory Functions: Including mandatory security assessments, audits, and approval of port security plans.
- Custodian of Security Information: It will manage the collection, analysis, and exchange of security-related information, with special focus on cybersecurity and protection of port’s IT infrastructure.
- Security Training: It will oversee the training, certification, and regulation of Private Security Agencies.
- Central Industrial Security Force (CISF) is designated as a Recognised Security Organisation for port facilities.
Significance
- The creation of BoPS institutionalises port security governance, enhances protection of critical maritime infrastructure, and strengthens India’s overall maritime and trade security framework.
WHO South-East Asia Regional Office
Context: Prime Minister Narendra Modi and the WHO Director-General inaugurated the new WHO South-East Asia Regional Office complex in New Delhi during the second WHO Global Summit on Traditional Medicine
- A WHO technical report on training in Yoga and the book “From Roots to Global Reach: 11 Years of Transformation in Ayush” were also released.
About WHO South-East Asia Regional Office
- The WHO South-East Asia Regional Office in New Delhi serves as the regional headquarters coordinating public health initiatives across South-East Asian countries.
- Objective: To strengthen regional health cooperation and support equitable, evidence-based, and sustainable health systems.
- Significance
- The new complex also houses the WHO India Country Office, deepening India’s institutional partnership with the World Health Organisation.
- The facility enhances India’s role as a hub for regional and global health diplomacy, policy coordination, and capacity building.
Community-Based Disaster Risk Reduction
Context: The Union Government has approved a nationwide project to strengthen community-based disaster risk reduction through model Gram Panchayats.
About the National Project for Strengthening Community-Based Disaster Risk Reduction
- The National Project for Strengthening Community-Based Disaster Risk Reduction Initiatives aims to embed disaster resilience within Panchayati Raj Institutions at the grassroots level.
- Objective: To integrate disaster risk reduction into local governance through a bottom-up, community-driven approach.
- Nodal Bodies: Ministry of Panchayati Raj (MoPR) and National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA)
Budget Outlay: ₹507.37 crore.
- Key Components
-
- Development of cluster-based Model Gram Panchayats in 20 States to demonstrate long-term, hazard-specific disaster mitigation strategies.
- Institutional strengthening and policy integration of disaster risk reduction into Panchayat planning, including Gram Panchayat Development Plans (GPDPs).
- Capacity building and awareness generation for State Disaster Management Authorities (SDMAs), District Disaster Management Authorities (DDMAs), elected representatives, Panchayat functionaries, and community volunteers.
- Use of digital platforms such as eGramSwaraj and Gram Manchitra for disaster planning, expenditure tracking, and real-time information dissemination.
Significance
- The project addresses multi-hazard disaster risks by creating replicable and scalable models of disaster-resilient Gram Panchayats.
- It aligns with the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction (2015–2030) by prioritising prevention, preparedness, and local-level resilience.
- It strengthens grassroots governance and community ownership, safeguarding rural lives, livelihoods, and infrastructure against disasters.
Bharat Taxi
Context: The Government has launched Bharat Taxi, India’s first cooperative, driver-owned ride-hailing service, starting operations in Delhi from January 1.
About Bharat Taxi
- Bharat Taxi is a cooperative-based mobility platform designed as an alternative to app-based cab aggregators, prioritising drivers and passengers.
- Objective: To provide affordable, transparent, and fair ride-hailing services while improving driver earnings and working conditions.
- Nodal Body: The service is managed by Sahakar Taxi Cooperative Limited, under the broader vision of the Ministry of Cooperation.
- Working Model: Bharat Taxi operates on a zero-commission, driver-owned cooperative model, where drivers collectively own, govern, and benefit from the platform.
- Driver-Centric Provisions: Drivers receive up to 80 per cent of the fare directly, improving income stability.
- Payments are managed through a monthly credit system, ensuring transparency and financial security.
Key Features
- Transparent and predictable fares, aimed at avoiding surge pricing and excessive peak-hour charges.
- Multi-modal options, including cars, auto-rickshaws, and two-wheelers through a single mobile application.
- Digital accessibility, with a multilingual app available on Android and iOS, enabling easy booking and real-time vehicle tracking.
- Safety-first design, featuring verified driver onboarding, integration with Delhi Police, and ride-sharing options with trusted contacts.
Significance
- Bharat Taxi strengthens cooperative entrepreneurship, ensures fair mobility services, and promotes inclusive, people-centric urban transport solutions.
India’s 1st Deep Brain Stimulation Workshop For Parkinsons
Context: Recently, the All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS), New Delhi, hosted India’s first advanced workshop on Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS).
- This landmark event focused on building national capacity to manage Parkinson’s disease and other movement disorders using cutting-edge device-assisted therapies.
About Deep-Brain Stimulation (DBS)
- Refers: A neurosurgical procedure where electrodes are implanted into specific brain regions to deliver targeted electrical impulses.
- Mechanism: Electrodes are connected to a pacemaker-like device (Implantable Pulse Generator) placed under the skin of the chest.
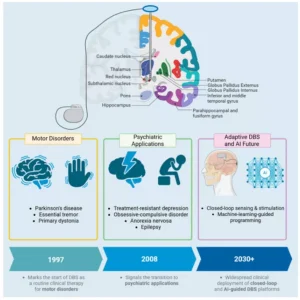 It works by modulating abnormal neural circuits and correcting neurochemical imbalances that cause motor and psychiatric symptoms.
It works by modulating abnormal neural circuits and correcting neurochemical imbalances that cause motor and psychiatric symptoms.
- Applications: Primarily used for Parkinson’s, Essential Tremor, and Dystonia.
- It is also FDA-approved for Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD).
- 2025 Milestone: In February 2025, the FDA approved Adaptive DBS (aDBS). Unlike traditional systems, this closed-loop system automatically adjusts stimulation in real-time based on the patient’s own brain signals (e.g., Medtronic’s BrainSense technology).
- Key Advantages: Reversible, non-destructive, and highly flexible through wireless programming.
- Limitations: It remains an invasive procedure with surgical risks and high costs; it is a symptom-management tool rather than a cure.
About Parkinson’s Disease
First described as “Shaking Palsy” by James Parkinson in 1817, this is a chronic, progressive neurodegenerative disorder that primarily affects movement, due to the gradual loss of dopamine-producing neurons in a specific area of the brain called the substantia nigra.
- Pathology: It results from the degeneration of dopamine-producing neurons in the substantia nigra.
- Dopamine is the neurotransmitter vital for smooth, coordinated muscle movement.
- Causes: Factors include genetic mutations, aging, and environmental toxins (pesticides, heavy metals).
- Demographics: Men are more frequently affected than women.
- Symptom Management: Initially treated with drugs (Levodopa), but DBS becomes critical when medications lead to “motor fluctuations” or narrowed therapeutic windows.
![]() 20 Dec 2025
20 Dec 2025

 It works by modulating abnormal neural circuits and correcting neurochemical imbalances that cause motor and psychiatric symptoms.
It works by modulating abnormal neural circuits and correcting neurochemical imbalances that cause motor and psychiatric symptoms.