Hayflick Limit
|
Context: Biomedical researcher Leonard Hayflick, who discovered that normal somatic cells can divide (and thus reproduce) only a certain number of times, died
About Hayflick Limit:
- Discovery: In the early 1960s, Hayflick discovered that cell division in somatic (non-reproductive) cells stopped after roughly 40-60 times.
- Reason for Aging: This cessation in cell division is what Hayflick posited causes aging — as senescent cells (those that have stopped dividing) accumulate, one’s body begins to age and decline.
- In Built Clock: This means that there is an in-built cellular clock in the human body (and that of other organisms) which determines how long one can live.
- Maximum Limit: This “ultimate Hayflick limit”, as scientists have termed it, is around 125 years for humans
- Beyond this no amount of diet, exercise, or even genetic tweaking against diseases can extend the human lifespan
- Various animals Limits: Hayflick’s discovery has been applied to cells from various animals, revealing different Hayflick limits based on species’ lifespans.
- Example: Galapagos turtles have cells that can divide approximately 110 times, whereas laboratory mice have a much lower limit of around 15 divisions.
- Significance of the Discovery: Hayflick’s discovery fundamentally changed the understanding of aging — especially the thesis that cells are capable of being immortal
- Ageing is simply a factor of externalities such as disease, diet, and solar radiation.
About Telomeres:
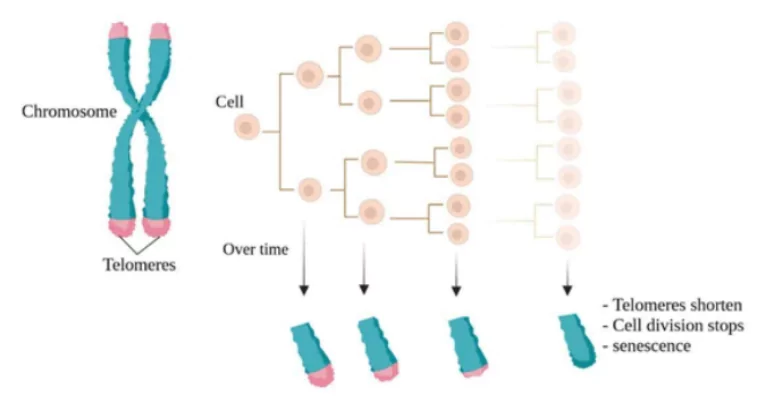
- Discovery: In the 1970s, researchers discovered telomeres, which are repetitive Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) sequences at the end of chromosomes that protect them during cell division.
- Eventually, the telomere loss reaches a critical point at which cell division ends.
- Ageing: While shortening telomeres is related to aging, the exact relationship between telomere length and lifespan remains unclear.
- For Example: Lab mice have telomeres that are five times longer than humans, but their lives are 40 times shorter.
- Critics: This is what has led to some researchers arguing that telomere loss and the Hayflick limit are not limits on aging, but rather symptoms of ageing
|
Nipun Munition
|
Recently, Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has handed over the Authority Holding Sealed Particulars (AHSP) of ‘Nipun’ munition to Directorate General of Quality Assurance (DGQA)
About Nipun:
- Location: At Armament Research & Development Establishment (ARDE), Pashan, Pune
- Development: NIPUN is a Soft Target Munition designed and developed by the ARDE in association with High Energy Materials Research Laboratory (HEMRL), Pune.
- Nipun is known for being highly user-friendly and deadly effective against enemy targets.
|
India’s GI-tagged agro-product Figs

|
The Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (APEDA) facilitated the first export of India’s ready-to-drink fig juice, made from GI-tagged Purandar Figs, to Poland.
About Purandar figs:
- Purandar figs are known for their unique tastes and textures.
- It has high pulp content and a rich source of vitamins & minerals. Moreover, it has an excellent sweet taste, an attractive violet colour.
- Reason: The Specialties are attributed to the climatic factors, red-black soil & Salt-free well irrigation technique followed in the Region.
|
Arogya Maitri Disaster Management Cube

|
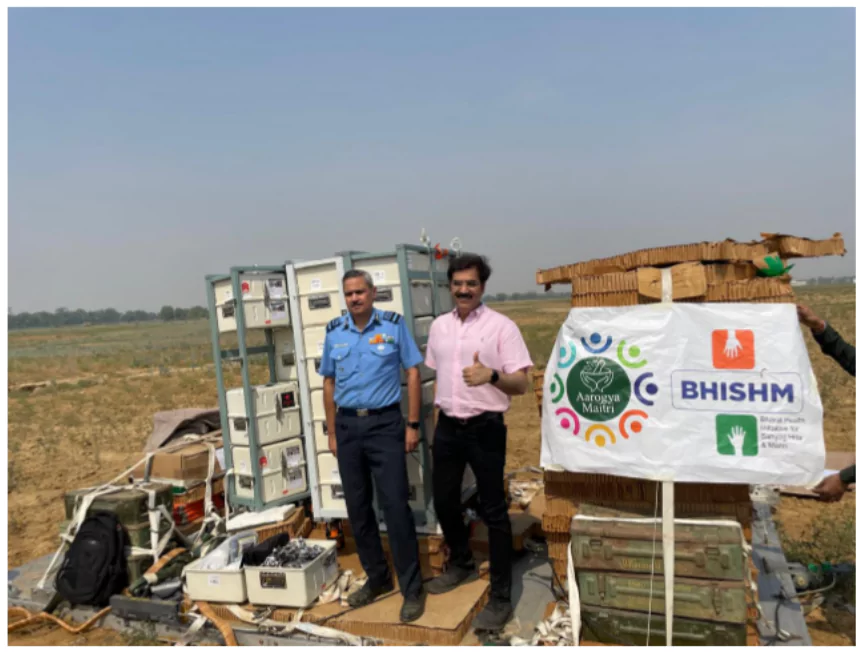
Recently, the Indian Air Force (IAF) successfully conducted trials of airdropping its Arogya Maitri Disaster Management Cube in Agra.
About Arogya Maitri Disaster Management Cube
- This cube is a part of the broader initiative named “Project BHISHM” – Bharat Health Initiative for Sahyog, Hita and Maitri,
- It is tailored to treat up to 200 casualties, emphasizing rapid response and comprehensive care.
- Features: The Aid Cube is equipped with several innovative tools designed to enhance disaster response and medical support during emergencies.
- Advanced Technology: It integrates Artificial Intelligence (AI) and data analytics to facilitate effective coordination, real-time monitoring, and efficient management of medical services in the field.
- Beneficial for Emergency: These cubes are robust, waterproof, and light, designed for various configurations, making them ideal for diverse emergency scenarios.
- Rapid Deployment: From airdrops to ground transportation, the cube can be rapidly deployed anywhere, ensuring immediate response capability.
- Aid Cube stands out with its ability to be deployed within an astonishing 12 minutes.
- Advanced medical equipment: RFID-tagged for efficient repacking and redeployment
- The state-of-the-art BHISHM software system integrated into a provided tablet allows operators to locate items quickly, monitor their usage and expiry, and ensure readiness for subsequent deployments.
|
Waterspout

|
Recently, there was a human casualty after a luxury yacht sank was hit by a violent storm off the coast of Sicily, Italy. Experts suggest the storm could have been a waterspout
About Waterspout:
- A waterspout is a large column of air and mist rotating over a water body.
- It is a weaker cousin of tornadoes and typically lasts for around five minutes — occasionally it can last up to 10 minutes.
- The average waterspout can be around 165 feet in diameter, with wind speeds of 100 kilometres per hour.
- On the other hand, the largest tornado path widths can exceed one mile. The usual diameter of a tornado is between 50 and 1,000 m (average ~ 100 m)
- Reason for Formation: Although waterspouts are more common in tropical waters, they can appear anywhere.
- They occur when there are high levels of humidity and relatively warm water temperatures compared to the overlying air.
- Types of waterspouts: There are two types of waterspouts: tornadic waterspouts and fair-weather waterspouts.
- Tornadic waterspouts: They are actual tornadoes that form over water or move from land to water.
- They are associated with severe thunderstorms, and are often accompanied by high winds and seas, large hail, and frequent dangerous lightning
- Fair-weather waterspouts: These are much more common, form over only water.
- As their name suggests, they are formed during fair weather. They are less dangerous and usually small.
- Frequency Increasing: as ocean temperatures are soaring, the frequency of waterspouts is increasing.
- Currently, the sea surface in the region of Sicily is about 2.5 to 3 degrees Celsius warmer than the 1990-2020 average
|
![]() 21 Aug 2024
21 Aug 2024