National Crisis Management Committee
Context: National Crisis Management Committee (NCMC) meets to review preparedness for the impending Cyclone Dana in Bay of Bengal.
About NCMC
- It was constituted under the National Disaster Management Act, 2005, which was a clear reflection of the philosophy of India toward an organised and efficient framework of disaster management.
- Aim: To lessen impacts, coordinate responses, and ensure quick recovery from disasters with a well-structured and integrated approach.
- The NCMC operates at the national level and works alongside the Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS) to make high-level decisions on disaster management.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Role of NCMC
- The NCMC plays a pivotal role in managing natural disasters by assessing preparedness measures, coordinating relief efforts, and providing logistical and financial support to state governments.
- It ensures that all necessary preventive and precautionary steps are taken to reduce damage and minimise the loss of life.
Composition
The NCMC is chaired by the Cabinet Secretary and includes Secretaries from various Ministries, Departments, and agencies responsible for specific disaster management functions
Galathea Bay Port
Context: A quarter century after Kamarajar Port was named the country’s 12th major port, the mega international container transshipment port (ICTP) at Galathea Bay, in the Great Nicobar island in the Bay of Bengal, has been notified as the 13th major port.
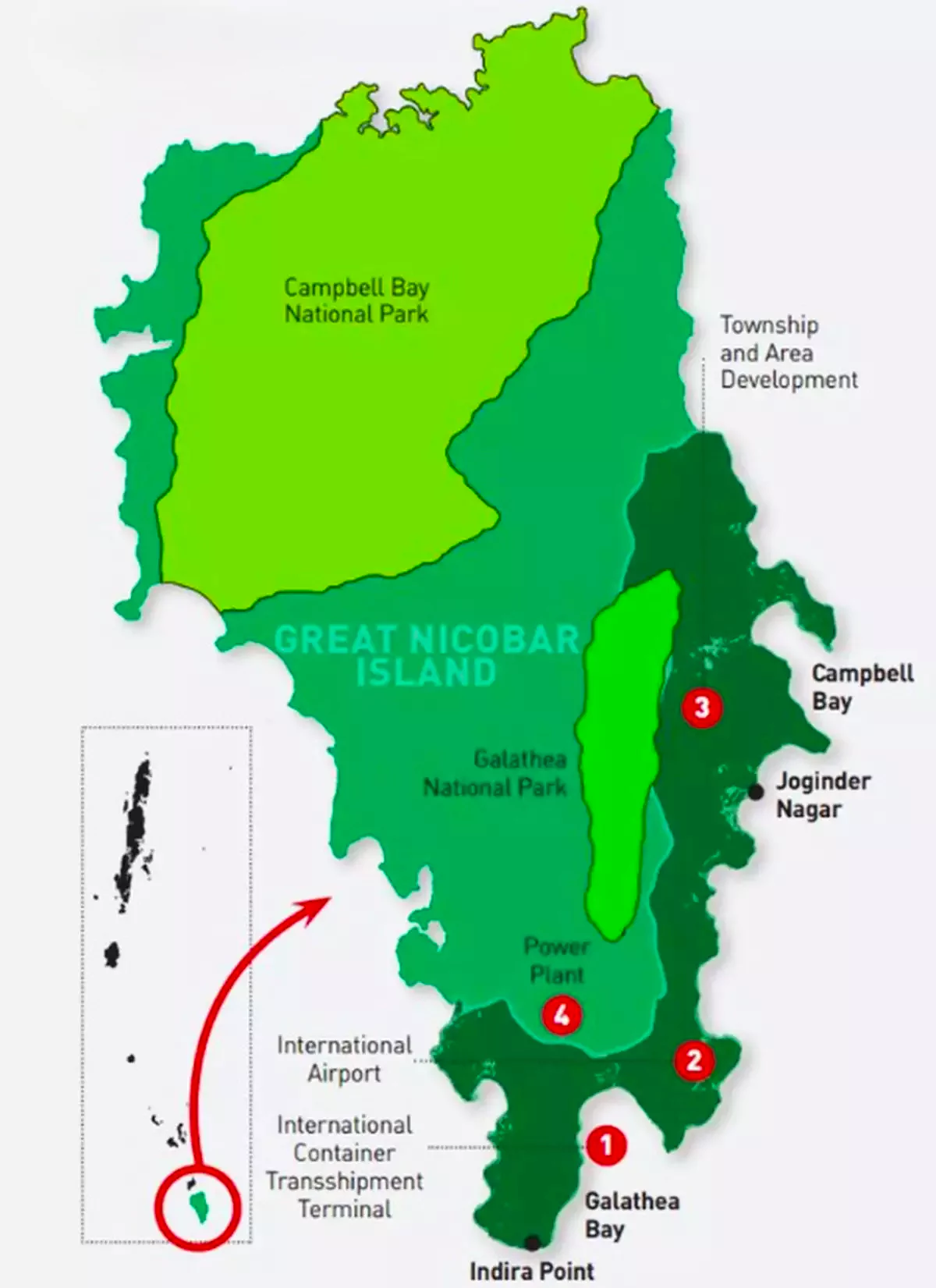
About Galathea Bay International Container Transshipment Port (ICTP) Project
- Location: Great Nicobar Island, Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- Purpose: Development of a mega International Container Transshipment Port (ICTP).
- Status: Notified as India’s 13th major port.
- Model: Public-Private Partnership (PPP) with central funding eligibility.
- Cost: Estimated at ₹41,000 crore (Phase 1: ₹18,000 crore).
- Capacity: The first phase will have a handling capacity of 4 million TEUs (twenty-foot equivalent units) by 2028.
- Final Phase: Handling capacity of 16 million TEUs by 2058.
Strategic Significance
- Proximity to International Trade Routes:
- Located 40 nautical miles from the Malacca Strait, which caters to about 35% of annual global sea trade.
- Positioned on the East-West international trade route, near major transshipment hubs like Singapore, Klang, and Colombo.
- Geopolitical Relevance:
- A key project in the Indo-Pacific geopolitical region.
- Aims to capture transshipment cargo from Indian ports on the east coast, Bangladesh, and Myanmar, reducing reliance on overseas ports.
- Natural Advantages:
- Deep Water: Natural draught of 20m, enabling it to handle large container ships.
- Transshipment Hub: Will save Indian ports $200-220 million annually by reducing transshipment charges currently paid to overseas ports (e.g., Colombo, Singapore).
European Sky Shield Initiative
Context: Recently, Switzerland has signed up to the European Sky Shield Initiative (ESSI).
About European Sky Shield Initiative (ESSI):
- Objective: A unified air and missile defence system across Europe.
- Initiator: Spearheaded by Germany after Russia’s invasion of Ukraine in August 2022.
- Purpose:
- Enable European countries to buy defence systems together, train together, and coordinate procurement projects, especially in the area of ground-based air defence.
- Focus on medium-range air defence but with future potential for short and long-range air defence cooperation.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Switzerland and Austria Joining ESSI
- Switzerland:
- Signed: Joined in October 2024.
- Neutrality Concerns: Controversial domestically due to Switzerland’s tradition of neutrality.
- Austria:
- Signed: Joined ESSI in July 2024.
- Benefits: Austria will be protected against short and medium-range missiles by 2024 with full airspace coverage by 2025.
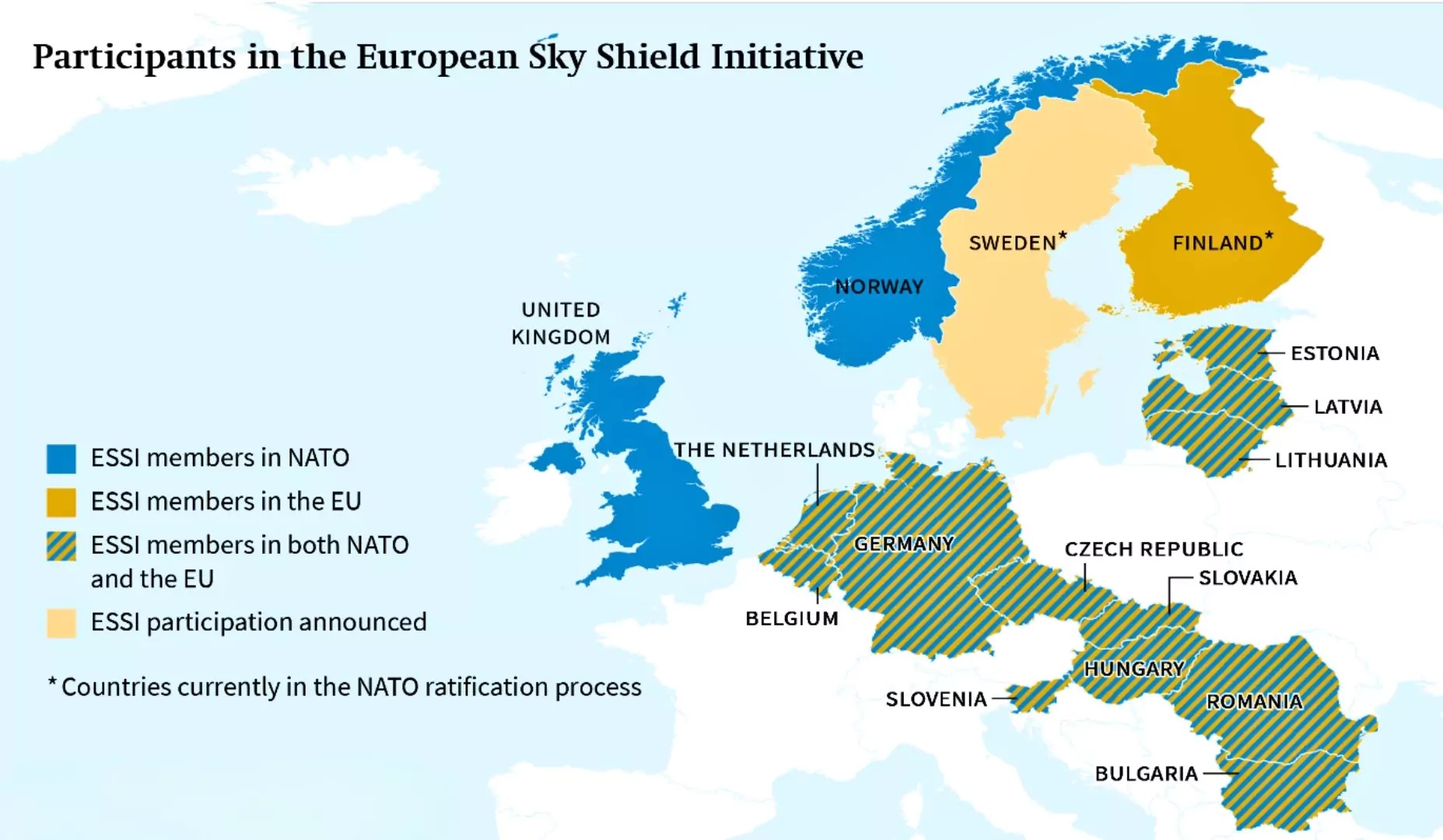
ESSI Member Countries
- Initial Members (October 2022):
- 14 NATO members: Belgium, Bulgaria, Czech Republic, Estonia, Germany, Hungary, Latvia, Lithuania, Netherlands, Norway, Slovakia, Slovenia, Romania, and the UK.
- Finland (Nordic country).
- Current Members (October 2024): 22 members,
- Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Latvia, Lithuania, Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Sweden, Switzerland, Turkey and the United Kingdom.
Yars intercontinental ballistic missiles
Context: Recently, Russia is testing the combat readiness of a unit equipped with Yars intercontinental ballistic missiles in a region northwest of Moscow.
About Yars missiles
- Russian-made mobile nuclear intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) that can be mounted on truck carriers or deployed in silos.
- Estimated to be 22.5 meters in length and 2 meters in diameter.
- Three-stage, solid propellant.
- Total launch weight: 49,000 kg.
- Minimum range of 2,000 km and a maximum range of 10,500 km.
- Warhead Capability:
- Multiple Independently Targetable Reentry Vehicles (MIRVs)
- Can carry up to 10 thermonuclear warheads, each with a yield of 300 kilotons
- Guidance System: Inertial and GLONASS (Russian satellite navigation system)
- Launch Platforms: Can be deployed in silos or mounted on mobile truck carriers
- Defensive Capabilities:
- Can manoeuvre during flight
- Equipped with active and passive decoys, making it more resistant to modern missile defense systems.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
About Ballistic missiles
- Ballistic missiles are weapons that use projectile motion to deliver warheads to a target.
- They are powered by rockets for a short time, and then follow an unpowered, arched trajectory to reach their target.
![]() 22 Oct 2024
22 Oct 2024

