Why is Iraq Sinking into Earth?
Context: A team of researchers has found a sinking oceanic “slab” below the Earth’s surface is pulling the northern region of Iraq down with it.
Key Findings
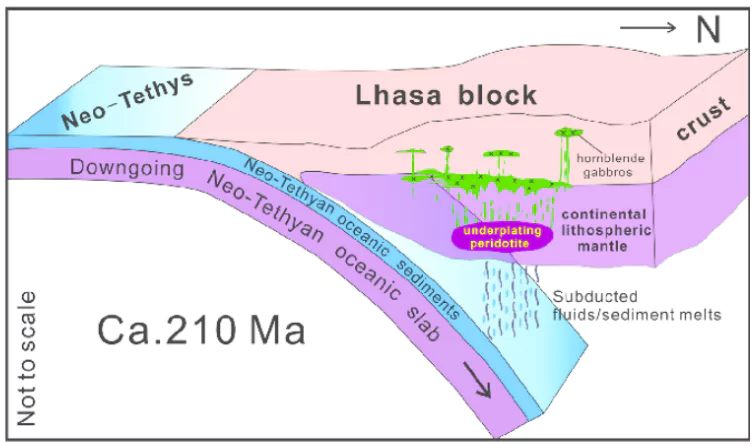
- The northern region of Iraq, particularly around the Zagros Mountains, is slowly sinking due to tectonic activity.
- The Zagros Mountains lie in modern-day Iran and Iraq.
- A sinking oceanic slab (Neotethys oceanic slab) beneath the Earth’s surface is pulling this region down.
Cause of the Sinking
- A sinking oceanic slab (Neotethys oceanic slab) beneath the Earth’s surface is pulling the northern region of Iraq down.
- The slab is part of the ancient Neotethys Ocean floor, which existed over 66 million years ago.
- The slab is splitting and sinking into the Earth’s mantle, a process that takes tens of millions of years.
- Geological Process:
- The sinking is due to plate tectonics.
- The Arabian and Eurasian continental plates are colliding, causing the oceanic slab to tear and sink.
- This process is extremely slow and occurs over millions of years, beyond human time scales.
Implications of the Research
- Earthquake Prediction: Understanding the geological configuration and rock geometry helps in predicting where and how strong earthquakes might occur.
- This is crucial for regions like Turkey, Syria, and Iraq, which are prone to earthquakes (e.g., the 2023 earthquakes in Turkey and Syria).
- Geothermal Energy: The research helps estimate the depth of the geothermal gradient, which can be used for electricity production.
- Geological Models: The findings contribute to more accurate geological models of the Earth’s interior, aiding in understanding tectonic activities.
UNESCO Heritage Status for 12 Forts of Shivaji
Context: Maharashtra Minister for Cultural Affairs and Information Technology led delegation left for Paris to get UNESCO World Heritage status for Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj’s forts developed between the 17th and 19th centuries.
- The proposal is submitted under the concept of “Maratha Military Landscape of India”.
Forts Included in the Proposal
- Maharashtra: Lohagad, Salher, Raigad, Rajgad, Pratapgad, Shivneri, Suvarnadurg, Vijaydurg, Sindhudurg, Panhala, Khanderi.
- Tamil Nadu: Gingee Fort.
Objective of the Proposal: To bring global recognition to Maharashtra’s cultural heritage.
About UNESCO World Heritage Status
- It is a designation given to cultural and natural sites that are considered to be of outstanding value to humanity.
- The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) manages the World Heritage List.
- UNESCO World Heritage Convention (1972):
- Adopted by UNESCO to protect cultural and natural heritage of outstanding universal value (OUV).
- Aims to preserve heritage for future generations and promote international cooperation.
- About World Heritage Site:
- A landmark or area with legal protection under the UNESCO Convention.
- Must have cultural, historical, scientific, or natural significance.
- Considered to be of Outstanding Universal Value (OUV), transcending national boundaries.
- Selection Criteria:
- Masterpiece of human creative genius.
- Important interchange of human values in architecture, technology, arts, or design.
- Unique testimony to a living or lost cultural tradition/civilization.
- Outstanding example of a building/architectural ensemble illustrating key historical stages.
- Exceptional traditional settlement or land-use representing a culture or human-environment interaction.
- Tangible link to significant events, traditions, beliefs, or works of universal value.
- Superlative natural phenomena or exceptional natural beauty.
- Key examples of earth’s history, geological processes, or landforms.
- Significant ecological/biological processes in ecosystem evolution.
- Vital habitats for conserving biodiversity, including threatened species.
- India’s World Heritage Sites:
- 43 Sites (as of Feb 2025): 35 Cultural Sites, 7 Natural Sites, 1 Mixed Site.
Tea Horse Road
Context: Recently, China’s Ambassador to India, Xu Feihong, highlighted The Tea Horse Road historical significance.
What Was the Tea Horse Road?
- It was not a single road but a network of routes spanning over 2,000 km.
- The road connected southwest China to India, Nepal, and Bangladesh through Tibet.
- The main pathways passed through Yunnan province cities like Dali and Lijiang, reaching Lhasa before branching into the Indian subcontinent.
- Though not as famous as the Silk Road, it played a key role in trade and cultural exchange.
Historical Background
- Tang Dynasty Origins: The Tea Horse Road dates back to the Tang dynasty (618-907 CE).
- Buddhist monk Yijing mentioned products like sugar, textiles, and rice noodles being transported from China to Tibet and India.
- Song Dynasty Trade: By the Song dynasty (960-1279 CE), the trade mainly focused on tea and horses, though other goods were also traded.
Importance of the Tea Horse Road
- Cultural and Commercial Pathway: The route facilitated the exchange of goods, culture, and technology between China, Tibet, and India.
- Tea Trade: Tea from China was transported to Tibet and then to Kolkata, from where it was sold in Europe and Asia.
- Demand for Tea: Tibetan nomads highly valued tea as a beverage, making it an essential trade item.
- Military Resources: Horses were vital for transportation and military purposes, and China imported them from Tibet and Yunnan.
Srisailam Left Bank Canal (SLBC) Tunnel
Context: A portion of the roof of the Srisailam Left Bank Canal (SLBC) tunnel has collapsed trapping eight people inside it.
- Rescue Efforts: The country’s top nine agencies are coordinating a rescue effort, these are,
- Indian Army, Indian Navy, National Disaster Response Force (NDRF), State Disaster Response Force (SDRF), Hyderabad Disaster Response and Asset Protection Agency (HYDRAA), National Hydrological Investigation agency, Singareni Collieries etc
About Srisailam Left Bank Canal (SLBC) tunnel
- The tunnel is being touted as the world’s longest irrigation tunnel.
- Start: An agreement to build the SLBC tunnel was made in 2005 during the regime of late Y.S. Rajashekar Reddy.
- Location: The tunnel is being constructed on the left bank of the Srisailam Reservoir in Telangana and runs through the Nallamala Hills in the Nagarkurnool district.
- The tunnel is 400 metres below the Amrabad Tiger Reserve.
- Purpose: The tunnel would draw 30 tmc ft of water to irrigate four-lakh acres in the drought-prone areas of Nalgonda and Khammam district in telangana.
- Features:
- Tunnel Length: It stretches for 44 kms from Srisailam to Devarakonda.
- Lining: 360 degrees of the tunnel is lined with prefabricated cement blocks to prevent collapse, seepage.
- Technology: The tunnel is built using Tunnel Boring Machines (TBMs).
Black Plastic
Context: A study conducted on Black Plastics made products has highlighted its adverse effects on human health.
- Published In: The study was published in the journal Chemosphere
- Conducted by: Team of scientists from Toxic Free Future and Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam
- Analysis: It analysed 203 black plastic household products sold in the United States including kitchen utensils, takeaway containers, and toys.
- Finding:
-
- The study found high levels of cancer-causing, hormone-disrupting flame retardant chemicals in a variety of household products made with black plastics
- BDE-209: The study found the presence of a flame-retardant chemical called decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209) in the products.
- It was phased out in the US more than a decade ago
- Safe limit: The estimated safe exposure limit of BDE-209 from black spoons and spatulas is found to be less than a tenth of the EPA’s recommended limit
- Leaching: The flame-retardant is toxic which could be leaching into food at hazardous levels and is linked to potential human health risks
About Black Plastic
- It is often made from recycled electronic waste such as computers, TVs, and appliances.
- Usage: The chemical-laced plastics from electronics are melted down and mixed with food grade plastics to create items like,
- children’s toys, single-use utensils and coffee stirrers, hot cup lids, cooking implements, insulated mugs, jewelry, garden hoses, and holiday decorations etc.
- Pigment: The black color is created by adding a substance called carbon black to the plastic.
- Recycling : Black plastic makes up 15% of all plastic recyclables (largely single-use food containers)
- Harmful Effects:
- Carcinogenic: Carbon black contains polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) which is classified as, possibly carcinogenic to humans by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC).
- Toxic Elements: The recycled e-waste contains toxic chemicals such as phthalates, flame retardants, and heavy metals such as cadmium, lead, nickel, chromium, and mercury which can leach into food.
- Developmental Disorders: Even at very low levels, serious reproductive and developmental problems with disruption in kidneys, human thyroid function causing long-term neurological damage.
12th Regional 3R and Circular Economy Forum in Asia
Context: India is set to host the 12th Regional 3R (Reduce, Reuse, Recycle)and Circular Economy Forum on 3- 4 th March 2025 in Asia and the Pacific at Rajasthan International Centre, Jaipur.
Key Highlights of the Forum
- The 12th Forum is being led by:
- Swachh Bharat Mission – Urban, Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs
- Japan’s Ministry of Environment
- UN ESCAP, UNCRD, UNDSDG, UNDESA
- Government of Rajasthan
- Theme: Realizing Circular Societies Towards Achieving SDGs and Carbon Neutrality in Asia-Pacific.
- Objective: To strengthen policy discussions, collaborations, and knowledge exchange.
- It will accelerate progress towards Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and a circular economy.
Background of the Forum
- Launched by : United Nations Centre for Regional Development (UNCRD) in 2009,
- The Forum supports governments in integrating 3R principles into policies.
- The last Forum (2023) was hosted by Cambodia.
- India previously hosted the 8th Forum in 2018 (Indore).
UN resolution on Ukraine War
Context: The draft resolution “Advancing a comprehensive, just and lasting peace in Ukraine” tabled by Ukraine and its European allies in the 193-member UN General Assembly for voting.
- The resolution comes on the third anniversary of the Russia-Ukraine conflict
About the Resolution
- Objective: The resolution called for a “de-escalation, an early cessation of hostilities and a peaceful resolution” of the war against Ukraine in line with the Charter of the United Nations and international law
- Voting: The Resolution was passed with,
- In Favour: 93 countries, including major European countries like Germany, UK, France and the G7 (minus the US) voted in favour
- Against: 18 countries including Russia, US, Israel and Hungary voted against
- Abstained: 65 countries including India, China and Brazil, abstained.
About US Shift of Stance
- The US had voted against the resolution along with Russia for the first time in the last three years of the Russia-Ukraine war.
- The Donald Trump Effect: The move signals a shift in the US policy on the topic marking a major departure from its position signalling a break from Europe.
- The USA has tabled a brief rival resolution ie,
- “The path to peace,” mourning the tragic loss of life throughout the “Russian Federation-Ukraine” conflict.
- Adoption: The resolution was adopted with 93 votes in favour, 8 against and 73 abstentions.
- The USA however abstained.
V.O.Chidambaranar Port
Context: The VOC Port Authority is exploring the possibility of setting up a shipbuilding facility in Thoothukudi.
About VOC Port
- Former Name: V.O. Chidambaranar Port was formerly known as Tuticorin Port.
- Location: It is situated on the southeastern coast of India, along the Gulf of Mannar.
- Strategic Importance: The port is positioned near the East-West International sea routes, making it a vital hub for maritime trade.
- Port Classification: It is a major port in India.
- Type of Port: V.O. Chidambaranar Port is an artificial port.
- Natural Advantages: The port is well-sheltered from storms and cyclonic winds, ensuring smooth and uninterrupted operations.
- Operational Capacity: It is a deep-water, all-weather port that functions round the clock, 365 days a year.
![]() 25 Feb 2025
25 Feb 2025

