Al-Fashir (Sudan)
Context: UN agencies warn, thousands of children in al-Fashir, Sudan, face imminent risk of death as malnutrition rates soar amid a 16-month-long siege.
- Over 250,000 civilians, approximately half children, are cut off from food and healthcare in al-Fashir during ongoing civil conflict.
About Al-Fashir
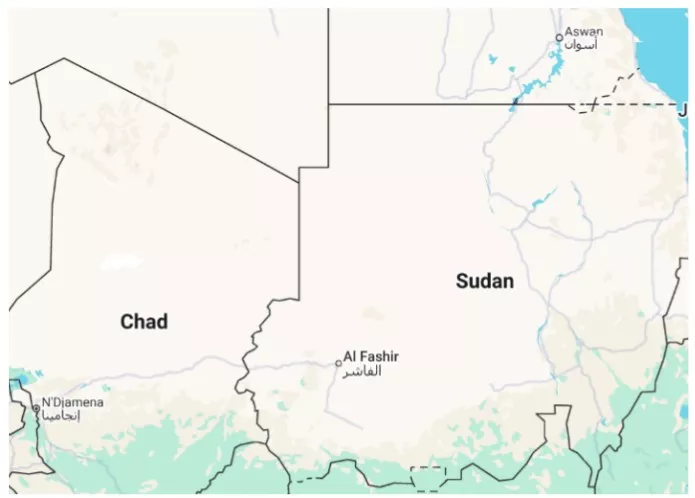
- Location: Al-Fashir is the capital of North Darfur in western Sudan, currently besieged by conflict between the Sudanese army and the paramilitary Rapid Support Forces.
- Issue: The city is the army’s last holdout in Darfur, facing collapsed health facilities and a severe humanitarian crisis.
- Over 30 million people in Sudan, including 15 million children, require urgent aid, while only 25% of the $4.2 billion UN Sudan Humanitarian Response Plan has been funded.
Carabid Beetles As Potential Bioindicators
Context: A new study highlights carabid ground beetles (family Carabidae) as promising bioindicators to detect microplastic pollution in soil.
About Carabid Beetle
- They are commonly known as ground beetles due to their habitat and behavior.
- They are found in a wide variety of habitats, including forests, grasslands, agricultural fields, wetlands, and even urban areas.
- They are known for their long legs and powerful mandibles which enable them to be voracious predators.
- Reproduction in carabids is typically sexual, with internal fertilization.
- Ecological Role: They are important for the biological control of insect pests on farms
Why Beetles as Bioindicators?
- Insects are abundant, sensitive to environmental changes, and quick responders to pollution.
- They provide early warnings of ecosystem degradation and are easy to sample across regions.
- Their short life cycles and adaptability make them ideal for long-term monitoring.
Bioindicators
- They are living organisms that, by their presence or absence, help scientists monitor the health and quality of an ecosystem.
- They are highly sensitive to environmental changes like pollution, temperature, or other disturbances.
- Examples include lichens for air quality, earthworms for soil health, and mayflies or stoneflies for water quality.
Mahe
Context: The Indian Navy commissioned INS Mahe, a new naval vessel, strengthening India’s maritime capabilities and coastal security infrastructure.
About INS Mahe
- It is a survey vessel designed for hydrographic surveys and oceanographic data collection.
- It is the first of eight Anti-Submarine Warfare Shallow Water Crafts (ASW SWC).
- 78-metre-long warship is the largest Indian Naval warship propelled by a diesel engine-waterjet combination
- Built by: It was built by Cochin Shipyard Limited (CSL) Kochi
- Naming: Named after Mahe, a coastal town in Puducherry (formerly a French colony), reflecting India’s maritime heritage.
- The warship named INS Mahe has been designed and constructed as per the Classification Rules of Det Norske Veritas (DNV).
- DNV: They are a set of technical standards that govern the design, construction, and maintenance of ships and offshore structures to ensure safety, reliability, and environmental compliance.
- Significance: Enhances the Indian Navy’s survey capabilities, crucial for maintaining navigational safety, supporting naval operations, and contributing to India’s Blue Economy initiatives.
Features & Capabilities
- Capacity: It has a displacement of around 1,100 tons
- Conducts hydrographic surveys for safe navigation. Collects oceanographic and meteorological data. Assists in coastal and offshore surveys
- Equipped with torpedoes, anti-submarine rockets, and advanced sonar/radar systems.
- Designed for Anti-Submarine Warfare (ASW), coastal surveillance, mine-laying, and Low Intensity Maritime Operations (LIMO).
Cyclone Montha
Context: The India Meteorological Department (IMD) has warned that a deep depression over the southeast Bay of Bengal will intensify into Cyclone Montha by October 27, bringing heavy rainfall across Andhra Pradesh, Odisha, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Telangana, and Chhattisgarh.
About Cyclone Montha
- Formation: The system originated as a low-pressure area over the southeast Bay of Bengal and is moving northwestwards.
- Expected Intensity: Likely to become a Severe Cyclonic Storm, with potential landfall on Andhra Pradesh’s coast.
- Wind Speed: Estimated 90–100 km/h, with gusts reaching 110 km/h.
- Name Origin: The cyclone is named ‘Montha’ by Myanmar, following the World Meteorological Organization / Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (WMO/ESCAP) rotational naming system.
Rashtriya Vigyan Puraskar (RVP)
Context: Recently, the Government of India has announced the second edition of the Rashtriya Vigyan Puraskar (RVP), honouring 24 individual scientists and one team for excellence in science and technology across four categories, recognising lifetime, recent, young, and team achievements.
2025-Rashtriya Vigyan Puraskar
- Vigyan Ratna: Pro. Jayant Vishnu Narlikar (Physics) – Posthumously
- Vigyan Team: Team- Aroma Mission CSIR (Agricultural Sciences).
About Rashtriya Vigyan Puraskar (RVP)
- Launch & Aim: Instituted in 2023 to unify and elevate existing science awards into a Padma-like national honour for scientific excellence.
- Awarding Authority: Conferred by the Ministry of Science & Technology, under oversight of the Office of the Principal Scientific Adviser (PSA).
- Categories:
- Vigyan Ratna: Lifetime achievement in science and technology.
- Vigyan Shri: Recent distinguished scientific contributions.
- Vigyan Yuva – Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar (SSB): For scientists below 45 years.
- Vigyan Team: For collaborative technological innovation or research.
- Cap on Awards: Maximum 56 awards per year.
- Features: No cash component, aligning with the Padma awards’ spirit of prestige over monetary reward.
- Selection Process: Recommendations made by the Rashtriya Vigyan Puraskar Committee, chaired by the Principle Scientific Advisor, including secretaries of scientific departments and academy members.
- Background: Created after a 2022 review found numerous departmental awards (like SSB Prizes) and recommended consolidation into a national-level honour with higher stature.
About National Science Awards in India
- Purpose: Recognise contributions in scientific research, innovation, and societal impact.
- Predecessor: The Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Prizes, instituted in 1958, previously India’s premier science awards.
- Shift to RVP: Aimed at streamlining recognition, enhancing visibility, and ensuring interdisciplinary parity.
- Significance: Strengthens India’s scientific culture, motivates young researchers, and aligns with the vision of “Viksit Bharat 2047.”
Green Cess
Context: To mark 25 years of statehood, the Uttarakhand government has announced a ‘Green Cess’ on vehicles entering from outside the state to tackle rising pollution and fund air quality improvement, green infrastructure, and smart traffic management initiatives.
About Green Cess
- A fiscal environmental measure levied to discourage pollution-causing activity while funding green projects.
- Key Focus Areas:
- Reduction of vehicular emissions through cleaner fuels and EV adoption.
- Control of road dust through modern cleaning mechanisms.
- Expansion of urban green cover and air quality monitoring networks.
- Vision: it will support India’s goals under the National Clean Air Programme (NCAP) and contribute to the “Lifestyle for Environment (LiFE)” mission.
Burevestnik Cruise Missile
Context: Recently, Russia successfully tested its nuclear-powered 9M730 Burevestnik cruise missile.
About the Burevestnik Missile
- Official Designation: 9M730 Burevestnik (“Storm Petrel”); NATO codename SSC-X-9 Skyfall.
- Weapon Type: Nuclear-powered, nuclear-capable cruise missile, capable of extremely long-range flight using a compact onboard nuclear reactor.
- Range & Capability: Claimed to possess “virtually unlimited range” and an unpredictable flight path, enabling it to evade detection and interception.
About Nuclear-Powered Cruise Missiles
- Technology Principle: It uses a small nuclear reactor to generate sustained propulsion, allowing ultra-long endurance flights at low altitudes.
- Purpose: To bypass ballistic-missile defences through erratic routing and near-unlimited range.
- Risks:
- Radiation hazards in case of crashes or failed launches.
- Environmental contamination risk from reactor debris.
- Arms-control complications — not clearly covered by existing treaties.
- Comparative Status: No other country currently possesses an operational nuclear-powered cruise missile.
- India’s nuclear deterrence rests on conventionally propelled, nuclear-capable missiles and nuclear-powered submarines, with no evidence of a nuclear-powered cruise missile programme.
- Global Nuclear Landscape:
- Russia: 5,459 warheads
- U.S.: 5,177 warheads (Federation of American Scientists, 2025)
- Together: ~87% of the world’s nuclear stockpile.
MAHA-MedTch Mission
Context: Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF), in collaboration with the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) and the Gates Foundation, has launched the Mission for Advancement in High-Impact Areas (MAHA)-Medical Technology.
About MAHA-MedTch Mission
- Aim: To accelerate innovation in India’s medical technology sector, reduce reliance on high-cost imports, and promote equitable access to affordable and high-quality medical technologies.
- Key objectives:
- Drive public health impact by supporting technologies that address priority disease areas and expand access to safe, high-quality care;
- Ensure affordability and accessibility by supporting solutions that reduce costs; and
- Enhance self-reliance and competitiveness by catalyzing indigenous MedTech development, manufacturing, and industry–academia collaboration.
- Scope: The scheme will cover a broad spectrum of innovative medical devices and in-vitro diagnostics, including advanced diagnostic imaging, minimally invasive technologies, point of care molecular diagnostics, AI/ML-enabled platforms, robotics and other emerging areas.
- Funding: It will provide funding support to a wide range of entities including Academic and R&D institutions, Hospitals, Startups, MSMEs, MedTech industry and collaborations between entities.
- With milestone-linked funding of ₹5–25 crore per project (and up to ₹50 crore in exceptional cases).
- Additional features: It will provide enabling support through national initiatives such as Patent Mitra (IP protection and technology transfer), MedTech Mitra (regulatory guidance and clearances), a Clinical Trial Network (for clinical validation and evidence generation), as well as mentorship from industry experts.
![]() 27 Oct 2025
27 Oct 2025


