Golan Heights
|
- Recently, Hezbollah rocket strikes Israel-controlled Golan Heights
Golan Heights:
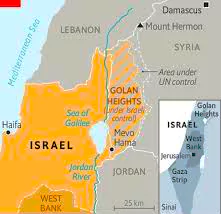
- About: The Golan Heights is a rocky plateau covering 1,800 km², situated on the border between Israel and southwestern Syria.
- Geography: It is bordered by the Jordan River and the Sea of Galilee to the west, Mount Hermon to the north, the seasonal Wadi Al-Ruqqād River to the east, and the Yarmūk River to the south.
- History: Israel captured the Golan Heights from Syria during the final stages of the 1967 Six-Day War. Most Syrian Arab residents fled during the conflict.
- An armistice line was established, placing the region under Israeli military control, and Israel began settling the area almost immediately.
- Syria attempted to recapture the Golan Heights during the 1973 Middle East war, but despite causing significant losses to Israeli forces, the attempt was unsuccessful. Both countries signed an armistice in 1974, and a UN observer force has monitored the ceasefire line since then.
- In 1981, Israel unilaterally annexed the Golan Heights.
- Strategic Importance: From the Golan Hills, the Syrian capital, Damascus, is clearly visible. Rainwater in this region flows into the Jordan River, which supplies water to arid areas and is believed to provide one-third of Israel’s water.
- Additionally, the land in the Golan Heights is highly fertile, making it excellent for farming.
|
Lithium Deposits
|
- Lithium deposits found in Karnataka’s Mandya and Yadgiri districts
Lithium:
- About: It is a soft, silvery-white non-ferrous metal, essential in rechargeable batteries for mobile phones, laptops, digital cameras, and electric vehicles. Additionally, it is used in some non-rechargeable batteries for devices such as heart pacemakers, toys, and clocks.
- Lithium Reserves in India : The Salal Haimna block in the Reasi region of Jammu and Kashmir contains the first known lithium discovery in India, which was put up for auction. Lithium and rare earth elements (REEs) from the Katghora block in Chhattisgarh are also up for auction.
Estimated Reserves
- Lithium Reserve: J&K and Chhattisgarh’s chunks of lithium reserves are being auctioned out for a CL.
- J&K Block: This block has an estimated resource of 5.9 million metric tonnes (mt) of bauxite column, which includes more than 70,000 tonnes of titanium metal and 3,400 tonnes of lithium metal.
- Chhattisgarh Block: Although drilling to determine total reserves has not yet been done, the block contains lithium and REEs.
- Reserves of nickel ore can be discovered in Gujarat, Odisha, and Bihar.
- Odisha Block: 3,908 tonnes of nickel metal content, or 2.05 million tonnes of nickel ore, is the inferred value.
- Blocks of Gujarat and Bihar: No drilling has been done.
- The only block with copper reserves is the Odisha block.
|
Asian Disaster Preparedness Centre
|
- India has recently assumed the Chair of the Asian Disaster Preparedness Centre (ADPC) for 2024-25.
Asian Disaster Preparedness Centre:
- About: Founded in 1986, it is an autonomous international organisation focused on cooperation and implementation of disaster risk reduction and climate resilience in the Asia-Pacific region.
- Vision: “Safer communities and sustainable development through disaster risk reduction,” covering the Asia-Pacific region.
- Member Countries: Founding members are India, Bangladesh, Cambodia, China, Nepal, Pakistan, the Philippines, Sri Lanka, and Thailand.
- Governance: According to the ADPC Charter, the organisation is governed by several bodies: the Board of Trustees, the Executive Committee, the Advisory Council, and the Regional Consultative Committee (RCC).
- These are the main governing and advisory entities of ADPC. The international Charter of ADPC, signed by nine founding member countries, came into effect in 2018 after ratification by all founding members.
- As of January 2020, ADPC functions as an autonomous international organisation overseen by the Board of Trustees.
- Headquarters: Bangkok, Thailand
|
Cultural Property Agreement
|
- India and the United States of America have signed their first-ever ‘Cultural Property Agreement.’
Cultural Property Agreement
- Aim: To prevent and control the illicit trafficking of antiquities from India to the USA. The CPA limits the importation of specific Indian archaeological and ethnological materials into the United States.
- It will facilitate the prompt seizure of Indian antiquities at US Customs and their return to India.
- Significance: Enhances cultural diplomacy, promotes tourism, and enriches education, among other benefits.
Efforts to Prevent Antiquities Smuggling
- Global Level: Article 9 of the 1970 UNESCO Convention aims to prohibit and prevent the illicit import, export, and transfer of ownership of cultural property.
- Additionally, the Kashi Culture Pathway, an Outcome Document of the G20 Culture Working Group, supports the creation of a robust global coalition to strengthen the fight against illicit trafficking.
National Level:
- Section 3 of the Antiquities and Art Treasure Act, 1972, prohibits the export of antiquities from India. When an antiquity is located abroad, the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) handles coordination with the foreign country and oversees the recovery process. Since 1976, the ASI has successfully retrieved 357 antiquities from other countries.
|
Critical mineral blocks
|
- The government has scrapped the auction of three critical mineral blocks, including a lithium mine in Jammu and Kashmir
Critical Minerals:
- About: Critical minerals are essential for economic development and national security. A shortage or concentrated extraction and processing in a few locations can create vulnerabilities in the supply chain and potentially disrupt supplies.
- Declaration of Critical Minerals: The declaration of critical minerals is a dynamic process that can change with advances in technology, market shifts, and geopolitical factors.
- Each country may have its own list of critical minerals, tailored to its specific circumstances and priorities.
|
Ariel’s Surface
|
- NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope discovered evidence of a subsurface ocean on Uranus’s moon Ariel, which accounts for the presence of frozen CO2 on its surface.
Key Findings:
- Findings :The presence of carbon monoxide on Ariel suggests either lower surface temperatures or a subsurface ocean generating carbon oxides.
- Implications: Cracks and grooves on Ariel’s surface may indicate the eruption of icy materials and carbon compounds.
- Additionally, signs of carbonate minerals point to water-rock interactions, potentially identifying Ariel as another moon with water.
About the Uranus Mission:
- Launch: Scheduled for 2031/32 aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy.
- Journey: Will include a gravity assist from Jupiter, arriving around 2044/45.
- Objectives: To investigate Uranus’ interior, with an orbiter studying its atmosphere, magnetosphere, and moons.
- Scientific Interest: To explore five large moons for insights into ocean worlds.
About Uranus:
- Position: The seventh planet from the Sun, discovered by William Herschel in 1781.
- Classification: A gas giant with an unusual axial tilt of 98°, leading to extreme seasonal changes.
Physical Characteristics:
- Size & Mass: Diameter of approximately 50,724 km; third-largest by diameter and fourth-largest by mass.
- Composition: Predominantly hydrogen and helium, with methane contributing to its blue-green color.
- Atmosphere: Features cloud bands, high-speed winds, and temperatures as low as -224°C.
Unique Features:
- Tilted Axis: Rolls along its orbit due to its extreme axial tilt.
- Rings: 13 faint rings were discovered in 1977.
- Moons: 27 moons, including Titania, Oberon, Ariel, and Miranda.
|
South Africa’s new law on climate change
|
- In October 2023, South Africa enacted a significant climate change law.
Climate Change Act:
- Objectives of the Climate Change Act: To reduce greenhouse gas emissions in South Africa, where coal is the main energy source.
- As one of the largest carbon dioxide producers, the country has struggled to meet its pollution reduction targets.
- Legal Framework and Responsibilities:For the first time, South Africa has enshrined its response to climate change into domestic law.
- All states and cities are required to assess climate change risks and develop strategies to address them.
- Additionally, emissions targets will be established for key sectors such as agriculture, transportation, and industry.
- Ministers responsible for these sectors will be required to implement measures to achieve these targets.
|
21st Khaan Quest exercise
|
- Recently, the Indian Army contingent has left for Exercise KHAAN QUEST.
Exercise KHAAN QUEST
- About: This exercise is a multinational military event, in Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia.
- Initially a bilateral exercise between the USA and Mongolian Armed Forces in 2003, it expanded into a Multinational Peacekeeping Exercise in 2006.
- The current edition is the 21st iteration of the exercise.
- Purpose: To unite military forces from around the world to collaborate and improve their peacekeeping abilities.
- Participants: The contingent comprises 40 personnel, primarily from a Battalion of the MADRAS REGIMENT, with additional members from other Arms and Services, including one woman officer and two women soldiers.
- Aim: To prepare the Indian Armed Forces for peacekeeping missions in a multinational setting.
- To enhance interoperability and military readiness for peace support operations under Chapter VII of the United Nations Charter.
- Activities: The exercise will include practising tactical drills like setting up static and mobile checkpoints and conducting cordon and search operations.
- It aims to improve interoperability, promote camaraderie, and strengthen relationships among soldiers from the participating countries.
|
![]() 29 Jul 2024
29 Jul 2024