Exercise Trishul
Context: Pakistan has issued a Notice to Air Missions (NOTAM) restricting airspace ahead of Exercise Trishul (Oct 30–Nov 10, 2025) — India’s major tri-service drill along the Sir Creek–Pakistan border.
About Exercise Trishul
- Nature: A tri-combat exercise involving the Army, Navy, and Air Force, aimed at testing integrated warfare and interoperability.
- Duration and Location: Scheduled for 10 days in the Sir Creek region of Gujarat and adjoining Rajasthan desert sectors.
- Objectives: To validate joint operational capabilities, promote Atmanirbharta (self-reliance), and enhance innovation within the armed forces.
- Scope: Encompasses land, air, and maritime operations, including amphibious drills, desert manoeuvres, and multi-domain warfare (cyber, electronic, and intelligence-based).
- Sub-Exercises: Includes Exercise Trinetra (Army – anti-UAV and electromagnetic warfare) and Exercise Mahagujraj (Air Force – air dominance and refuelling missions).
Loktak Lake
Context: Recently, a Nagaland University study warns that land-use change and farm expansion are degrading Loktak Lake’s water quality and threatening its biodiversity.
Key Findings of the Study
- Primary Cause: Changes in land use — agriculture, human settlements, and shifting (Jhum) cultivation — are directly deteriorating the water quality of rivers feeding the lake.
- Sampling and Analysis: Field research covered nine major rivers — Khuga, Nambul, Imphal, Kongba, Iril, Thoubal, Heirok, Sekmai, and Western — using Land Use Land Cover (LULC) mapping and water quality indicators.
- Water Quality Results: Observed high biological oxygen demand (BOD), low dissolved oxygen (DO), and increased sediment levels, indicating declining aquatic health.
- Pollution Sources: Rising agricultural runoff, domestic waste, and urban encroachment are accelerating nutrient pollution and siltation.
- Impact: The lake is witnessing reduced fish populations, loss of biodiversity, and livelihood challenges for local communities.
- Recommendations: The study calls for community-based land management, control of agricultural runoff, and waste discharge regulations to restore ecological balance.
About Loktak Lake
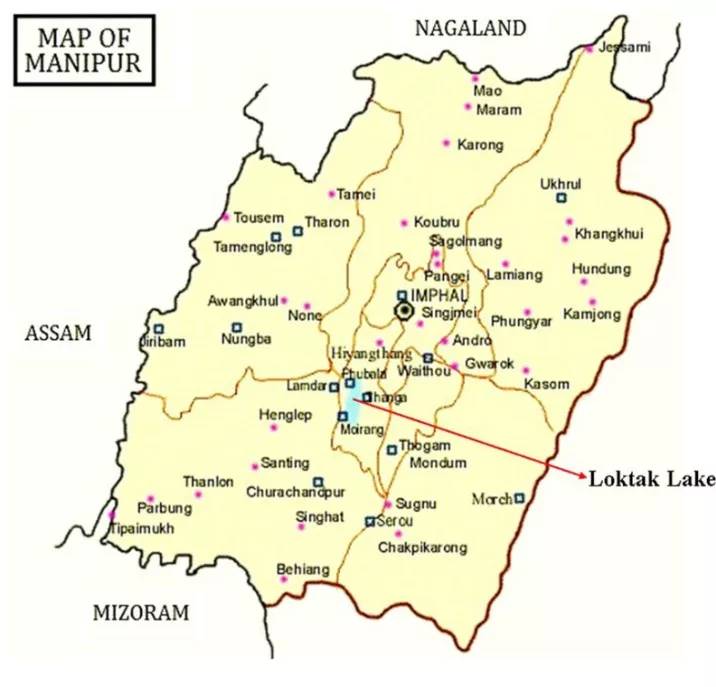
- Location: Situated in Manipur, Loktak is India’s largest freshwater lake and a designated Ramsar Site of international importance.
- Biodiversity: Home to 132 plant species and 428 animal species, including the endangered Sangai deer in Keibul Lamjao National Park.
- Keibul Lamjao National Park: Located on Loktak Lake, it is the world’s only floating national park, celebrated for its circular floating swamps known locally as phumdis.
- Economic Role: Supports fisheries, hydropower, transport, and tourism, forming the ecological and economic lifeline of the region.
- Environmental Status: Listed under the Montreux Record as a wetland facing serious ecological degradation from pollution and land-use change.
- Conservation Need: Urgent wetland management and catchment protection are essential to preserve Loktak’s ecological balance and biodiversity.
Koyla Shakti
Context: The Ministry of Coal is set to launch “Koyla Shakti” under the SHAKTI Policy (Scheme for Harnessing and Allocating Koyala Transparently in India), ensuring transparency and efficiency across the coal ecosystem.
About Koyla Shakti
- It is a Smart Coal Analytics Dashboard that will serve as a unified platform for real-time monitoring and analysis of coal sector operations.
- Objective: Provide a single-window digital platform for all coal-related transactions and monitoring.
- Integration: Combines systems of Coal India Limited (CIL), Singareni Collieries Company Limited (SCCL), and the Ministry of Coal for coordinated operations.
- Features: Real-time tracking of coal linkages, auctions, dispatch, and quality data through digital dashboards.
- Policy Linkage: Supports the revised SHAKTI Policy (2025) for transparent, market-based coal allocation.
- Benefits: Promotes transparency, improves supply efficiency, reduces import dependence, and strengthens Atmanirbhar Bharat in the coal sector.
Hurricane Melissa
Context: Recently, Hurricane Melissa, Jamaica’s strongest-ever storm, made landfall as a Category 5 hurricane with winds of 185 mph (≈295 km/h).
About Hurricane Melissa
- Formation: Originated over the central Caribbean Sea, rapidly intensified due to high sea-surface temperatures.
- Landfall: Struck Westmoreland County in southwestern Jamaica, causing 4 m storm surges, flooding, and nationwide power outages.
- Impact: Severe damage to infrastructure, agriculture, and tourism; over half a million people displaced.
- Current Path: Moving northwest toward eastern Cuba (Santiago de Cuba region) with ongoing evacuations.
- Climate Link: Rapid intensification attributed to warming oceans and climate change-induced variability in tropical cyclones.
Hurricane Categories (Saffir-Simpson Scale)
- Category 1 (Minimal Damage): Wind Speed: 74-95 mph; Impact: Minor damage to homes, trees, and coastal flooding.
- Category 2 (Extensive Damage): Wind Speed: 96-110 mph; Impact: Significant damage to buildings, trees, and power outages lasting days to weeks.
- Category 3 (Devastating Damage): Wind Speed: 111-129 mph; Impact: Major structural damage, widespread tree uprooting, power outages for weeks.
- Category 4 (Catastrophic Damage): Wind Speed: 130-156 mph; Impact: Extensive home destruction, power outages for months, roads blocked by fallen trees.
- Category 5 (Catastrophic Damage): Wind Speed: 157 mph+; Impact: Complete destruction of homes, total power loss, widespread isolation for weeks.
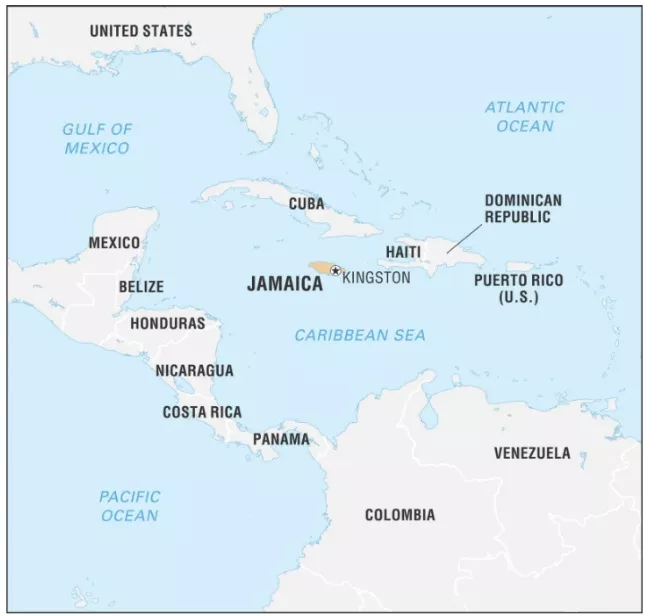
About Jamaica
- Location: Island nation in the Caribbean Sea, part of the Greater Antilles; lies south of Cuba and west of Haiti.
- Capital: Kingston.
 Geography: Predominantly mountainous terrain with narrow coastal plains; the Blue Mountains are the highest range.
Geography: Predominantly mountainous terrain with narrow coastal plains; the Blue Mountains are the highest range.- Rivers: Major rivers include the Black River (longest) and the Rio Minho.
- Economy: Relies on tourism, bauxite mining, and agriculture (sugar, bananas, coffee).
- Climate: Tropical maritime, influenced by trade winds; prone to hurricanes and tropical storms from the Atlantic basin.
- Regional Grouping: Member of the Commonwealth of Nations and CARICOM (Caribbean Community).
- Significance: Lies in the Atlantic hurricane belt, making it highly vulnerable to extreme weather events.
8th Central Pay Commission (CPC)
Context: The Union Cabinet, chaired by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, has approved the Terms of Reference (ToR) of the 8th Central Pay Commission (CPC) on 28 October 2025.
About the Central Pay Commission
- The Central Pay Commission is a temporary expert body constituted periodically to review and recommend changes in the emolument structure, pensions, and service conditions of Central Government employees.
- Background: Such Commissions are generally set up every ten years, with recommendations implemented thereafter.
- The 8th CPC’s recommendations are expected to take effect from 1 January 2026.
- Constitutional Basis: Although not a constitutional body, the Pay Commission is set up by the Union Government under its executive powers.
- Composition: The 8th CPC will include one Chairperson (Justice Ranjana Prakash Desai (Retd.)), one Part-Time Member, and one Member-Secretary.
- It will submit its report within 18 months from its constitution and may provide interim reports if required.
Considerations While Making Recommendations
- Economic Conditions: The Commission must assess the economic situation and maintain fiscal prudence.
- Developmental Priorities: It must ensure that adequate resources remain for welfare and developmental expenditure.
- Pension Liabilities: It will review the unfunded cost of non-contributory pension schemes.
- State Finances: It will consider the impact of recommendations on State Governments that often adopt CPC outcomes with modifications.
- Comparative Pay Structures: The Commission will also examine emoluments and working conditions in Central PSUs and the private sector for parity and balance.
AmazonFACE Project
Context: Scientists in Brazil have created a unique “climate time machine” called AmazonFACE Project to simulate future atmospheric carbon dioxide levels ahead of COP30.
About AmazonFACE Project
- Objective: To study how tropical rainforests respond to elevated CO₂ concentrations expected in future decades.
- Location: Near Manaus, the largest city in Brazil’s Amazon region.
- Design: Six large steel tower rings, each surrounding 50–70 mature rainforest trees, simulate future atmospheric conditions.
- Three rings will be infused with higher CO₂ levels while others remain as controls for comparison.
- Technology: Uses the FACE (Free-Air CO₂ Enrichment) technique to release carbon dioxide into the canopy.
- Monitoring: Sensors record real-time forest responses such as CO₂ absorption, oxygen release, and water vapor exchange every 10 minutes.
- Significance: It is the first large-scale FACE experiment in a tropical forest, supported by Brazil and the United Kingdom.
About COP30 (UN Climate Summit 2025)
- The 30th Conference of Parties (COP30) under the UNFCCC will focus on global climate commitments and adaptation strategies.
- Venue: Belém, in northern Brazil, where the Amazon Basin meets the Atlantic Ocean.
- Dates: Scheduled from November 10–21, 2025.
- Key Agenda: Assessing the resilience of tropical rainforests like the Amazon in mitigating and adapting to climate change.
![]() 29 Oct 2025
29 Oct 2025


 Geography: Predominantly mountainous terrain with narrow coastal plains; the Blue Mountains are the highest range.
Geography: Predominantly mountainous terrain with narrow coastal plains; the Blue Mountains are the highest range.