The National Institute of Animal Biotechnology (NIAB) is using Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) and genotyping technology to identify and conserve indigenous cattle breeds.
Alignment with BioE3 Policy
- NIAB’s research aligns with the BioE3 policy, which focuses on biotechnology for boosting the economy, environment, and employment.
About NIAB
- It is located in Hyderabad, Telangana and established in 2010.
- NIAB focuses on advanced research in animal genetics and biotechnology.
- Aim: To enhance animal health and productivity.
- Conducts research in genomics, reproductive biotechnology, infectious diseases, and bioinformatics.
- Develops innovative vaccines, diagnostics, and therapeutic molecules.
|
-
- Industry Hand Holding: The institute aims to support industries and startups in transforming the livestock-based economy.
- The main goal behind this step is to position India as a global leader in bio-manufacturing through biotechnological interventions.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Next Generation Sequencing (NGS)
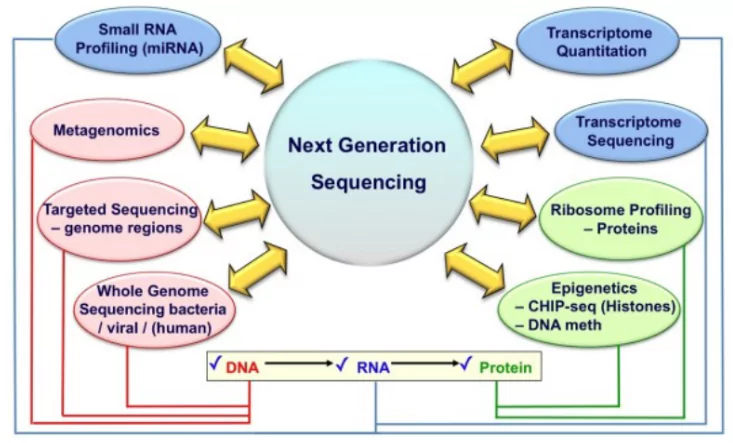
- NGS is a modern DNA sequencing method that has transformed genomic research.
- It allows for the rapid and cost-effective sequencing of DNA and RNA.
- It makes it a faster and cheaper option compared to older techniques like Sanger sequencing.
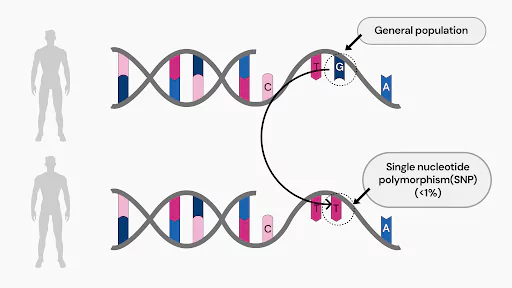
- NGS can identify a wide range of genetic variations, including single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), insertions, deletions, and structural changes in the genome.
- NGS Advantages
- Speed: Quickly sequences large amounts of DNA/RNA.
 Cost-Effective: Lower sequencing costs.
Cost-Effective: Lower sequencing costs.- Comprehensive: Detects various genetic variations.
- Scalable: Adaptable for small to large studies.
About Genotyping
- Genotyping is the process of identifying genetic differences by analysing an individual’s DNA sequence.
- Comparison of DNA Sequences: It involves comparing an individual’s DNA to another person’s sequence or a reference sequence to reveal inherited alleles.
- Traditional Use of Genotyping: Traditionally, genotyping uses DNA sequences to categorise biological populations with molecular tools, without focusing on defining individual genes.
India’s efforts towards Genome sequencing
- Genome India project
- Launched in 2020.
- Objective: It aims to establish a comprehensive reference genome that represents the genetic diversity of the Indian population.
- Funded by: Department of Biotechnology
- Spearheaded by: Centre for Brain Research (CBR)
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
IndiGen Programme
- This programme was launched in 2019.
- Objective: It aims to sequence the genome of thousands of individuals from diverse ethnic groups in India.
- Endorsement: it is endorsed by the Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR).
Indian Initiative on Earth Bio-Genome Sequencing
- It is a part of the Earth Biogenome Project.
- Launch date: 2020
- Main objective: Focuses on collecting and preserving endangered and economically important species.
- The decoded genetic information will help in protecting against biopiracy.
- Key institutions : The Jawaharlal Nehru Tropical Botanic Garden and Research Institute (JNTBGRI).
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Difference between NGS and Genotyping Technology
| Aspect |
Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) |
Genotyping Technology |
| Definition |
Determines the order of nucleotides in entire genomes or targeted regions |
Identifies specific genetic variations (e.g., SNPs) |
| Scope |
Whole genome, exome, or targeted regions |
Targeted regions or specific variants |
| Data Output |
Comprehensive sequence data |
Specific genetic markers |
| Resolution |
High resolution, detailed information |
Lower resolution, focused on known variants |
| Applications |
Research, personalized medicine, evolutionary studies |
Disease association studies, genetic screening |
| Cost |
Generally higher |
Generally lower |
| Time |
Longer processing time |
Faster processing time |
| Complexity |
More complex data analysis |
Simpler data analysis |
| Examples |
Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS), Exome Sequencing |
SNP Genotyping, HLA Typing |
![]() 3 Sep 2024
3 Sep 2024

 Cost-Effective: Lower sequencing costs.
Cost-Effective: Lower sequencing costs.