NITI Aayog released a report titled “Designing a Policy for Medium Enterprises”, outlining a roadmap to transform medium enterprises into growth engines for India’s economy.
Definition of Medium Enterprises
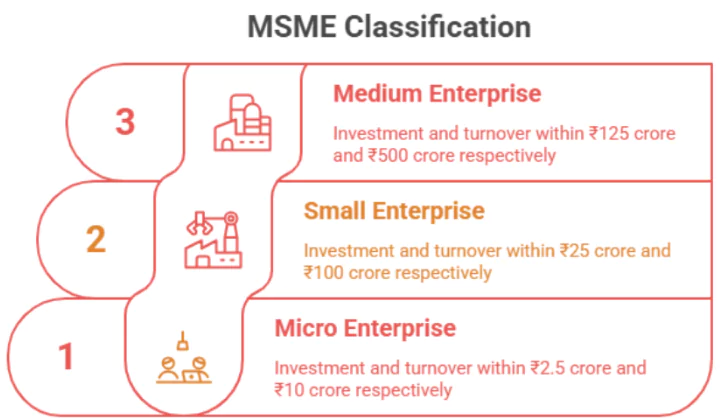
- Statutory Classification: Medium enterprises are those with an investment in plant and machinery or equipment not exceeding ₹50 crore and turnover not exceeding ₹250 crore.
- Proportion within MSMEs: Only 0.3% of all registered MSMEs qualify as medium enterprises, despite the sector’s vast base of over 6 crore units.
Role in Economic Growth and Job Creation
- GDP Contribution: MSME sector contributes 29% to India’s GDP.
- Export Contribution: Medium enterprises contribute nearly 40% of MSME exports, highlighting their capacity for global competitiveness.
- Innovation and Scale Potential: They are innovation-led, scalable units with the potential to become future large enterprises and support Atmanirbhar Bharat.
- In sectors like auto-components and electronics, medium enterprises form critical links in domestic and global value chains.
- Job Creation: MSMEs employ over 60% of India’s workforce, and medium enterprises are positioned to generate more formal, skilled employment with proper support.
Key Indian Government Initiatives Related to MSMEs
- Udyam Registration Portal (2020): Aimed at simplifying MSME registration and promoting formalization of enterprises.
- PM Vishwakarma Scheme (2023): Supports traditional artisans and craftspeople with credit, skill training, and digital enablement.
- Prime Minister’s Employment Generation Programme – PMEGP (2008): Provides financial assistance for self-employment through micro-enterprise creation.
- Scheme of Fund for Regeneration of Traditional Industries – SFURTI (2005): Revives traditional industries by organizing artisans into clusters and enhancing infrastructure.
- Public Procurement Policy for MSEs (2012): Mandates 25% of all central government and PSU purchases from MSEs, boosting market access.
|
Key Challenges Faced by Medium Enterprises
- Access to Finance: Inadequate financial instruments tailored to their unique scale and working capital cycles.
- Technology Lag: Limited adoption of Industry 4.0 tools and insufficient access to advanced manufacturing solutions.
- Weak R&D Ecosystem: Minimal institutional support for innovation, especially for cluster-based and high-impact projects.
- Testing Infrastructure Deficit: Absence of sector-specific testing and certification centres restricts compliance and product standardization.
- Skilling Mismatch: Current training programmes are misaligned with sectoral and regional requirements of medium enterprises.
- Digital Fragmentation: Lack of centralized, easy-to-navigate platforms for accessing government schemes and compliance tools.
Key Recommendations of NITI Aayog for Medium Enterprises
- Tailored Financial Solutions: Introduction of a working capital financing scheme linked to enterprise turnover; a ₹5 crore credit card facility at market rates; and expedited fund disbursal mechanisms through retail banks, overseen by the Ministry of MSME.
- Technology Integration and Industry 4.0: Upgradation of existing Technology Centers into sector-specific and regionally customized India SME 4.0 Competence Centers to promote the adoption of Industry 4.0 solutions.
- R&D Promotion Mechanism: Establishment of a dedicated R&D cell within the Ministry of MSME, leveraging the Self-Reliant India Fund for cluster-based projects of national significance.
- Cluster-Based Testing Infrastructure: Development of sector-focused testing and certification facilities to ease compliance and enhance product quality.
- Custom Skill Development: Alignment of skilling programmes with enterprise-specific needs by region and sector, and integration of medium enterprise-centric modules into existing Entrepreneurship and Skill Development Programmes (ESDP).
- Centralized Digital Portal: Creation of a dedicated sub-portal within the Udyam platform featuring scheme discovery tools, compliance support, and AI-based assistance to help enterprises navigate resources effectively.
Conclusion
Empowered through inclusive policies, collaborative governance, and strategic support, medium enterprises can become key drivers of innovation, exports, and employment forming a vital pillar in realizing the vision of Viksit Bharat @2047.
![]() 27 May 2025
27 May 2025


