Recently, American researchers have found a method to be able to trace the origin and the destination of forever chemicals.
What are Forever Chemicals? Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS)
- These are a class of synthetic man-made chemicals.
- They are called “forever chemicals” because the bonds in their chemical compounds are so strong they don’t degrade down for hundreds to thousands of years.
- Example: Perfluorooctane sulfonic acid (PFOS)
- They are used to make fluoropolymer coatings and products that resist heat, oil, stains, grease, and water.
- Found in: Fluoropolymer coatings can be in a variety of products and industries including,

-
- Health risk: They pose a negative health effect such as decreased immune system performance and vaccine response, infant and child learning and developmental issues, certain cancers, decreased fertility, endocrine disruption etc.
- PFOS, PFOA and PFHxS are transferred to fetus through cord blood and to infant through breast milk
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Concerns
- Difficulties in tracking forever chemicals: The molecular bonds of the chemicals make them difficult to trace. That’s because conventional chemical fingerprinting involves breaking molecules apart in a mass spectrometer which doesn’t work well with the tough molecular bonds of forever chemicals
- Widespread occurrence: PFAS contaminated water or food is the most likely source of exposure, by using products made with PFAS, or breathing air containing PFAS.
- Studies find PFAS in the blood and urine of people with 97% of Americans having traces of PFAS in their blood.
- Persistent: They remain in the environment for an unknown amount of time as they do not break down in the environment easily.
- Bioaccumulation: Over time, people may take in more of the chemicals than they excrete, a process that leads to bioaccumulation in bodies. Also it can move through soils and build up (bioaccumulate) in fish and wildlife.
- Contaminate drinking water sources: A study by the Environmental Protection Agency found that about 31 percent of groundwater samples tested around the world had PFAS levels considered harmful to human health.
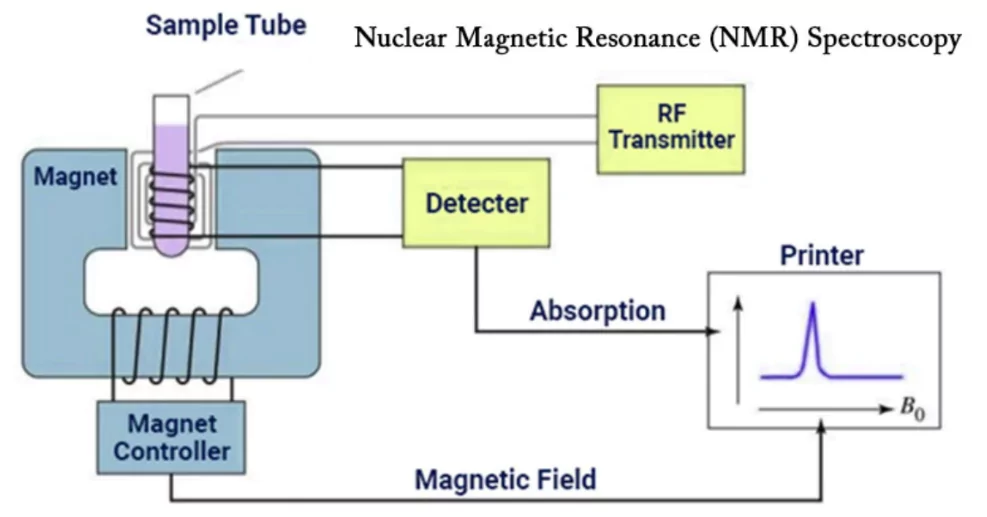
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy
- The technology is used to measure a molecule’s structure and identify its isotopes without breaking it apart.
Isotopes
- It refers to chemical elements with differences in the number of neutrons in its atoms.
- Forever chemicals are made by bonding carbon isotopes to the element fluorine, which almost never happens in nature. Once the molecular bonds form, they are virtually unbreakable
|
- It’s like a built-in barcode for molecules: The researchers’ technique uses the NMR instrument alongside their own computational tools to determine the mix of carbon isotopes at each position in the molecule.
- Because the mix of carbon isotopes bonding to each fluorine atom is unique to how the chemical was manufactured, this information can be used like a fingerprint to trace a chemical
Future Course
- Few researchers are presently engaged in conducting a pilot study to check how the technique will fare on pollutants that show up in the city of Austin’s creeks and wastewater. If successful:
- Disease Track: The technique could be useful for state and federal agencies who want to track the spread of water-borne forever chemicals
- Organic Chemistry: It has opened up a new layer of isotope information in organic chemistry that could find diverse applications transcending the scope of tracking forever chemicals, such as detecting counterfeit drugs or astrobiology.
- Historical Metabolism: It’s given us a whole range of possibilities to learn really interesting things about metabolism on early Earth
- Formation: It could even tell us whether organics on Mars are the last remnants of some ancient Martian life
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
![]() 20 Aug 2024
20 Aug 2024

