In September, astronomers predict a rare nova explosion ( explosion of T Coronae Borealis) will brighten our night sky.
T Coronae Borealis
- T Coronae Borealis is known as the “Blaze Star” or “T CrB.”
- The T CrB nova was last observed from Earth in 1946.
- This event will occur approximately 3,000 light-years from Earth.
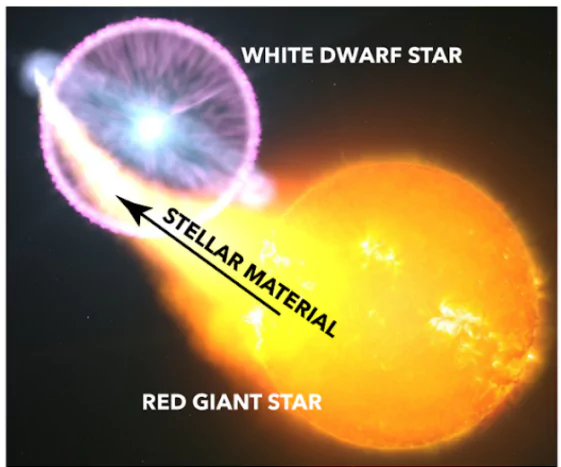
What is a Nova Explosion?
- A nova explosion occurs when a star explodes due to its interaction with a nearby star.
- Explosion Trigger: When the heat and pressure become excessive, a thermonuclear explosion occurs.
- Brightness Change: This explosion makes the white dwarf appear much brighter in the sky.
- Post-Explosion: After the explosion subsides, the star returns to its original brightness.
- Mechanism: It is a recurring event during the prolonged death of two neighbouring stars within the same system.
- Visibility of the Nova
- Naked Eye Observation: The nova can be seen without a telescope for about a week.
- Appearance: During this time, it will look like a new star has appeared in the sky.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
About Nova
- Origin of Name: The term “nova” comes from the Latin word for “new.”
- A nova is a transient astronomical event.
- In this event, a new bright star appears suddenly and then fades over weeks or months.
- Nova occurs with a system of two stars.
- Red giant
- White dwarf
- It revolves around each other.
- White dwarf attracts matter from red giant’s atmosphere when they are close
- This causes nuclear explosions and ejection of gases.
Causes and Characteristics
- Star Involvement: All observed novae involve white dwarfs in close binary systems.
- Variations: The appearance of a nova depends on the circumstances of the two progenitor stars.
- Main Sub-Classes: Novae are categorised into classical novae, recurrent novae (RNe), and dwarf novae. All are types of cataclysmic variable stars.
About Supernova
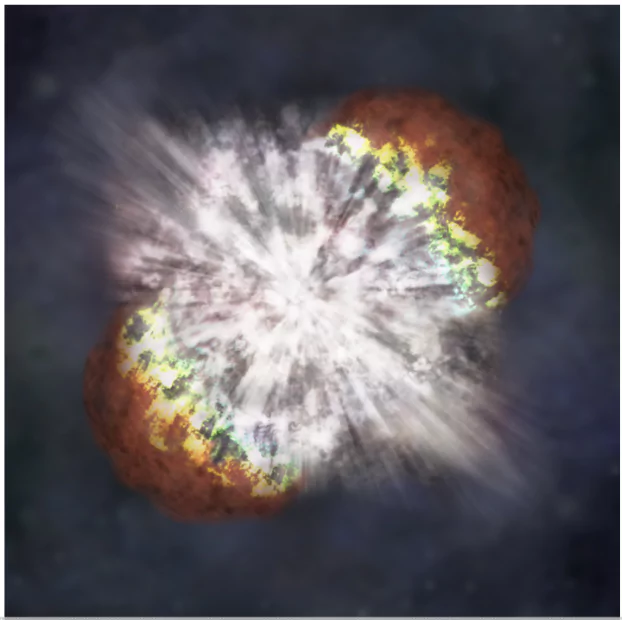
- A supernova is the explosion of a massive star.
- Main Types of Supernovae
Supernovae are broadly categorised into two main types based on their explosion mechanisms.
- Type 1: Thermonuclear Runaway (Type Ia SNe)
- Occurrence: Happens in binary star systems where at least one star is a white dwarf.
- Mechanism: The white dwarf undergoes a thermonuclear explosion.
- Type 2: Core-Collapse
- Occurrence: Occurs in stars with masses greater than eight times the mass of our sun.
- Mechanism: The star collapses in on itself and explodes.
- Subtypes of Supernovae
- Classification by Spectra: Each main type has various subtypes, which are classified based on the elements observed in their spectra.
Causes of Supernovae
1. Supernova from a Dying Massive Star
- One type of supernova occurs when a massive star ends its life with a huge explosion.
- Mass Requirement: This happens in stars at least five times the mass of our sun.
- Fuel Consumption: Massive stars burn a lot of nuclear fuel in their cores, producing immense energy and heat.
- Balance of Forces:
- Gravity: Tries to compress the star into a tight ball.
- Nuclear Pressure: The burning fuel creates outward pressure, balancing the inward pull of gravity.
- Collapse and Explosion:
- When the star runs out of fuel, it cools, reducing pressure.
- Gravity takes over, causing the star to collapse rapidly.
- This rapid collapse creates shock waves, leading to an explosion of the outer part of the star.
2. Supernova from a Binary Star System
- Binary Systems: Another type of supernova can occur in systems where two stars orbit each other.
- White Dwarf: Involves at least one Earth-sized white dwarf, the remnant of a star similar to our sun after it has run out of fuel.
- Collision or Accretion:
- If a white dwarf collides with another star or accumulates too much matter from its companion, it can explode.
- This explosion is a powerful event, resulting in a supernova.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
Difference between Nova and Supernova
| Feature |
Nova |
Supernova |
| Number of stars involved |
Two (white dwarf and red giant) |
One (massive star) |
| Explosion type |
Relatively small eruption |
Largest explosion ever witnessed |
| Elements produced |
None |
Elements heavier than iron |
| Rarity |
Relatively common |
Relatively rare |
![]() 1 Jul 2024
1 Jul 2024

