About Crude Oil
- Crude oil is a naturally occurring, non-renewable fossil fuel composed mainly of hydrocarbons, formed over millions of years from buried organic matter under heat and pressure.
- Oil provides approximately 30% of the world’s total energy supply.
- Crude Oil is refined into essential fuels such as petrol, diesel, aviation turbine fuel, liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), and petrochemical feedstocks, making it a cornerstone of modern economies.
- Process of Crude Oil Extraction: Crude oil is extracted primarily through drilling into underground reservoirs located on land or beneath the seabed.
- It is often found along with natural gas and saline water.
- After extraction, crude oil is transported to refineries, where it undergoes distillation and further processing to produce usable petroleum products.
Types of Crude Oil
- Light Crude Oil: Light crude oil has low density and flows easily.
- It yields a higher proportion of high-value refined products such as petrol, diesel, and aviation fuel.
- It is cheaper to refine and preferred by most modern refineries.
- It is commonly found in the United States (shale oil fields), North Sea (Brent crude), parts of West Africa (Nigeria), and Azerbaijan.
- Heavy Crude Oil: Heavy crude oil has high density and viscosity. It produces more residual products and requires complex refining techniques such as coking and hydrocracking, increasing processing costs.
- Heavy crude oil is mainly found in Venezuela (Orinoco Belt), Canada (oil sands), Mexico, and parts of the Middle East.
- Sweet Crude Oil: Sweet crude oil contains low sulphur content (generally less than 0.5%).
- It produces fewer pollutants, causes less corrosion in refinery equipment, and meets environmental standards more easily.
It is produced in the United States (WTI crude), North Sea (Brent), Libya, Nigeria, and parts of Indonesia.
- Sour Crude Oil: Sour crude oil has high sulphur content (more than 0.5%), making it more polluting and technically challenging to refine.
- It requires desulphurisation and advanced refining infrastructure.
- It is predominantly found in the Middle East (Saudi Arabia, Iraq), Canada, Venezuela, and Russia.
Oil Trade Benchmark
- Brent Crude: The most widely used global benchmark, derived from North Sea fields, pricing most waterborne crude, known for being light and sweet.
- West Texas Intermediate (WTI): A key US benchmark, also light and sweet, heavily traded in North America.
- Dubai/Oman: Used to price Middle Eastern oil, especially for Asian markets, often linked to Brent.
- OPEC Reference Basket: Used by OPEC for pricing decisions.
- Western Canadian Select (WCS): A heavy, sour benchmark for Canadian oil. Bonny Light (Nigeria) & Urals (Russia): Regional benchmarks.
Organisations Related to Crude Oil
- Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC): It is an intergovernmental organisation founded in 1960 to coordinate petroleum policies among member countries, stabilise oil markets, and ensure fair prices for producers.
- Members (12 as of 2024): Includes Saudi Arabia, Iran, Iraq, UAE, Kuwait, Venezuela, Nigeria, Algeria, Libya, Congo, Equatorial Guinea, and Gabon.
- Angola (withdrew in January 2024)
- OPEC+: It is a broader coalition formed in 2016, comprising the 12 OPEC members and 10 additional non-OPEC oil-exporting nations, including Russia, Mexico, Kazakhstan, and Oman, that coordinate on production levels to influence the global market.
Current Crude Oil Production
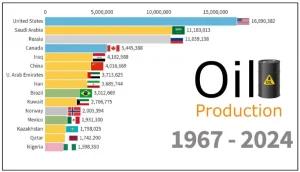
Top Producers
- United States
- Saudi Arabia
- Russia
- Canada
- Iraq
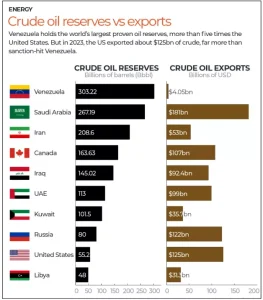
Top Crude Oil Reserves:
- Venezuela
- Saudi Arabia
- Canada
- Iran
- Iraq
|
![]() 12 Jan 2026
12 Jan 2026