Ovarian Cancer Awareness Month is celebrated in the month of September so as to build awareness about this elusive disease of the female reproductive organ.
About Ovarian Cancer
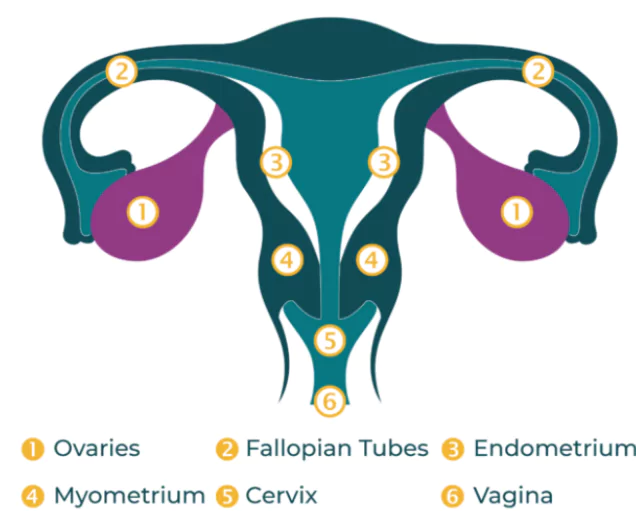
- Ovarian cancer is the most malignant of the female cancers and every person assigned female at birth is at risk. It occurs when abnormal cells in the ovaries, and peritoneum or fallopian tubes grow and multiply out of control.
- The Female Reproductive System: It contains two ovaries, one on each side of the uterus. The ovaries (almond sized) produce eggs (ova) as well as the hormones estrogen and progesterone.
- Risk Statistics:
- World: As per Globocan’s 2022 projections,
- Incidence: The number of women diagnosed with ovarian cancer will rise over 55% to 503,448 by 2050.
- Mortality: The number of women dying from ovarian cancer may increase to 350,956 showing an almost 70% increase from 2022.
- India: Ovarian cancer is ranked amongst the top three cancers, contributing to 6.6% of all women’s cancers in India.
- In 2022, India reported 47,333 new ovarian cancer cases and 32,978 deaths
- Symptoms: A 2004 study reported women with ovarian cancer typically experience these symptoms 20 to 30 times a month.
- Persistent Bloating, loss of appetite, feeling full quickly, constipation
- Pelvic/abdominal pain,back pain, persistent fatigue, weight loss,
- Urinary Symptoms: Urgent or frequent need to urinate, and postmenopausal vaginal bleeding
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
- Types: Ovarian cancer is an umbrella term comprising more than 30 different types of cancer which are named after the type of cell they come from.
- Epithelial Ovarian Cancer: It begins in the tissue covering the ovary, in the lining of the fallopian tube ( (which deliver eggs from the ovaries to the uterus) and the peritoneum (which lines the abdominal wall and covers the abdominal organs)
- Germ Cell Ovarian Cancer: It comes from the reproductive cells of the ovaries (eggs) and is quite rare.
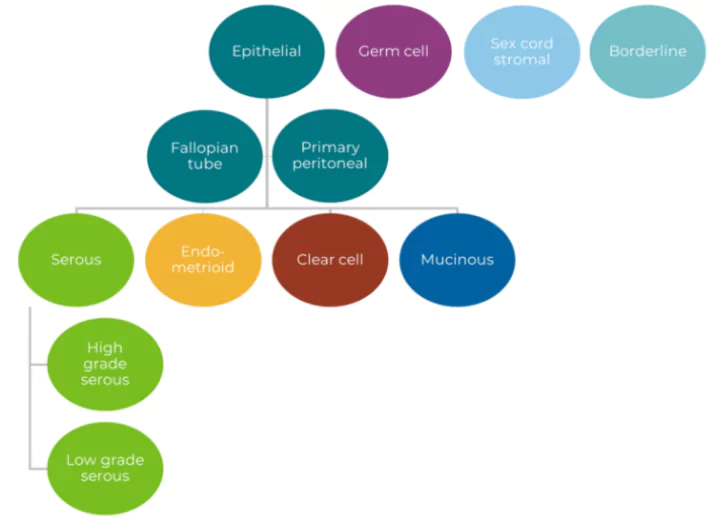 Stromal Cells Ovarian Cancer: It comes from connective tissue cell.
Stromal Cells Ovarian Cancer: It comes from connective tissue cell.- Small cell carcinoma (SCCO) of the ovary: This is an extremely rare ovarian cancer.
- Cause: Certain lifestyle factors are linked to ovarian cancer risk.
- Family history, inherited gene mutations: Ovarian Cancer is the most heritable of all cancers with 65-85% of hereditary ovarian cancer cases involving mutations in the BRCA1 or the BRCA2 genes.
- Use of talcum powder containing asbestos ( known carcinogen) in the genital area
- Use of chemical hair products with studies showing a possible link between the prolonged use of hair dyes and an increased risk of ovarian cancer.
- frequent use of hair straighteners, relaxers or pressing products that release formaldehyde gas
- Hormone replacement therapy (HRT), commonly used to alleviate menopausal symptoms, has been linked to a higher risk of ovarian cancer
- Detection and Diagnosis: There are no effective screening tests for ovarian cancer.
- The CA125 blood test is however useful to monitor ovarian cancer only after diagnosis but is less effective at screening asymptomatic women as it can lead to false positives.
- Early detection can come from an awareness of risk factors and symptoms and family history with regular consultations with healthcare providers
- Survival Rates: Five-year ovarian cancer survival rates vary between countries with the developed countries rates ranging from 36% to 46%.
- India: The 10-year survival rate is estimated to be 15–30% due to screening at an advanced stage (70-80%) In general, women diagnosed before age 65 have better outcomes than older women.
- Treatment:
- Surgery: It is a standard treatment for ovarian cancer to remove as much of the cancer as possible.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy is often used after surgery, especially for advanced ovarian cancer. Platinum-based drugs like cisplatin or carboplatin are often used.
- Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy can be used after surgery to remove any remaining cancer cells. It can also be used to manage symptoms of advanced ovarian cancer, such as abdominal pain.
- Hormonal treatment: Some women benefit from hormonal treatment with drugs like anastrozole, letrozole, or tamoxifen.
- Prevention: The survival rate for patients with ovarian cancer depends on the stage of detection and access to appropriate treatment.
- Personalised Risk Management: It includes genetic testing, tailored clinical surveillance, chemoprevention, and prophylactic surgeries, which can reduce the risk of developing ovarian cancer in high-risk women.
- Detecting Endometriosis: It is a condition where uterine-like tissue grows outside the uterus, has been linked to an increased risk of certain types of ovarian cancer, particularly endometrioid and clear-cell cancers.
- Genetic Counselling: The process helps identifying individuals at risk for hereditary cancers and provides tailored guidance on preventive measures and potential treatments.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Government Initiatives Related to Cancer Care
- The Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PMJAY): It offers health insurance up to INR 5 lakhs per family for secondary and tertiary care hospitalisation, covering many cancer-related treatments.
- The National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases & Stroke (NPCDCS): It aims to prevent and control chronic non-communicable diseases, including cancer.
- The Rashtriya Arogya Nidhi (RAN): It provides financial assistance to patients living below the poverty line suffering from life threatening diseases ie. cancer at government hospitals.
- The Health Minister’s Cancer Patient Fund (HMCPF) within Rashtriya Arogya Nidhi provides financial assistance for cancer treatment through the procurement of generic drugs.
- First Cancer Care (FCC) initiative: It was introduced in 2022 and utilises advanced technology to transform cancer prevention and treatment, focusing on quality, timeliness, precision, and fairness.
- State Illness Assistance Funds: It is set up by various state governments, offering financial aid to poor patients to cover treatment costs for different diseases, including cancer.
- The Tertiary Care Cancer Centres (TCCC): The scheme is complemented by the Pradhan Mantri Swasthya Suraksha Yojana (PMSSY), and aims to set up state cancer institutes and tertiary care cancer centres across the country to improve facilities for cancer treatment.
- National Cancer Grid (NCG): It is a network of cancer centres, research institutes, patient groups, and charitable institutions across India to establish uniform standards of patient care for the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of cancer and provide specialised training and education in oncology
- Awareness campaigns: Measures targeting tobacco control and the promotion of healthy lifestyles are vital in reducing the risk factors associated with cancer.
|
![]() 11 Sep 2024
11 Sep 2024

 Stromal Cells Ovarian Cancer: It comes from connective tissue cell.
Stromal Cells Ovarian Cancer: It comes from connective tissue cell.