![]() 13 Apr 2024
13 Apr 2024
English
हिन्दी
The Ear, Nose & Throat (ENT) department at Command Hospital in Pune conducted two piezoelectric Bone Conduction Hearing Implants (BCI).
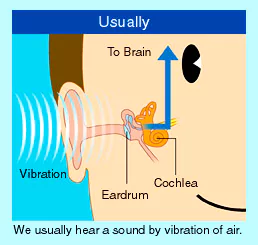
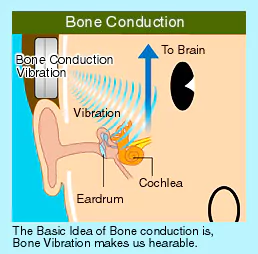
What is the Piezoelectricity?
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>