The Government of India and the Asian Development Bank (ADB) signed a $98 million loan to promote plant health management in India’s horticulture.
- The loan agreement is to support India’s Atma Nirbhar Clean Plant Programme.
About Atma Nirbhar Clean Plant Programme (CCP):
- Announced: It was announced in the Union Budget of 2023-24 under the Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH) to boost the horticulture sector.
- Objective: To improve farmers’ access to certified disease-free planting materials, increasing crop yields, quality, and resilience to climate impacts.
- Implementing Agencies: The project will be implemented by the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare through the National Horticulture Board and the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR).
- Collaboration with Stakeholders: The project involves consultations with private nurseries, researchers, state governments, and growers’ associations for its successful implementation.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
- Establishment of Clean Plant Centres: Clean Plant Centers (CPCs): They are the core components of the CPP.
- The project will establish centres to maintain disease-free planting materials, equipped with laboratories and trained experts.
- Advanced CPCs will be established across India, each focusing on specific fruit types.
- These centers will be equipped with modern diagnostic and therapeutic facilities, including tissue culture labs.
- Clean Plant Certification Scheme: The initiative will roll out a certification scheme under the Seeds Act of 1966 to test and accredit private nurseries for disease-free planting materials.
- Alignment with Broader Initiatives: The Clean Plant Programme aligns with broader initiatives such as Mission LiFE (Lifestyle for Environment) and the One Health approach.
About Plant Health Management
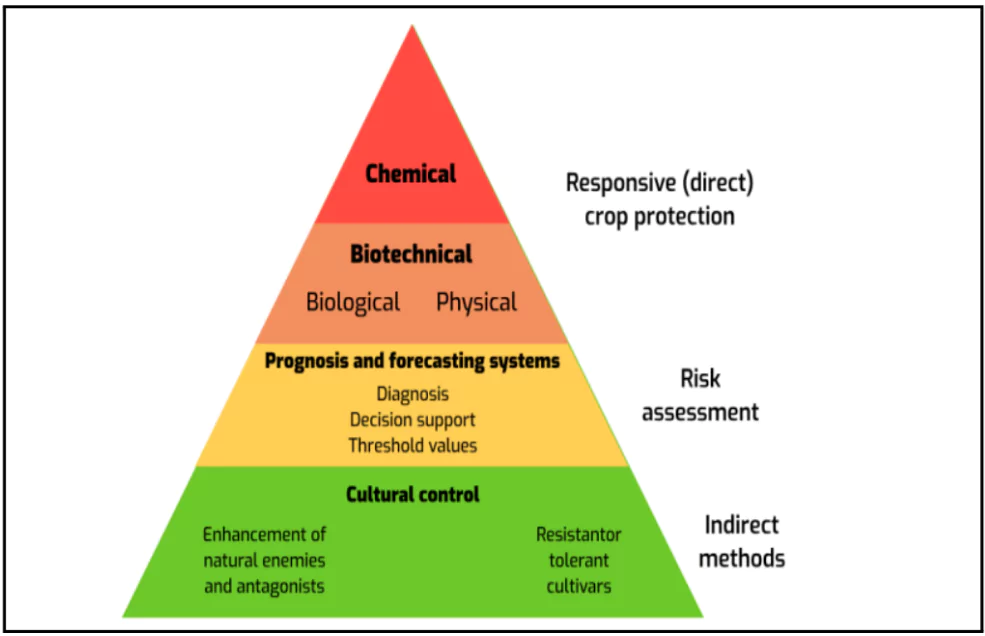
- Plant health management is the science and practice of protecting plants from diseases, pests, and environmental stressors. It aims to maintain plant health, productivity, and quality.
- Principles of Plant Health Management
-
- Exclusion: Preventing the introduction of pests and diseases to new areas.
- Eradication: Eliminating existing pests and diseases.
- Protection: Shielding plants from pests and diseases using physical barriers or chemical treatments.
- Resistance: Utilizing plant varieties with natural resistance to pests and diseases.
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM): A comprehensive approach combining multiple strategies to manage pests in a sustainable and environmentally friendly manner.
Horticulture Sector in India
- In 2022-23, India’s horticulture production reached 351.92 million tonnes, exceeding the production of foodgrains.
- Fruits and Vegetables accounted for almost 90% of India’s total horticulture production.
- Contribution to Agriculture Gross Value Added (GVA): Horticulture contributes 33% to the Agriculture GVA.
- India ranks 2nd in global fruits and vegetable production, after China.
- Exports of Horticultural Products
-
- Vegetable Exports: India ranks 14th in global vegetable exports.
- Fruit Exports: India ranks 23rd in global fruit exports.
|
Key Government Schemes to Revolutionise India’s Horticulture Sector
- Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH)
- Objective: MIDH is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme aimed at the holistic growth of the horticulture sector.
- Implementing Ministry: The Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare has been implementing MIDH since 2014-15.
- Part of Green Revolution: MIDH is implemented under the Green Revolution – Krishonnati Yojana.
- Funding Pattern
- General States: The Government of India (GoI) contributes 60% of the total outlay for developmental programmes, while State Governments contribute 40%.
- North Eastern and Himalayan States: For these regions, GoI contributes 90% of the total outlay, with State Governments contributing the remaining 10%.
Check Out UPSC Modules From PW Store
- Sub Schemes of MIDH:
- National Horticulture Mission (NHM): Launched in 2005, the NHM is a centrally sponsored scheme aimed at promoting the holistic growth of the horticulture sector.
- Horticulture Mission for North East and Himalayan States (HMNEH): The HMNEH focuses on the comprehensive development of horticulture in the North Eastern and Himalayan regions.
- It promotes crops suited to the unique agro-climatic conditions of these areas, aiming to improve farmers’ livelihoods and promote sustainable horticulture practices.
- Enhanced Support for Horticulture Under PMFBY: Under the Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY), premium contributions for farmers are capped at:
- 2% for Kharif crops
- 1.5% for Rabi crops
- 5% for commercial and horticultural crops
- Horticulture Cluster Development Programme (HCDP): The HCDP promotes integrated and market-led development of horticulture clusters based on geographical specialization.
- It focuses on identified crops in specific regions, aiming to optimize productivity, increase exports, and enhance the global competitiveness of Indian horticulture products.
- Post-Harvest Infrastructure Development Scheme: This scheme addresses post-harvest losses by providing support for modern facilities, such as pack houses, ripening chambers, cold storage units, and processing facilities.
- Soil Health Card Scheme: Though not exclusive to horticulture, this scheme significantly benefits horticultural farmers.
- It involves soil testing and provides health cards with crop-wise recommendations on nutrients and fertilizers, helping farmers make informed decisions, potentially improving yields and reducing input costs.
![]() 4 Dec 2024
4 Dec 2024

